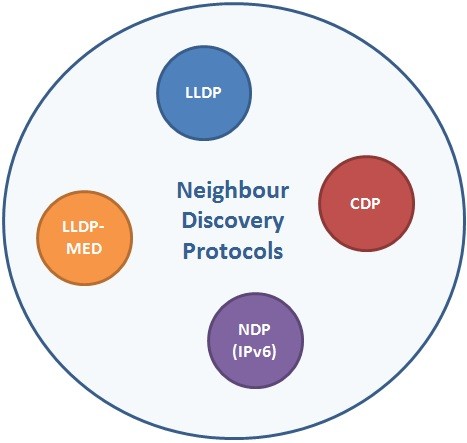
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) is a Standard Neighbour Discovery Protocol that is used by all vendors. Like all other Neighbour Discovery Protocols like Cisco CDP, LLDP works on Layer 2 (Data-link Layer). By using this Neighbor Discovery Protocol, directly connected neighbours are discovered. You can also view wiki definion here. If you would like to view CDP Protocol, you can also go to CDP Lesson.
To discover a neighbour device, Link Layer Discovery Protocol must be enabled both on the discovering device and the discovered device.
With this protocol, ethernet devices advertise their identification, configuration etc. to the directly connected LLDP enabled devices.
As we mentioned before, there are many Neighbour Discovery Protocols and they are vendor specific. To build a one common protocol, Link Layer Discovery Protocol is developed and it is used on all vendors’ devices. It is independent from the brand of the device used.
There are some specific times of this protocol as other protocols. Theese aere Hello Timer and Dead Times. Hello Timer is 30 seconds for Link Layer Discovery Protocol and Dead Timer is 120 seconds.
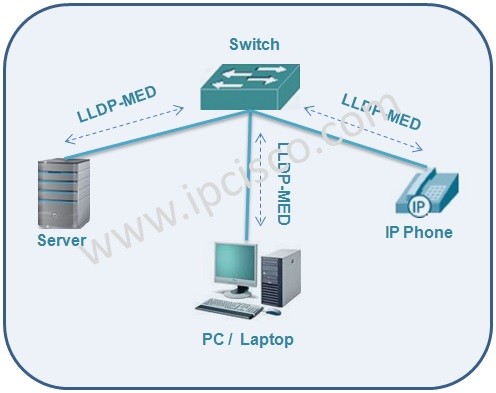
Link Layer Discovery Protocol has an extension version that provide end devices’s discovery. With this extention, it discovers the endpoint PCs, IP Phone. This extended version is LLDP-MED (Media Endpoint Discovery). We will talk about LLDP-MED, in the following articles. Here, in this article, our main focus is the classic one.
Table of Contents
How LLDP Works?
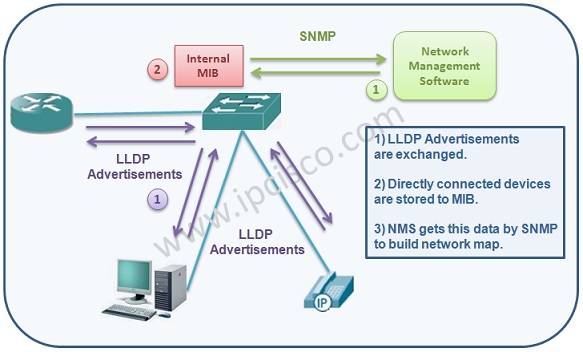
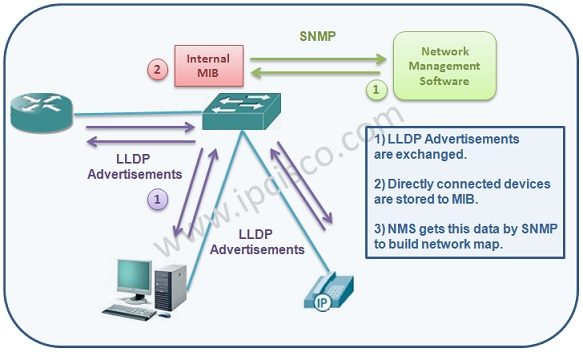
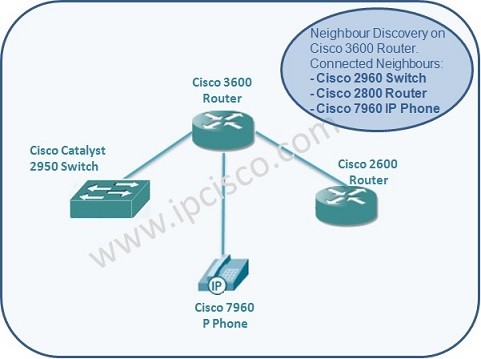
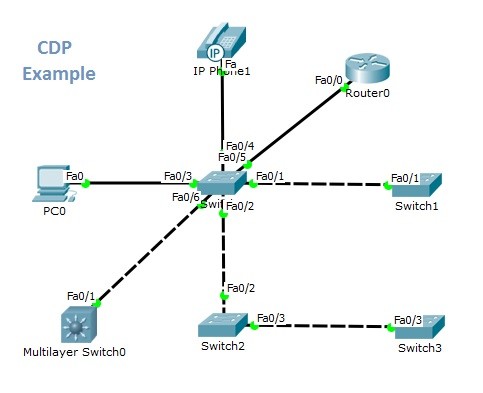
As we have mentioned above, Link Layer Discovery Protocol must be enabled on the devices firstly. After that, LLDP enabled devices send LLDP advertisements each other and the device information are stored in the MIB databases on the devices. Any Network Management Software gets this data by SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). And with this data, it builds the network map.








Informative sites, very nicely designed by gokhan kosem.