Table of Contents
Sequence & Acknowledgement Number
Sequence and Acknowledgement fields are another important fields in TCP Header. Each of these TCP Header Fields are 32 bits long.
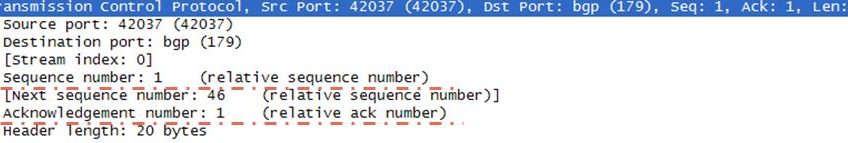
These fields are in the features that make TCP connection oriented. With sequence and acknowledgement numbers, packet reache to the destination without lost. If any of the packet do not reach to the destination, it is known by its sequence number and requested again. This results no loast during the session.
Before data transfer a new TCP connection is created. The host’s first sequence number that is used during starting of the connection is called “Initial Sequence Number(ISN)”.
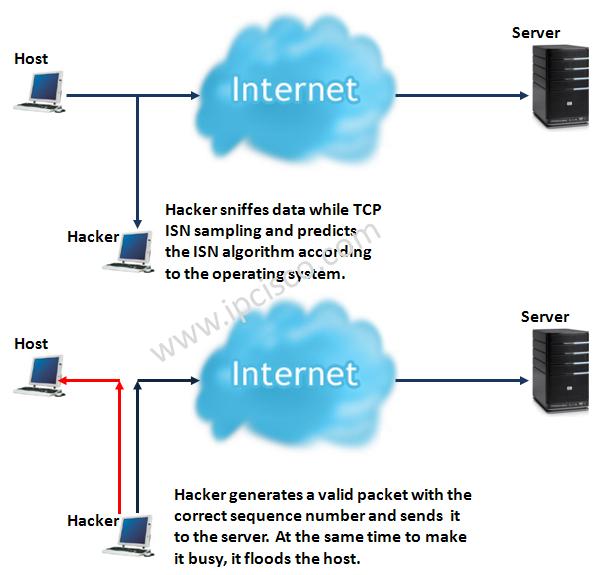
From the point of security, this is open to the hijacking attacks. It is easy for an hacker to hijack the system. Different operating systems handle sequence and acknowledgement parameters differently. A hacker checks the ISN number and then determines the operating system. After that hijacking is almost completed. He predict the next sequence number and after that the destination do not understand that it is an hacker. Hacker also use flooding towards the sending host in order to be busy. You can check this scenario better with the below picture.
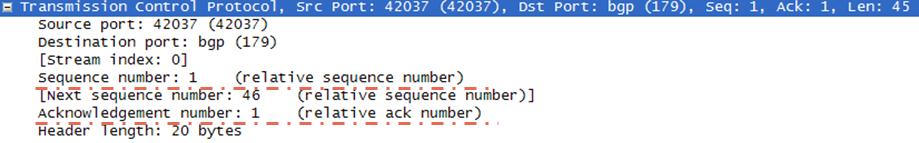
Let’s explain these sequence and acknowledgement numbers with the below picture.
You can reach the TCP Header article series below…
TCP Header Part – 1
TCP Header Part – 2
TCP Header Part – 3
TCP Header Part – 4
TCP Header Part – 5








Leave a Reply