With the development of network world, new requirements has appeared in AAA. For this requirements a new protocol was developed as an enhanced version of RADIUS. This protocol is Diameter Protocol. Here, we will focus on this protocol details and Radius vs Diameter.
Diameter Protocol supports many protocols beside IP and it is a solution for new access requirements. With these characteristics of Diameter Protocol, it is mosty used in mobile service providers and mobile world.
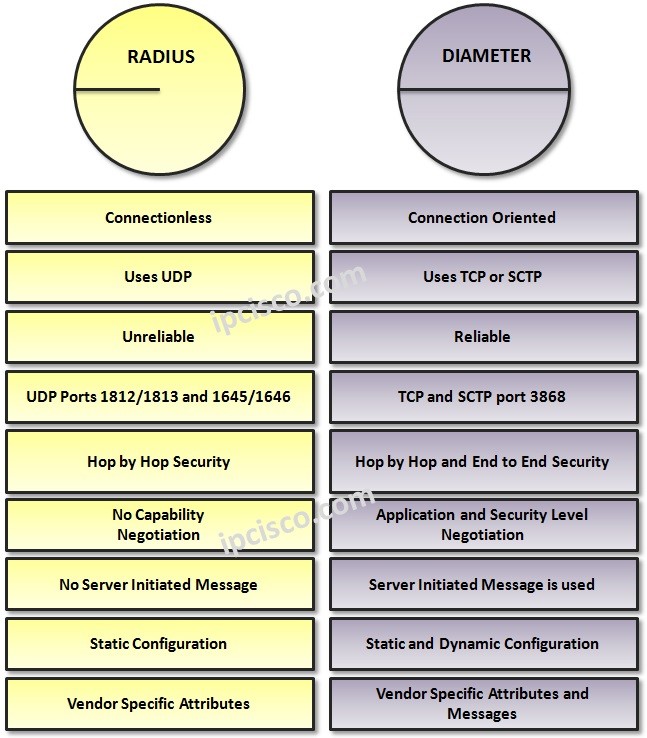
RADIUS uses UDP port 1812 and 1645 for Authentication. It also uses 1813 and 1646 ports for Accounting. Because of this the reliability of RADIUS is low. On the other hand, Diameter Protocol uses TCP and SCTP port 3868. This make Diameter Protocol more secure than RADIUS Protocol. To learn each difference between of TCP and UDP, you can the related lesson.
You can find the comparison table of Radius and Diameter Protocols, Radius vs Diameter below:
Table of Contents
Diameter Protocol Messages
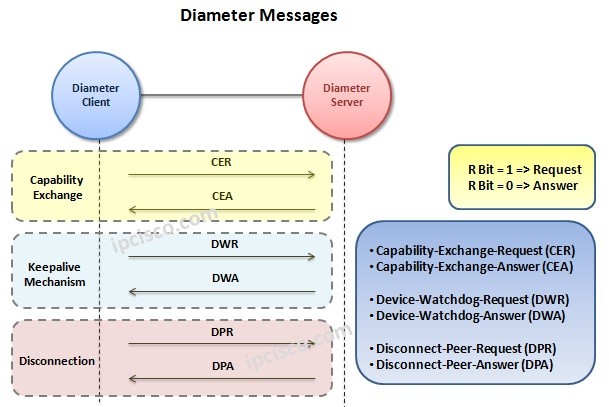
In Diameter Protocol messaging, mainly there are two messages. These are “Request” and “Answer” messages.If the R bit in the Diameter header is set (1), it is a Request message. If it is unset (0), then it is a Answer Messeage.
Beside this common types, there are some specific messages used for various aims. The Diameter messages are given below:
- Capability-Exchange-Request (CER)
- Capability-Exchange-Answer (CEA)
- Device-Watchdog-Request (DWR)
- Device-Watchdog-Answer (DWA)
- Disconnect-Peer-Request (DPR)
- Disconnect-Peer-Answer (DPA)
What are the main roles of Diameter Messages?
First of all CER and CEA messages are used for Capability Exchange between Diameter Client and Server. CER messages includes AVPs(Attribute/Value Pairs) that are application related information.
Secondly, DWR and DWA messages are used as keepalive messages between Diameter Client and Server devices.
And for DPR and DPA messages are used to terminate the Diameter session.
Diameter Packet and Diameter AVPS
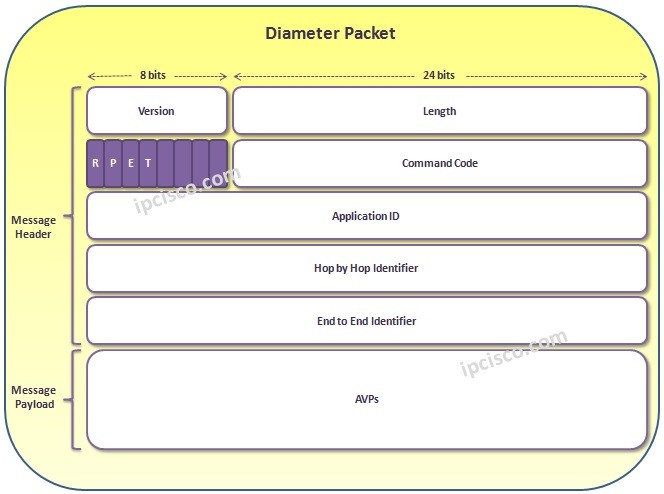
Diameter Packet consist of two main areas. These Diameter Packet areas are :
- Diameter Packet Header
- Diameter Message Payload
In the Diameter Header, there are different parts as mentioned below:
- Version
- Length
- Flags
- Command Code
- Application ID
- Hop by Hop Identifier
- End to End Identifier
Here, 4 flags are important for us, the others are reserved for the future use. What are these flags? These are:
- R (equest) : Shows that the message is Request or Response.
Request : 1,
Response: 0
- P (roxiable) : Shows that the message can be Proxied, relayed, redirected. Or locally processed.
Proxied, relayed, redirected : 1
Locally processes : 0
- P (roxiable) : Shows that the message can be Proxied, relayed, redirected. Or locally processed.
- E (rror) : Shows that there is an error if it is set.
- T : Retransmitted message after a link failure. It is also used to remove duplicate messages after a link failure.
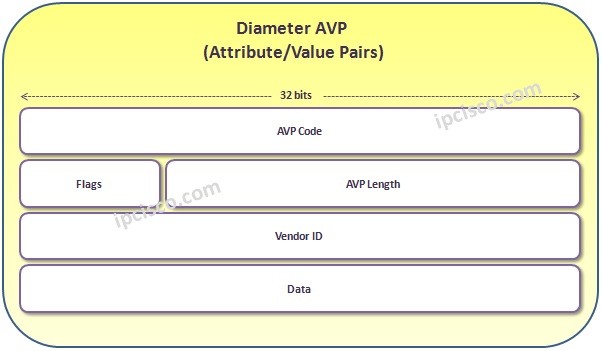
The Diameter Payload part is consist of AVPs (Attribute / Value Pairs). AVPs has the below fields:
- AVP Code
- Flags
- AVP Length
- Vendor ID
- Data








I am currently working with networking company and want to know more about Networking