- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
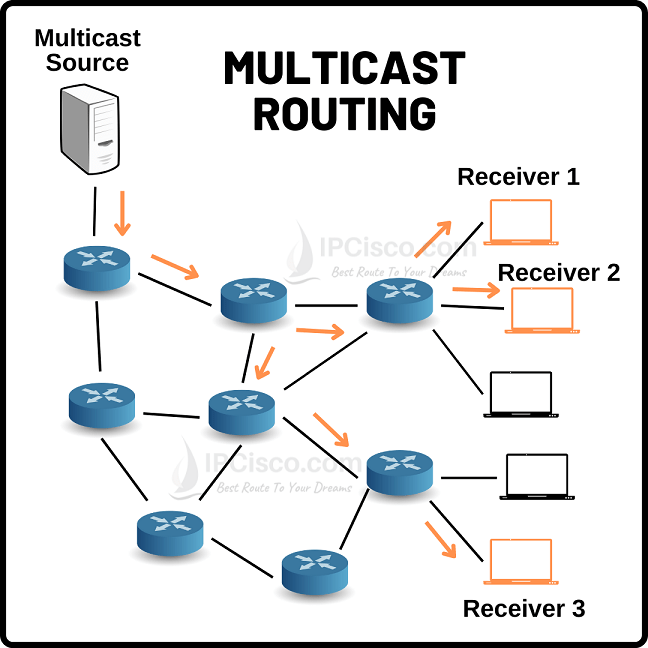
Routing is one of the most important and popular lesson of computer networking. Network engineers like to work on routing too much. Especially on routing protocols. And while working on routing with routing protocols, routers use entries in the routing tables. These routing entries are generally unicast entries and so, network engineers work on Unicast Routing. How about Routing in Multicast networks? If a packet comes to a router which has a multicast destination address, how a router will route this packet? And what is Multicast Routing? Multicst Routing is the routing process used for multicast destinations. Routers do this Routing with the help of Multicast Routing Protocols.
So, what is Multicast and what is Multicast Routing? Let’s firstly start with this question.
You can test yourself with IP Multicast Questions!
Table of Contents
The first question of this lesson is what is multicast? So, what is multicast really? Multicast is basically a data transfer method which sends the data to the multiple receivers belongs to a specific group. The three key thing in this transfer type is, there is a multicast source, a multicast group and there are multicast group members which can receive the data sent by the multicast source.

Multicast Routing
Let’s explain multicast with an example. For example, you are giving an IPTV service and you have many subscribers. If there was no multicast, you had to send your IPTV traffic to each subscriber as unicast one by one. Think about thousands of receivers. How a bandwidth and performance insulting thing is it. But with multicast, you can send one copy of the traffic to multiple receivers. Instead of creating a copy for each receiver, you send only one. And this reduces bandwidth usage and increase network performance.
We have answered what is multicast question. Now, it is time to answe What is multicast routing question.
The second question that we will answer in this lesson is what is Multicast Routing? Multicats Routing is basically an efficient method for one-to-many multicast traffic. This multicast traffic can be an IPTV traffic, a video conference traffic, gaming, live streaming etc. With an efficient way, this routing provides sending only one stream of a multicast traffic to multiple receivers.
Multicast Routing has some similarities and differences with normal routing. Normally, when we check a routing table of a router, we see routing entries. These entries can be static route, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP entries etc. Each of these routes shows us the required next hop for the given destination address. But all of them are unicast entries. When a packet comes to the routers with a multicast destination address, routers do not know how to route this packet if they are not using Multicast Routing Protocols. But if a router uses a Mutlicast Routing Protocol, it can send this multicast packet to the interfaces that are members of the specific multicast groups.
In normal routing, each router needs to know the address of the next router in the path to the destination. But in multicast routing, there is no need for this. Having only the next router address is enough for mutlicast routing. This reduces bandwidth usage and increases performance a lot!
For multicst routing, all routers need to have a multicast address with which they can send packets each other.
There are different Multicast Routing Protocols used for multicst routing. So, what are these Protocols? These are given below:
PIM is the most used routing protocol in multicast world. We will detailly discuss PIm in other lessons.
Leave a Reply