- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
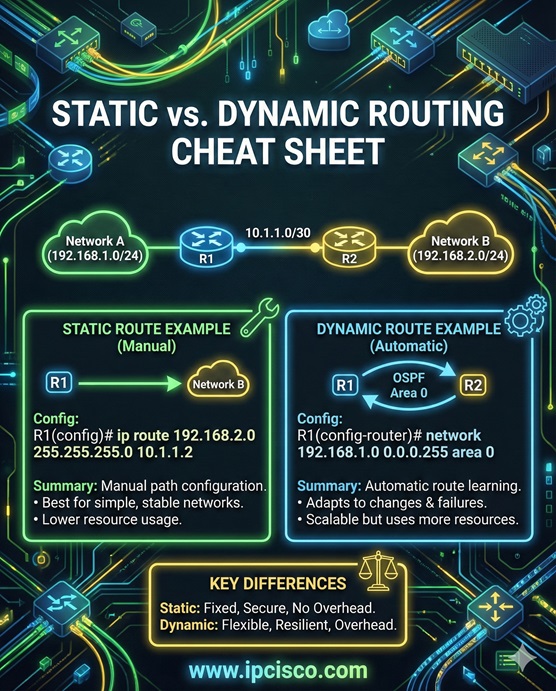
Static routing is the manual routing that is done with static routes that we write manually. Dynamic routing is the routing that learns routing automatically with the help of Routing Protocols. Basically, static routing is manual and dynamic routing is automatic routing process. This is a very important lesson for CCNA, CCNP ENCOR and CCIE level exams and Network Engineer Job Interviews.
Static routing is used in small networks in which writing routes can be easily handled with manual routes. It provides more admin control. But in large networks it is impossible to write all routes manually. So, dynamic routing is used. Using dynamic routing is a scalable solution for middle or large networks. Even we use dynamic routing in a network, we can also use static routing in some parts of the network.
Dynamic Routing uses routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP and IS-IS. When you configure routing protocols in a network for dynamic routing, these protocols calculate and determine routes dynamically without any manual configuration.
Table of Contents
In different routers, we configure static routing with different commands. Here, we will focus on Static Route Configuration on Cisco Routers. On Cisco routers, to write a static route, we use “ip route” command with the “destination network address” and “destination subnet mask” followed by the “next hop ip address”.
For example, to write a static route towards 192.168.1.0/24 with next hop 10.0.0.1, we will use the below Cisco command under the configuration mode.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1
Another way to write a static route is using outgoing interface name instead of next hop ip address. For example, let’s use Gi0/0 interface as outgoing interface instead of next hop ip address.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Gi0/0
There are different types of routing protocols. These are given below:
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a Distance Vector protocol. OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and IS-IS (Intermediate System – Intermediate System) are Link-State protocols. EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a Hybrid protocol that has both distance vector and link-state characteristics. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a Path Vector protocol.
In another classification, RIP, OSPF, IS-IS and EIGRP are Interior Gateway Protocols that are used within a single Autonomous System. BGP is the single Exterior Gateway Protocol that is used between Autonomous Systems.
Correct Answers: 1C, 2C
Leave a Reply