- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
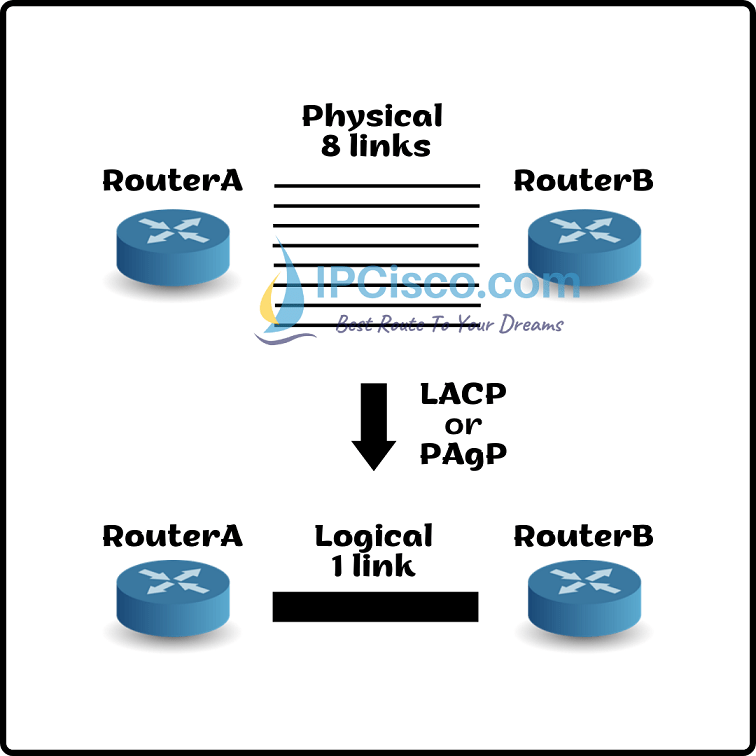
Table of Contents
Link Aggregation is bundling two or more links as one logical link for increasing bandwidth and availability. This bundle is called Link Aggregation (LAG). To configure link aggregation, there are two way. One of them is using Cisco proprietary EtherChannel, the other is IEEE 802.3ad standard. EtherChannels can be done by one of the two network bundling protocols. One of them is the Cisco proprietary PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) and the other is LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol). IEEE 802.3ad standard can be used only with LACP. These two protocols does not interoperate each other. You can use only one of them to configure link aggragation. You can also check wiki definion, here.
Here, we will focus to the standard based, Link Aggregation Control Protocol. In another lesson, we will learn How to Configure LACP on Cisco , Juniper LACP Configuration and Nokia LACP Configuration. The latest Cisco devices are already use LACP instead of PagP.
To aggragete physical links to a single logical link, firstly we need more than two ports with the same characteristics such as data rate, duplex capability, etc. After that, we can bundle different physical links into one logical link to increase bandwith and the availability of the link.
How many links can we bundle together? There is also a limitation about ports in the bundle. In Cisco platforms the ports in a bundle is limited by 8 ports . This can be change in some platforms. For example in Cisco 10000 series, only 4 port is supported in a bundle. We can name the created logical name as “port channel”. Up to 64 port channels is supported per device. As a summary, maximum 8 ports are allowed in a bundle and maximum 64 bundles are allowed in a device.
What about loops? Loop is prevented with a mechanism and returning of a multicast or a broadcast packets to the other ports in the bundle, is blocked.
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is a data link layer protocol defined in IEEE 802.3ad standard. It is a standard based link aggregation protocol which can be used in different vendor devices. With this protocol we can bundle several physical links and form single logical link as a bundle. Here, the link aggregation is created by LACP packets that are sent every second. And these packets are exchanged between ports in two different LACP modes. These LACP modes are Active and Passive modes.
What is the difference between LACP Active and Passive modes? How about PAgP Modes? What is the meaning of these modes?
LACP and PAgP are two link aggregation protocols. They have both two different modes. The name of LACP and PAgP channel group modes are given below.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol operates in two modes. These LACP modes are given below:
LACP Active mode initiates connection by sending LACPDUs. In other words, it actively tries to establish bundle.
LACP Passive mode waits the other end to initate the connection. In other words, it waits passively.
If both ends are configured as Active, LACP link aggregation is established. If at least one end is configured with Active mode, LACP link aggregation is also established. But, if both ends are configured with Passive mode, link aggregation is not established.
Port Aggregation Protocol operates in two modes. These PAgP modes are given below:
PAgP Desirable mode actively initiates connection for PAgP negotiation. In other words, it actively tries to establish bundle.
PAgP Auto mode waits the other end to initate the connection. In other words, it only responds to connection requests.
If both ends are configured with PAgP Desirable mode, link aggregation is established. If at least one end is configured with Desirable mode, PAgP link aggregation is also established. But, if both ends are configured with PagP Auto mode, link aggregation is not established.
When we enable LACP on each end, they sends LACPDUs each other according to their modes. After receiving these LACPDUs, firstly, LACP System IDs are compared.
LACP System ID = LACP System Priority + MAC Address
Here, the part that has the higher LACP System ID is elected as actor. But the key point is “the higher the number, the lower the priority.” In other words, the lower number is elected as actor. The other will be partner.
So, firstly, system priorities will be checked and the higher system priority (lower value) will be elected as actor. If they have same priority values, MAC addresses is used as tie breaker. Then the one that has the lower MAC address is elected as actor.
LACP Port Identifier = LACP Port Priority + Port Number
After actor selection, according to LACP Port Identifiers, active ports are determined. Again the lower number will be highest. So, the priority value that has the lovest value will be elected. If they are same, then tie breker will be port numbers. Lower ports will be elected as active ports.
After selecting these ports, port channel is established. After that load balancing is used between these active links. If one of the ports is failed, then the traffic is switched to the other ports.
There are some parameters that we can use during Link Aggregation Control Protocol configuration. These parameters are given below.
LACP System Priority: This is configured per router. It is used with MAC address to create Link Aggregation Control Protocol System ID. The default system priority is 32768. It can take any valid value between 1 to 65535. The key point is: The higher the number, the lower the priority.
LACP System ID = LACP System Priority + MAC Address
LACP Port Priority: It is confiured per port. It is used to form Port Identifier with Port Number. It can take any valid value between 1 to 65535. The key point is: The higher the number, the lower the priority.
LACP Port Identifier = LACP Port Priority + Port Number
It is also used to determine which port should be in standby mode during an hardware limitation.
LACP Administrative Key : It is automatically calculated equal to the channel group identification number on each LACP configured port. It defines the ability of a port to aggregate with other ports. The aggragation abiliy is determined by, port characteristics and configuration restrictions.
LACP Max-bundle : It is the number of bundled ports in a bundle. As I mentined below it is maximum 8.But in some platforms it can be 4.
If all the compatible ports can not be aggregated by Link Aggregation Control Protocol, the the remaining ones go to teh standby state. When there is a failure of one of teh bundled ports, then they become active one by one.
Here, there is also another important information about a MAC address. We use MAC address 01:80:C2:00:00:02 to send LACP packets with multiple grouping.
We have learned the details of this aggregation standard. So, what is an advantage of using lacp? What are the benefits of this protocol? There are differet benefits of Link Aggregation Control Protocol. These are given below:
Link aggregation is used to increase bandwith and provide redundancy with multiple links as a logical link. With this configuration, we provide higher bandwith and availability.
LACP allows maximum 8 Active links and 8 standby links in a Bundle.
PAgP allows maximum 8 Active links.
No. These protocols can not used together. They are not interoperable.
Sure. When we bundle multiple links into a single logical link, it adds each link’s bandwith to the total bandwidth.
Exactly. When we combine several links into one link, this new link provides greater speeds.
EtherChannel is a Cisco standard and IEEE 802.3ad is an open standard that we use for LAGs.
IEEE 802.1AX standard is the upgraded version of IEEE 802.3ad standard. IEEE 802.1AX standard provides a MAC-independent Link Aggregation capability and provides general information relevant to specific MAC types.
You can also view the below LACP Configuration Lessons for different vendors:
Leave a Reply