- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
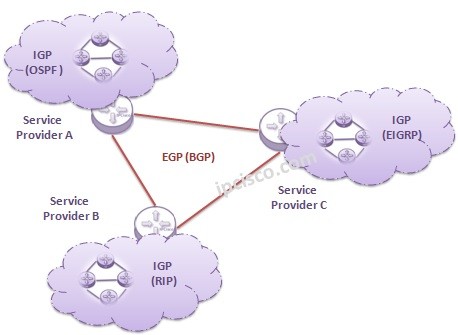
Table of Contents
Dynamic Routing is the routing process that is done via a Routing Protocols in networking. The protocols that are used for this aim in Layer 3 are also called Dynamic Routing Protocols. In this lessons, we will focus on the types of protocols used for routing in networking.
Routing Protocols can be divided into different categories according to their purpose and their operation behaviour. Here, we will see these categories and the types of these protocols in networking.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP Route Practice Tests Page!
If we divide these protocols according to their purpose, there are two types: These are:
IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) is a Routing Protocol category that are used inside an Autonomous System(AS). With Autonomous System(AS), we try to meant a network of an organization.
What are these IGPs (Interior Gateway Protocol). The generaly used IGPs in Today’s network worl are given below:
You can view Administrative Distance values of Routing Protocols for different vendors like Cisco, Nokia, Juniper and Huawei
Beside IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol), the other Routing Protocol type according to their purpose is EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol). Today, there is only one EGP being bused. This EGP is the wellknown protocol of Internet BGP.
EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) is used for routing between Autonomous Systems(AS). In other words, it is responsible routing between different Organizations. This is because, BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is used as Internet protocol. It manages the routing between diffent networks in the world and this build internet.
Another Routing Protocol Types are more detailed and according to their operation style. Here, we can divide Dynamic Routing Protocols in networking into four main category. These main categories are:
You can find the table of dynamic routing protocols below:
Distance Vector Protocols are RIP, IGRP. As its name implies, Distance Vector Protocols use distance to determine the best path. This distance can be hop, cost, delay or any other parameter. According to these values, the best route is selected. Beside, Distance Vector Protocols use the outgoing interface to determine the best path. In other words, it uses both distance parameter (hop or cost or delay) and vector(direction) parameter to determine the best path.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP Route Practice Tests Page!
Distance Vector protocols view the network from the neighbour perspective. All routers send frequent updates to their neighbors. This consumes more resources.
Link-State Protocols are OSPF, ISIS. They both use SPF (Shortest Path First) Algorithm. All the routers in the network has a network topology view and this is same in all routers in the network. In other words, Link State Protocols see whole network not the only network that its neighbour see like Distance Vector Protocols.
Link State Routing Protocols use different Tables. These are Topology Table, Neighbour Table and Routing Table.
The updates of Link State Routing Protocols are triggered not periodic like Distance Vector Protocols. In other words, link-state protocols use triggered updates. The convergence time is short in Link State Routing Protocols. But as a disadvanatge, they need only more memory than Distance Vector protocols. But the resources they use is less than Distance Vector Protocol.
You can find the all differences of Distance Vector and Link State Protocols in the below table:
Hybrid Protocol is EIGRP. EIGRP is a protocol that has both Distance Vector and Link-State properties. So, Hybrid is a nice name to imply EIGRP. Hybrid Protocol EIGRP, uses metrics like Distance Vector Protocols. Beside, it uses Triggered Updates like Link-State Protocols.
Path Vector Routing Protocol is BGP. BGP Uses Policies instead of Algorithms. It is a slow protocol because of path exploration. For loop free mechanims, it relies on not distance like Distance Vector Protocols. Instead it uses Path analysis.
We can also divide Routing Protocols into two according to used Routed Protocol (IPv4 or IPv6). These types are also explained in an other lessons. So, here we will only give the type names.
IPv4 Routing Protocols:
IPv6 Routing Protocols:
Leave a Reply