- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
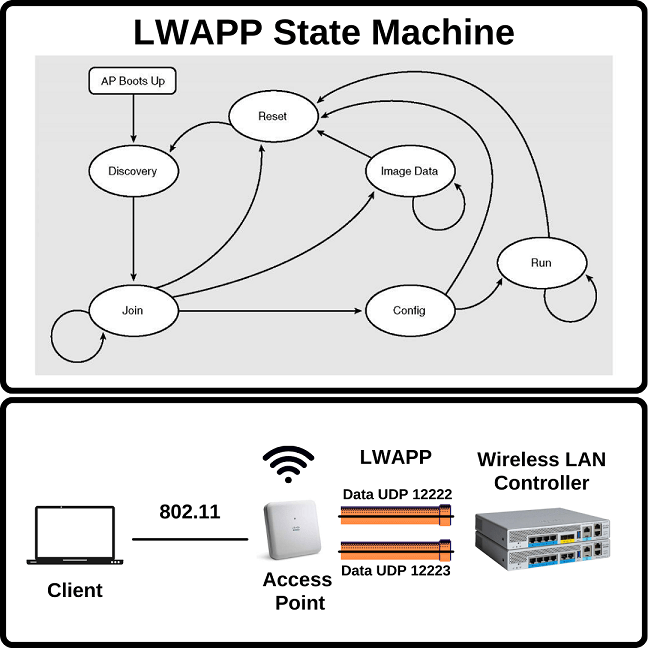
Table of Contents
In this lesson, we will learn another wireless tunneling protocol, LWAPP. We will answer what is LWAPP protocol question detailly. LWAPP (Lightweight Access Point Protocol) is a wireless tunnel protocol used between WLC and Access Points like CAPWAP Protocol. With this protocol, WLCs can manage APs, distribute software and configurations to these devices. You can also check RFC 5412 for detailed information about LWAPP. For Access Point Discovery and Join Process overview, you can check the releated lesson.
CAPWAP versus LWAPP: Comparison
LWAPP protocol was developed by Airespace and then Cisco bought this protocol in 2005.
When, wireless clients send packet to the access point, AP gets these packets and encapsulates it with LWAPP Header. Then it forwards it to the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). At the WLC side, WLC removes this LWAPP Header and forwards the packets to the destination.
LWAPP both supports layer 2 and layer 3 transport mode. Layer 2 LWAPP communication uses EtherType value 0x88BB. Layer 2 LWAPP is not routable. But layer 3 LWAPP is routable and it provides changing LWAPP messages over IP with UDP encapsulated packets.
LWAPP communication is done with two messages. These are:
LWAPP protocol uses UDP 12222 port for control plane messages for configuration, session management, software management etc. It uses UDP 12223 port for data plane messages for the encapsulated data traffic.
LWAPP (Lightweight Access Point Protocol) is used between AP and WLC for both control plane and data plane messages. So, how does this achieved?
Firstly, AP sends Discovery Request message to start AP discovery process. The aim of this message is to explore that if are there any WLC in the network. As we have talked about before, LWAPP supports both layer 2 and layer 3 mode. Firstly, it sends an Ethernet broadcast LWAPP discovery message to check if are there any WLC in layer 2 domain. If it can not find, then it sends a layer 3 LWAPP Discovery message. If it can not find again, then it reboots and retry from the beginning again.
WLCs, in the network replies with Discovery Response messages. In the LWAPP Response message, WLC sends the below information to the Access Point.
After that, Access Point determine one of these Access Points and then send a Join Request to this WLC. WLC replies with Join Response message. After this join process, WLC and AP exchange configuration parameters. Now, Access Point is ready for operation.
There are different steps in LWAPP operation. You can use these steps for troubleshooting during a wireless access problem. So, what are these steps. These are given below:
Discovery: Access Points tries to learn if are there any WLC around.
Join: Access Point determines a WLC and tries to join it.
Image: Access Point determines its software version is not same with WLC, then it updates its software.
Configure: Access Point has joined to WLC and it receives configurations.
Run: Normal state of operation. Access Point and WLC has same software version.
You can also check CAPWAP Protocol and Access Point Discovery and Join Process to learn related lessons about LWAPP.
Leave a Reply