- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
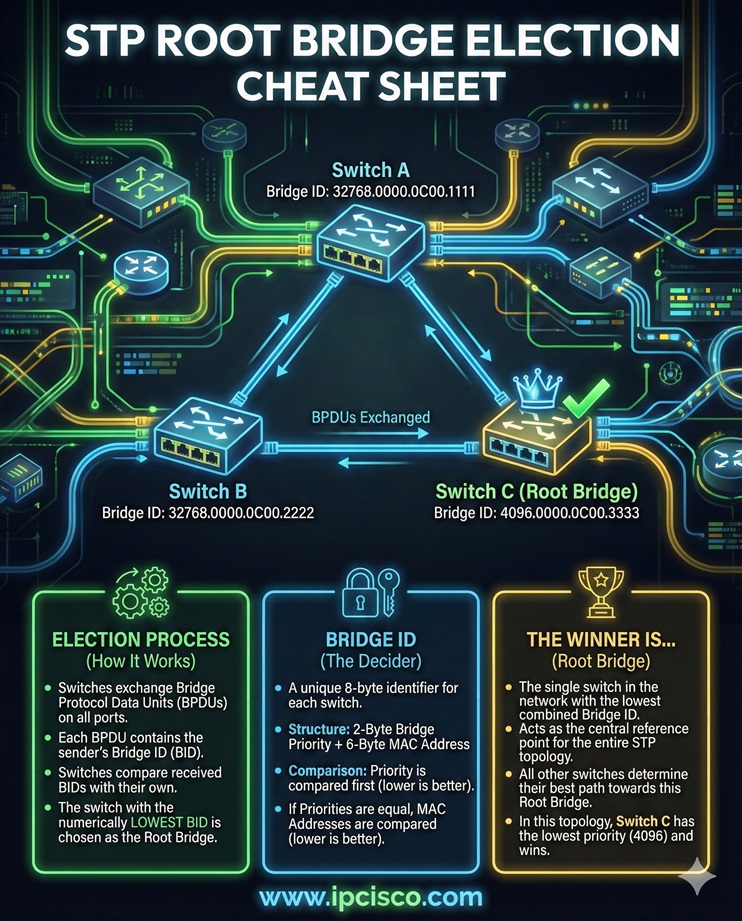
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a switching mechanism that disables redundant links to prevent layer 2 loops, broadcast storms in a switched network. STP is a layer 2 protocol and it works on switches. Spanning Tree is an important lesson in all level Cisco certifications like Cisco CCNA, CCNP ENCOR and CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure.
In networks, sometimes switches are connected together to form a large switched network. These connections can cause broadcast storms or layer 2 loops. This is an undesired situation in a network. To prevent these problems, various types of STP introduced.
By default, STP is enabled on the switches. In a switched network that uses STP, Root Bridge Election is done. According to this election, a root bridge is elected and different port roles are assigned to the different ports. Here, two key roles are forwarding state and blocking state.
If a role is in forwarding state, it works as normal port. If it is in blocking state, switch do not send and receive any data on this port.
Table of Contents
One of the most important mechanisms in STP is Root Bridge Election. STP Root Bridge Election is done based on Bridge ID.
Bridge ID = Bridge Priority + MAC Address
Here, the most important part is Bridge ID. Because the switch that has the Lowest Bridge ID becomes root bridge. The default Bridge Priority is 32768. If we do not change these default priorities in the switches, the switch that has the Lowest MAC Address becomes STP Root Bridge.
As a best practice, network engineers set a lower priority on a switch manually, to manipulate root election. By doing this, they ensure that this switch becomes the root bridge. In other words, they do not rely on MAC Addresses for this election.

There are several port roles in STP mechanism. With these port roles, STP prevents a switched network from layer 2 loops. What are STP Port roles? These are:
Root Port: The port that ahs the lowest cost to the root bridge. They are on the switches that are not root bridge.
Designated Port: It is the best port on a network segment that forwards traffic toward the root bridge.
Non-Designated Port: The ports that placed in blocking state to prevent loops.
There are also other port roles like Alternate port and Backup port in other STP types to create more efficient Spanning Tree mechanism.
There are different Spanning Tree Protocol types. All these types have different performance in a switched network. What are these STP types? These are given below:
STP (802.1D) is the original Spanning Tree version. The convergence of this version is slow.
RSTP (802.1w) is another version that improves convergence. Here Port state transitions are faster significantly.
PVST+ is a Cisco’s STP implementation. Here, STP per VLAN is used.
Rapid PVST+ is another implementation that combines per-VLAN operation with RSTP speed.
MSTP (802.1s) is an STP version that allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning-tree instance. It is used in large networks to provide improved scalability.
Correct Answers: 1B, 2B
Leave a Reply