Service perspective is a Nokia‘s view for providing internet and VPN services to the customers. In other words Nokia MPLS VPN is called as Services. There are many services in Nokia Service Routers. For this services some configurations must be done under Nokia Service Routers. As a beginning learning some service related terms used in Nokia Service Routers will be good.
Some of the terms that will be used during Nokia MPLS VPN Service Configurations on Nokia Service Routers are mentined below:
Subscriber : Customer part.
Customer ID: Customer indentical ID that will use the service.
Service ID : The identical ID of the service.
Service Type : Which service? IES, VPWS, VPLS or VPRN. It is configured with Service ID.
SAP (Service Access Point) : A logical term that used for customer access point to the service.
SDP (Service Distribution Point) : A logical term used for the transport tunnel that carries service data.
Transport Tunnel: This is the Logical LSP tunnel that is signalled with LDP or RSVP-TE. SDP is associated with transport tunnel.
Service Tunnel: Logical tunnels that carries service. This is representeby service labels.
VC-ID : Term that is used to identify the service when signalling the labels. Generally equal to Service ID.
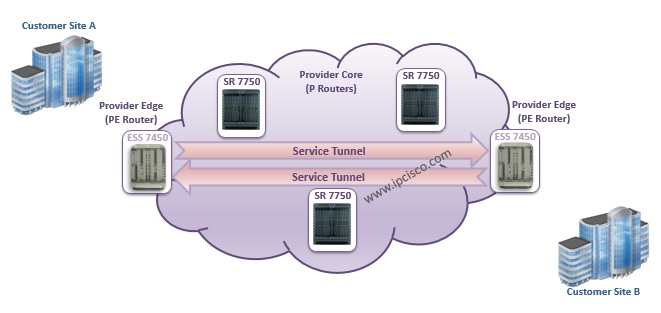
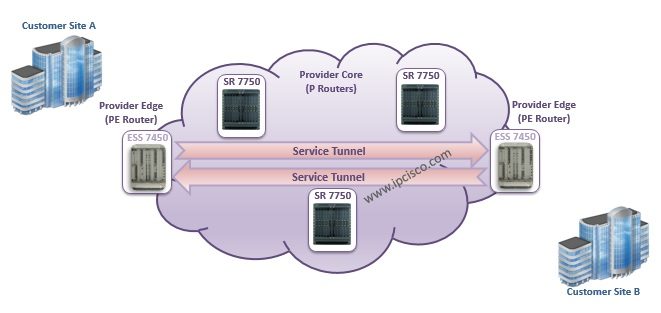
As you know in the general IP/MPLS topology, there is a MPLS Core and the routers in this core is called P (Provider) Routers. There are also routers in the Edge of this MPLS Core. These routers are called PE (Provider Edge) Routers.
In Nokia, in the MPLS Core, generally Nokia 7750 Service Router(SR) devices are used as a P Routers. So in this usage, they do not knwo anythign about services. At the Edge of MPLS Core, Nokia 7450 ESS (Ethernet Service Switch) is used. This Edge devices are service avare and the service definitions of customers are done here.
In the below diagram, you can see the usage of these devices in the MPLS Core Network.
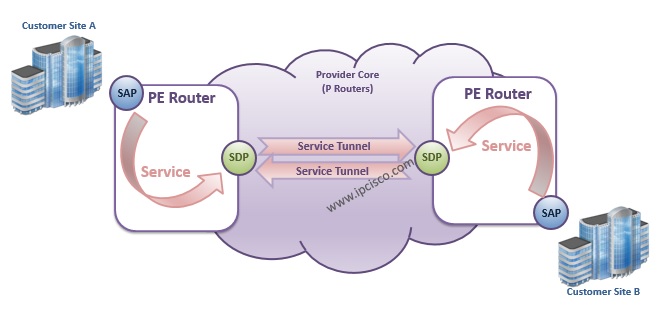
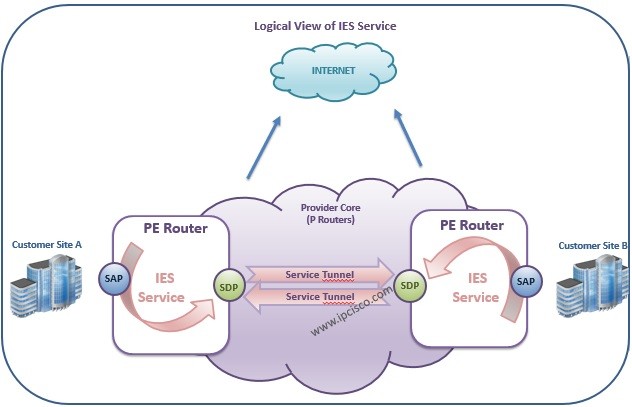
You can check also logical service diagram below. In this diagram, SAP and SDP point is showed logically in the PE Routers. As you can see, SAP is the Customer Face and SDP is the MPLS Service Tunnel Face.
Service Creation Steps
- Create a Customer with a Customer ID,
- Create a service that is associated with this Customer ID,
- Create SAP on access ports that is connected to the subscriber,
- Create SDP on the port that is connected to the remote router.
- Enable the service.
Basically, the service creation are like above. In this point I will not give any configuration example. Because to begin to the configuration of a service, some preparation must be done before. In the next article, we will talk about this steps and after next article, service configuration will be explained.
The steps that must be done in the network before service creation are mentioned below.
Configuration of the Network Before Service Configuration
- Enable IGP and be sure that the network is converged.
- Enable MPLS and LDP or RSVP.
- If RSVP is choosen, create MPLS path.
- If RSVP is choosen, create LSP and bind MPLS path to the LSP.
- Create SDP and SDP characteristics.
- Create customer facing ports as access port.
If all the steps are OK, then you are ready to create services that mentioned above with 5 steps. It looks a little complex,right?:) Do not worry, with the next article, we will make all these configurations orderly. Keep on IPcisco.com;)








Thanks , Very useful information.
Shouldn’t the green circles labeled SAP be labeled SDP as it appears that the service tunnel is connected to two PE routers, PE1 and PE2?
thanks alot for your effort
Sir,
would you confirm what is spoke:sdp . why we use spoke:sdp command in Epipe
Thanks , very Useful
Thank you for sharing very useful topic
This is the nice article. I understand some point that is very helpul.
Thanks
Always welcome Arif :)
very simple very easy to understand
Thank you very much gokhankosem . Currently i am working at ISP