There are two main types of redundacy mechanims on Ethernet. These are:
- Link Redundancy
- Topology Redundancy
You can also download all Nokia Labs, on Nokia Configuration Labs Page.
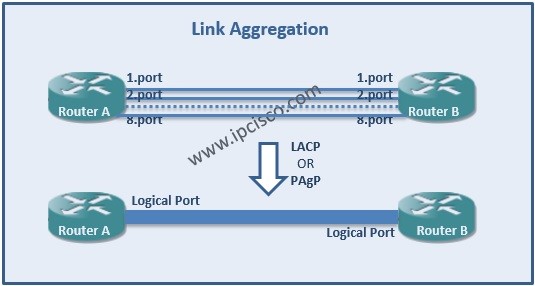
Link Redundancy is done via bundling multiple links logically between two devices. After bundling, this link seems as one link logically. But in real, multiple links are active and even one of them fails, the link continue to be active.
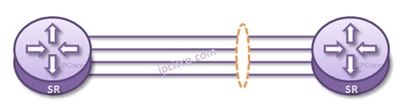
Table of Contents
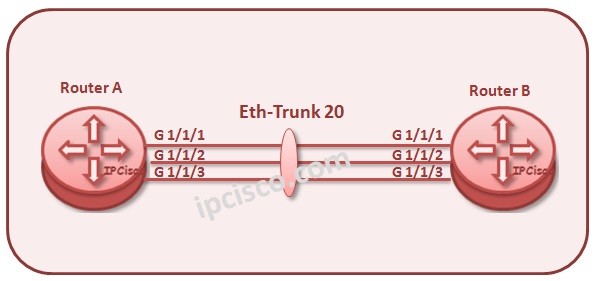
Ethernet Redundancy with LAG (Link Aggregation)
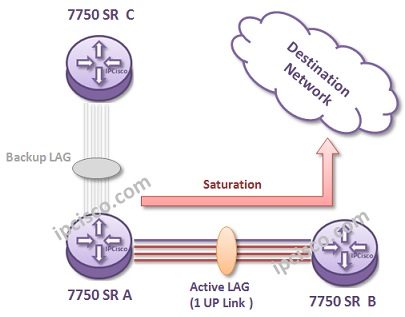
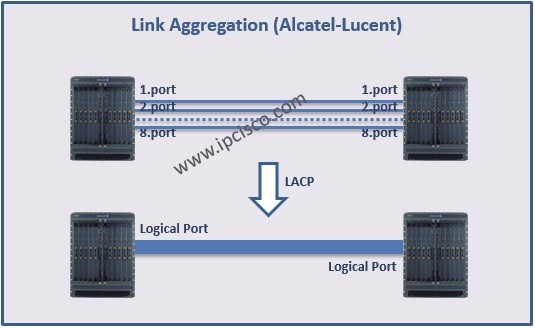
Link Aggregation is one of the link redundancy and capacity increase technique on any links. With bundling multiple links between different locations, you can build one logical link with more bandwidth. This bundle is also redundant. Even if one of the links between this devices fails, the logical link continue to work. The failover time is less than a second on a LAG. It is very few.

In a LAG all the links must have the same characteristics. The links’ speed, duplex type, hold-timers, etc. must match. The offered configuration is configuring the ports with no autonegotiate and full duplex in a LAG.
In a Link Aggregation (LAG), maximum 8 links are allowed. In other words, you can only aggragate 8 links under a LAG. And maximum 200 LAGs can be formed in Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) 7750 SR-12 Routers. This value is maximum 64 for Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) 7750 SR-1.
You can test yourself with Nokia NRS I Questions or Nokia NRS II Services Architecture Questions.








Leave a Reply