- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this lesson, we will learn a security feature named Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (uRPF). We will focus on what is uRPF and how it works. We will also focus on Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding Configuration on Cisco routers. We will explain how to configure uRPF with an example.
Cisco CCNA Course & Cisco CCNP ENCOR Course
Table of Contents
uRPF is the abbreviation of Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding. So, what is uRPF, what is Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding? Unicast Reverse Path Forwardig is an antispoofing security feature with which, we can check the incoming traffic source ip address if it is known by the router and this interface is also used to reach that source. If there is no match, the packets are dropped.
With this mechanism, router verifies the source ip address on its routing table. It checks that if this source ip address is known and/or the receiving interface is also used to reach that source ip address.
What if we do not use this antispoofing security mechanism? At this time, whenever an attacker sends malicious traffic which has a manipulated source address, this traffic will pass through the interface and this can cause harmful attacks to our router. Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding prevents such ip spoofing attacks.
There are two modes of Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding. These uRPF modes are given below:
Now, let’s learn what are these Unicast Reverse Path Forwardng modes.
uRPF Strict Mode is one of the modes of Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding. In this mode, router checks two things related with the incoming packet. One of them is routing table check. It checks if are there any entry in the routing table related with this source ip address. The second one checking if the same interface is used to reach the source. In other words, here the packet must be received from the interface that it is also used to forward it back. In uRPF Strict Mode, if the packet passes these two checks, the packet is forwarded. If it can not pass this process, the packet is dropped.
Loose Mode is the other Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding mode. In this mode, router checks only routing table if are there any entry related with the source. Again, if the packet finds any entry in the routing table, it passes this single check and the packet is forwarded. If there is no entry related with the source ip address, then the packet is discarded.
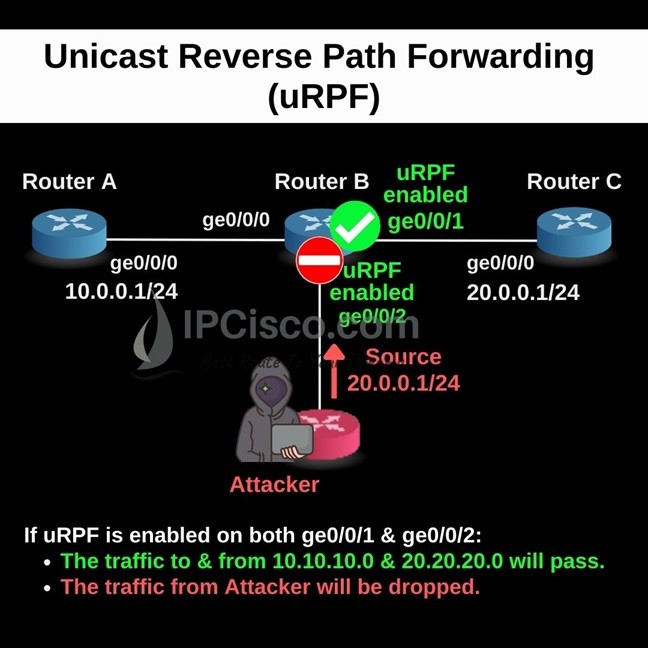
To understand Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding better, let’s give an example. For our uRPF example, we will use the below topology. Here, we will see the case that we use Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding and the case that we do not use this security mechanism.
On the below topology, If uRPF is enabled on both ge0/0/1 & ge0/0/2. And with the configuration;

We have learned what is uRPF and how uRPF works. Now, it is time to configure uRPF on Cisco routers. Here, we will focus Cisco Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding Configuration.
To configure uRPF Strict Mode on a Cisco router, we will enable cef firstly with “ip cef” command. This is required for uRPF check. After that, we will go to the related interface and under this interface we will configure uRPF strict mode with “ip verify unicast reverse-path [access-list-number]” command. Here, we can use any access list also. In this example, we will not use access list.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip cef
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Router(config-if)# ip verify unicast reverse-path
Router(config-if)# end
To configure uRPF Loose Mode on a Cisco router, we will enable cef firstly with “ip cef” command again. After that, we will go to the related interface and under this interface we will configure uRPF loose mode with “ip verify unicast source reachable-via any [access-list-number]” command. Here, we can use any access list also. In this example, we will not use access list.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip cef
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Router(config-if)# ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
Router(config-if)# end
To verify uRPF, we can use the below show and debug commands on a Cisco router.
With show cef interface, we can display Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding is enabled or not.
Router# show cef interface
With show ip traffic, we can display the drops related with Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding.
Router# show ip traffic
With debug ip cef drops rp, we can display the detailed information about Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding dropped packets.
Router# debug ip cef drops rpf
This is basically what is Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding and how Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding works. To have a more secured router towards ip spoofing attacks, it is good idea to use this security mechanism.
DOWNLOAD Cisco Packet Tracer Configuration & Cisco GNS3 Configurations
Leave a Reply