- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
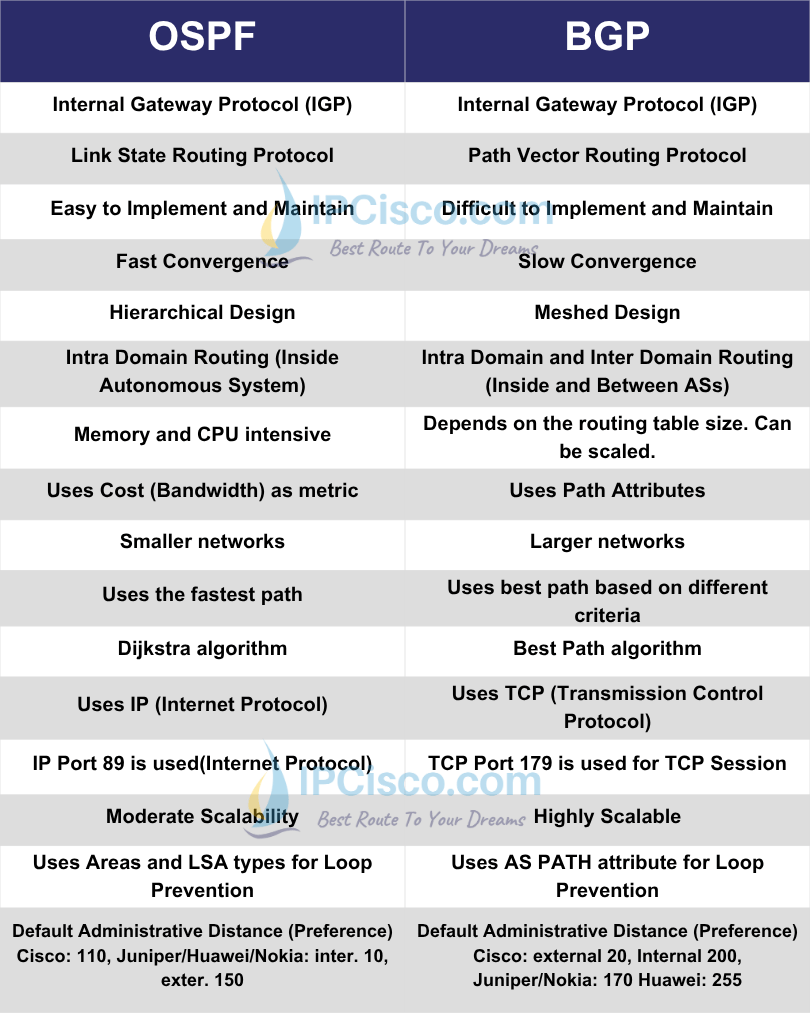
Table of Contents
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) are two widely used dynamic routing protocols in network world. OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) and BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). But what else? If we compare OSPF and BGP, what is the differences of these two dynamic routing protocols? In this OSPF vs BGP lesson, we will do this OSPF and BGP comparison and you will learn the difference of these Layer 3 protocols. You can find the BGP and OSPF COMPARISON TABLE at the end of this lesson.
Before comparing BGP vs OSPF, let’s focus on each protocol separately and remember their characteristics.

You can also check Network Protocol Cheat Sheets
OSPF is basically a Link-State Dynamic Routing Protocol. It is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), in other words it is used for intra-domain routing. Here, intra-domain means, inside an Autonomous System.
Open Shortest Path First protocol is an open, standard based network protocol which requires a hierarchical network design. It works with different area hierarchy. There is a backbone area, Area 0 and there are other areas in an OSPF network. Using multiple hierarchical areas improves network performance. There are different OSPF area types used for different purposes.
Open Shortest Path First protocol uses different router types. Internal router, Backbone router, Area Border Router (ABR) and Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) are different router types used in OSPF network.
OSPF uses Dijkstra Algorithm for route calculations and finding the best path during routing. According to the cost values, OSPF determines the best path.
OSPF uses different packet types. These five OSPF packet types are Hello, Data Description (DD), Link State Request (LSR), Link State Update (LSU) and Link State Acknowledgment (LSAck). These packets have the same 24 bits header. One or more link-state advertisements (LSAs) are sued with these packets.
Convergence is the term used to show the route recalculation period after a change. OSPF has fast convergence mechanism. This characteristic recalculates routes quickly after a change. By doing this, network downtime is minimized.
OSPF supports VLMS (Variable Lenght Subnet Mask) and CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing). By doing this it uses ip addresses efficiently.
OSPF also support MD5 and plain-text authentication for route updates.
There are two OSPF versions. These are OSPFv2 and OSPFv3. Version two is used with IPv4 (For more information, you can check RFC 2328). Version three was developed for IPv6 (RFC 5340).
There are multicast addresses in Open Shortest Path First protocol. With these multicast addresses, it uses multicast instead of broadcast. This reduces bandwidth usage. What are the multicast addresses used by OSPF? These are: 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6.
224.0.0.5 is known as All OSPF Routers address. It is used to send LSAs to all OSPF routers on the network. 224.0.0.6 is known as All OSPF Designated Routers address. It targets only Designated Routers (DRs) and Backup Designated Routers (BDRs). These are the addresses used by OSPFv2.
For IPv6 version of OSPF, OSPFv3, FF02::5 is used for all OSPF Routers and FF02::6 is used for all DR Routers.
By the way Open Shortest Path First protocol uses protocol number 89. This number is in IP header (Internet Protocol Header). OSPFv3 runs also on top of IPv6. Here the IPv6 Next Header value is also 89.
The default Administrative Distance (Preference) of OSPF is 110 for Cisco routers. On different vendors, there are different preference values for internal and external OSPF. For example, for Juniper, Huawei and Nokia routers, internal OSPF preference value is 10 while external OSPF preference value is 150.
First of all, let’s start with the advantages of OSPF.
The first advantage of OSPF is Convergence Time. OSPF is a fast converged protocol. With this mechanism, network downtime during a change is minimum.
The second advantage is about Load Balancing. OSPF uses equal cost load balancing toward the same destination. With this mechanism, bandwidth management can be done over links.
Another advantage of OSPF is about adaptation to different types of networks. You can use Open Shortest Path First protocol both on small networks and on large networks. This makes this protocol a common protocol for both enterprise networks and ISP internal networks.
How about disadvantages of OSPF?
The first disadvantage is about management. OSPF is difficult to manage on large networks.
Anther disadvantage is about route calculation. OSPF route calculation needs more information.
One disadvantage is also about memory. OSPF uses more memory than other routing protocols.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a Path Vector Dynamic Routing Protocol. It is also known as the protocol of Internet. BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), in other words it is used for Inter-domain routing. This means that, Border Gateway Protocol is mainly developed to be used between Autonomous Systems. This is eBGP (Exterior Border Gateway Protocol) But it can be also used inside Autonomous Systems to advertise networks. If we use BGP for this purpose, it works as IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol). And this is iBGP (Interior Border Gateway Protocol).
BGP is a path vector protocol. It uses BGP Path Attributes to determine the best path through a destination. With path attributes we can manage traffic paths according to our needs.
BGP has two types. These BGP types are: eBGP (Exterior Border Gateway Protocol) and iBGP (Interior Border Gateway Protocol). eBGP is commonly used between different Autonomous Systems. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use this type of BGP more to connect different ISPs. iBGP is sued inside an Autonomous system. The main duty of this type of BGP is advertising eBGP learned routes to internal network.
For Cisco routers, the default eBGP administrative distance value is 20 while the default iBGP administrative distance value is 200. This is also different for different vendor devices. For Juniper and Nokia routers, the default BGP preference value is 170. For Huawei routers, the default BGP preference value is 255.
There are different advantages of BGP. Let’s talk about these advantages one by one.
The first advantage of BGP is about the size of a network. BGP is a routing protocol good on large networks.
Another advantage is with BGP, we can easily manage routes. This provides an efficient routing mechanism according to changing needs.
BGP is a scalable routing protocol.
One advantage is also about Policy-based routing. With this mechanism, we can manipulate routing.
How about BGP disadvantages?
The first disadvantage of BGP is about convergence time. This time was very fast in OSPF networks. But BGP convergence time is slow.
Another disadvantage is about security. BGP has less internal security mechanism.
And BGP is not suitable for small networks. It needs a large network to operate good.
The other disadvantage of BGP is about expertise. BGP need expert engineers because it is difficult to configure and maintain BGP.
Asa real world example, we can think an ISP network which provides Internet access to a country. In this ISP network, as an internal routing protocol, OSPF is used. There is a backbone Area, Area 0 and there are other OSPF areas that cover all the Service Provider network. This ISP uses also BGP to connect to the different ISPs. As a summary, here, it uses OSPF as Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) and it uses BGP as Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP).
In ISP OSPF network, area 0 is used as backbone area. The other areas are connected to this backbone area. Here, a hierarchical design is used for easy management.
Towards other ISPs, BGP is used. And with different path attributes, route management is done.
After explaining each routing protocol detailly, now it is time to compare BGP and OSPF. Here, we will compare the key features of these two important routing protocols. After this comparison, you will be ready for the comparison of OSPF vs BGP.
| OSPF (OPEN SHORTEST PATH FIRST) | BGP (BORDER GATEWAY PROTOCOL) |
|---|---|
| Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) | External Gateway Protocol (EGP) |
| Link State Routing Protocol | Path Vector Routing Protocol |
| Easy to Implement and Maintain | Difficult to Implement and Maintain |
| Fast Convergence | Slow Convergence |
| Hierarchical Design | Meshed Design |
| Intra Domain Routing (Inside Autonomous System) | Intra Domain and Inter Domain Routing (Inside and Between ASs) |
| Memory and CPU intensive | Depends on the routing table size. Can be scaled. |
| Uses Cost (Bandwidth) as metric | Uses Path Attributes |
| Smaller networks | Larger networks |
| Uses the fastest path | Uses best path based on different criteria |
| Dijkstra algorithm | Best Path algorithm |
| Uses IP (Internet Protocol) | Uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) |
| IP Port 89 is used(Internet Protocol) | TCP Port 179 is used for TCP Session |
| Moderate Scalability | Highly Scalable |
| Uses Areas and LSA types for Loop Prevention | Uses AS PATH attribute for Loop Prevention |
| Default Administrative Distance (Preference)
Cisco: 110, Juniper/Huawei/Nokia: inter. 10, exter. 150 |
Default Administrative Distance (Preference)
Cisco: external 20, Internal 200, Juniper/Nokia: 170 Huawei: 255 |
First of all OSPF is an Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) while BGPm is an External Gateway Protocol (EGP). This means that, OSPFm is used for Intra Domain Routing inside an Autonomous System. BGP is used both for Intra Domain and Inter Domain Routing. In other words, we can use BGP both inside an Autonomous system and between between Autonomous systems.
OSPF is a Link-State routing protocol like Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS). But Border Gateway Protocol is a Path Vector routing protocol.
Open Shortest Path First protocol need an experience for the implementation and maintain process. BGP need special expertise to implement and maintain. So, it is easy to configure and manage OSPF, but it is difficult to configure and manage BGP.
Another difference between BGP and OSPF is about convergence times. After a failure or an update, OSPF convergence time is short while BGP convergence time is long. So, OSPF convergence is fast and BGP convergence is slow.
OSPF has a Hierarchical Design ehile BGP has a Meshed Design.
OSPF protocol is Memory and CPU intensive protocol. This is up to the routing table size on BGP and this can be scaled.
As a metric, OSPF uses Cost (Bandwidth). On the other hand, BGP uses Path Attributes.
OSPF is used in small or medium networks while BGP is used in large networks.
OSPF uses Dijkstra algorithm (SPF Algorithm) while BGP uses Best Path algorithm. According to these algorithms, Open Shortest Path First uses the fastest path while BGP uses best path based on different criteria.
Open Shortest Path First protocol uses IP (Internet Protocol). IP Port 89 is used (Internet Protocol) by OSPF. BGP uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). TCP Port 179 is used for TCP Session establishment for BGP.
OSPF scalability is Moderate while BGP scalability is High.
For loop preventaton, OSPF uses Areas and LSA types. BGP uses AS PATH attribute for Loop Prevention.
The Default Administrative Distance (Preference) values are also different for OSPF and BGP. They are also different in different network vendors. Below, you an find these default preference values.
Default OSPF Administrative Distance (Preference):
Default BGP Administrative Distance (Preference):
Leave a Reply