- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
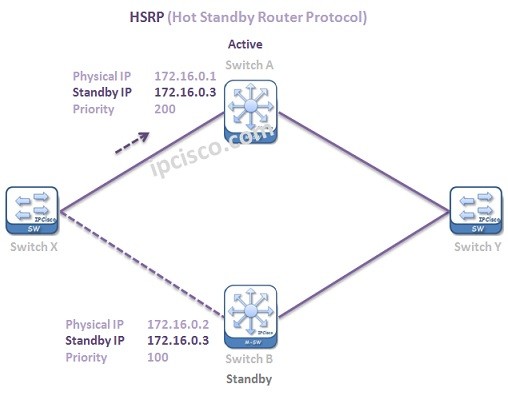
Table of Contents
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP). Hot Standby Router Protocol first hop redundancy mechanism provides an alternative path as a redundant and a proactive action for any failure on a device. In this HSRP tutorial, we will learn this gateway redundancy protocol and in the following lessons, we will also learn Cisco HSRP Configuration. You can also view related RFC 2281.

By the way, HSRP Group numbers is mention at the beginning of the confiugration after “standby” keyword. There can be multiple groups of Hot Standby Router Protocol on an interface.
Hot Standby Router Protocol works with HSRP Groups. For each group, there are different routers that has different roles. These roles are:
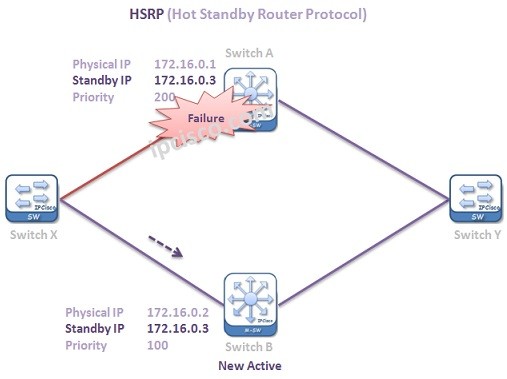
The Active Router is the router that the traffic flow goes through. It is the router that provides active traffic flow.
The Standby Router is the backup of Active Router. When the active router fails then this router becomes Active and the traffic goes through this router.
Lastly the Listening Routers are the other routers that are participating in the HSRP group.
The main two roles of HSRP are Active and Standby. For these roles, routers does an election between them. In this election two parameters are important. The elections are done according to two parameters. These are:
First of all, HSRP Priority values are used for Active/Standby election. The highest Priority wins and the router that has highest priority becomes Active Router. If the Priority values of HSRP Routers are equal, then the Interface IP addresses are used as tie breaker.The highest IP address wins and become Active Router. The router that has the second highest IP address, becomes Standby Router.
Priority values can be manually set to any value between 0 and 255. The default HSRP Priority is 100.
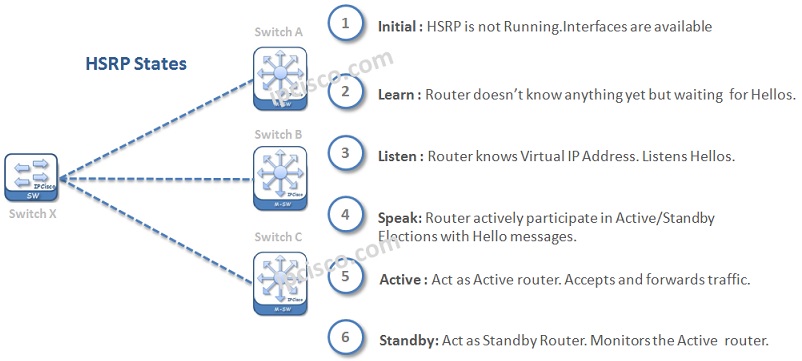
After the configuration of Hot Standby Router Protocol, some states are passed one by one. After these steps, Active and Standby routers are elected and the HSRP become active. So, what are these states?
These HSRP states are mentioned below respectively:
Only in three states, hellos are sent. Speak, Standby and Active states. As you know standby and active routers already send hellos each other. In the last one, in speak state, hellos are sent to determine the active and standby routers.
There are two HSRP versions. These Hot Standby Router Protocol versions are:
The default version is HSRPv1. It is used by IPv4 networks. In v1, Group numbers can be from 0 to 255. v1 uses 224.0.0.2 as Hot Standby Router Protocol Multicast Address to send Hellos. This is also the address that CGMP Leave process uses.The packet format of v1 is different than v2 packet format.
HSRPv2 is the enhanced version of v1. v2 supports IPv6. For Hello messaging, v2 uses a different Multicast address than v1. The new Multicast addres that v2 uses is224.0.0.102. v2 uses Group numbers from 0 to 4095.The packet format of v2 is different than v1.
In the Cisco HSRP Configuration example, we will also configure Hot Standby Router Protocol versions.
By default periodic HSRP Hello packets are sent every 3 seconds. Active router is controlled by standby router with periodic hello packets by default every 3 seconds. In case of a failure of active router, this mechanism provide switching to the backup router.
The Hold Time value is 10 seconds.
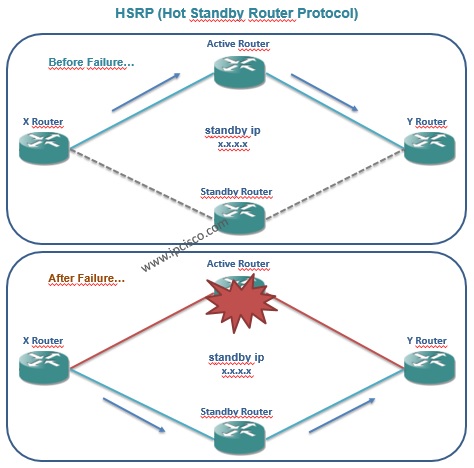
In critical systems, we need a resundant mechanism with multiple devices. Even one of these devices fails, the traffic continues over another. Gateway redundancy protocols provide this mechanism by ensuring seamless gateway failover.
The “preempt” command is used to allow taking the active role again with a higher priority. Here, if a device has higher priority, it takes active role without waiting for the failure of the standby device.
Beside Hot Standby Router Protocol, there are two other gateway redundancy protocol. These are VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) and GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol).
Cisco default priority value is 100 for Hot Standby Router Protocol.
To track an interface you can use standby <group> track <interface> <decrement> command. After this configuration, whenever this interface goes down, HSRP priority is reduced.
For verification, you can use “show standby brief” or “show standby” commands on Cisco devices. With these commands, you can check states (Active/Standby), VIP, priority, timers, and tracking status
Hello
Hello Mehdi :)
We are sorry
Full access is only for IPcisco cres
:)