WANs (Wide Area Networks) interconnect different networks over long distances. Various wan topologies used to build a WAN network. In this Cisco CCNA Certification Lesson, we will focus on these main WAN topology types. So, what are these WAN types?
The main WAN types used on WANs are given below:
- Point-to-Point Topology
- Hub and Spoke Topology
- Full Mesh Topology
- Dual-Homed Topology
Now, let’s talk about these WAN Topologies one by one.
Table of Contents
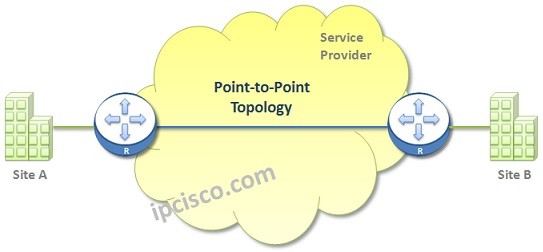
Point-to-Point WAN Topology
Point-to-Point is the topology is the topology that connect one site to the other like they are connected directly. These type of topology is also called Leased Lines. They are leased from a Service Provider based on required bandwidth and the distance between the two sites. They are not a shared solution. So, if we compare Point-to-Point connections with the other WAN solutions, they are an expensive solution.
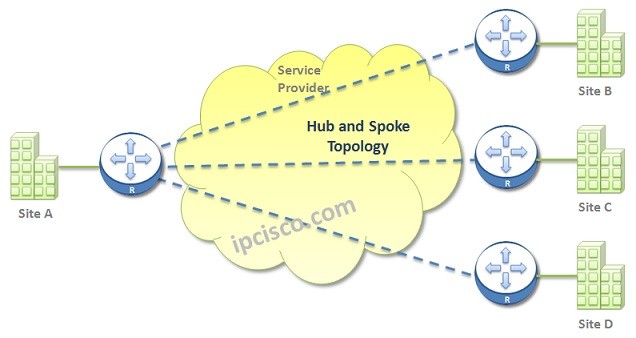
Hub and Spoke WAN Topology
Hub and Spoke Topology is the topology that is used to connect multiple sites. In this type of WAN topology, there are two roles as its name implies. Hub and Spoke. Hub is the central device at one site that is connected to all the other devices. Spoke is the name of each of the other sites and devices. The Spokes are only connected to the Hub. There is not a direct connection between Spokes.
Hub and Spoke WAN Topology is less expensive if you compare this design with a Point to Point one. Because, there is no need to connect each site one by one to other sites. The only needed connection is towards Hub site.
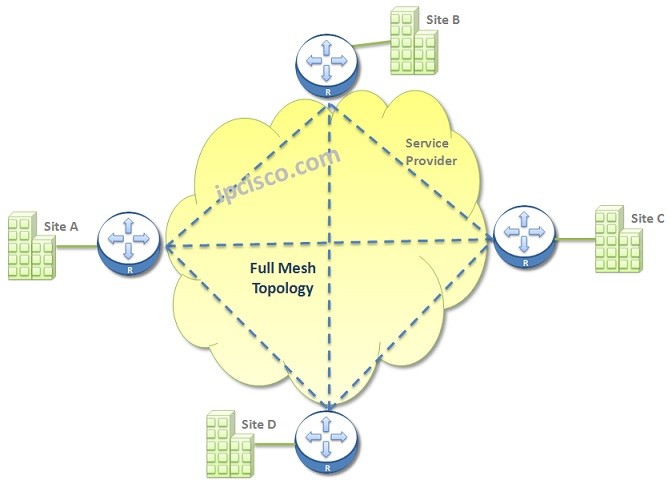
Full Mesh WAN Topology
Full Mesh WAN Topology is the topology that each sites are connected to the other sites one by one. This topology needs more resources and expensive. Beside, it needs an extra effort beucae of the number of the connections.
The connection number that we need for a Full Mesh Topology is calculated with the below formula:
N x (N-1) / 2
You can also watch WAN Topologies Video Lesson below:
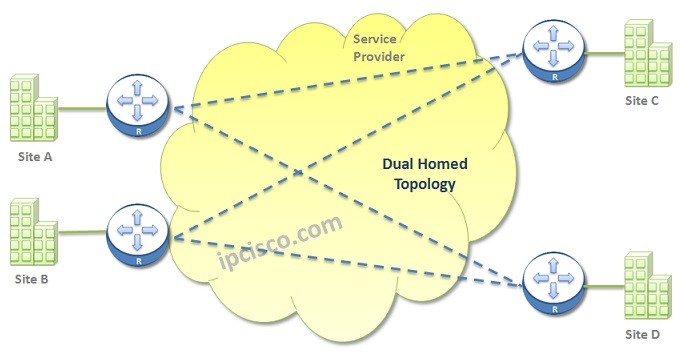
Dual-Homed WAN Topology
Dual-Homed WAN Topology is a very good solution for better performance, load balancing and redundancy. But it has a disadvantage about the cost. It is an expensive solution. In Dual-Homed Topology, a site is connected to another two central sites. Even if one of these sites are go down, the connection continues. During normal situations, lad balancing is also provided between two links








Leave a Reply