- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Ethernet is the most used technology in LANs in network world. There are various technologies can be used on LANs like Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI. But the most popular and widely used one is Ethernet. In your career, you will work on Enternet more than other LAN standards. You will see Ethernet Frame and other Ethernet basics.
Ethernet is a technology that is based on broadcast adio that is going through various cables. It is a cable technology. In Ethernet technology, all the nodes are connected with cables over various network devices.
Basically Ethernet has standards for Layer 1 and Layer 2 of OSI Referance Model. Here, from cabling to the physical addressing, there are different concepts.
Table of Contents
Ethernet has a number of sub standards. Some of these are given below:
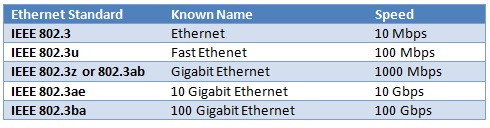
Above we have listed different Ethernet standards. Let’s talk about these Ethernet Standards one by one.
Ethernet term is the common name used for all of the Ethernet Standards. But specifically it is used to mention the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet (10 Mbps).
It can operate on three mediums. These are :
The widely type of Ethernet is 10baseT with Twisted Pair Cables. Especially the Category 5 (CAT 5) and Category 6 (CAT 6) is the most used one. These cables types will be explained in this article.
Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) is the Ethernet technologhy that is 10 times faster than Ethernet (10 Mbps).
Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) can operate on :
Fast Ethernet is used with CAT 5 and CAT 6 10BaseTX cables. It also use Multi Mode Fiber cables.
The switches that support both Ethernet and Fast Ethernet are mentioned as 10/100 Swicthes.
IEEE 802.3z is the Gigabit Ethernet Standard provided with Fiber Optic cables and IEEE 802.3ab is the Gigabit Ethernet Standart provided with copper(twisted pair) cables.
Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) can operate on :
The cables that Gigabit Ethernet can be sued is Cat 5e cables. But generallt Gigabit Ethernet can be used with fiber optic cables. Both Multi Mode and Single Mode fibers are used for Gigabit Ethernet.
IEEE 802.3ae is the 10 Gigabit Ethernet Standard provided with Fiber Optic cables.
10 Gigabit Ethernet (10000 Mbps) can operate on :
IEEE 802.3ba is the 100 Gigabit Ethernet Standard provided with Fiber Optic cables.
100 Gigabit Ethernet (100000 Mbps) can operate on OM3 and OMD Multi Mode Fiber cables and Single Mode Fiber Cables.
100 Gigabit Ethernet is used for aggregation, high performance computing, high speed swicthing and routing on Datacenters ans Service Provider networks.
Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex terms is used for media access type.
Half-Duplex provide only one way communication at the same. Send or receive. Half-Duplex mechanism provides this by using Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detect (CSMA/CD).
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detect (CSMA/CD) is a mechanism that provide only one way communication. It controls the media and if there is nobody in that media (no body sending or receviving data), then it allows to send or receive data. By doing this, it avoids the media from collisions.
The duplex of a port in a switch can be automaticall and manually changed. For manual configuration, network engineers must be careful to avoid Duplex Mismatch. Duplex Mismatch is the problem that occurs because of the missconfiguration. The duplex configuration must be same at both end. If you configure the two end point with different duplex configuration, Duplex Mismatch occurs.
There are some common traffic types used with Ethernet. These traffic types are named accordin to the receivers. These Ethernet Traffic Types given below:
• Unicast
• Broadcast
• Multicast
• Anycast
Firstly, Unicast is the traffic type whose destination is one node.
Secondly, Broadcast is the traffic type whose destinaion is all nodes in the network.
Thirdly, Multicast is the traffic type who se destination is a specific Multicast group members.
And lastly, Anycast is the traffic type that is introduced with IPv6. It is the traffic whose destination is the closest node between multiple same IP nodes.
We can divide Ethernet into two Sublayer. These are :
• MAC Sublayer
• LLC Sublayer
To start with MAC Sublayer, the data travel is controlled. Here, there is an important parameter that is used in this part. This is MAC Addresses.
Secondly, with LLC Sublayer, encapsulation and identification of the protocols are done. There are two types of LLC frames. These are SAP (Service Access Point) and SNAP (Subnetwork Access Protocol).
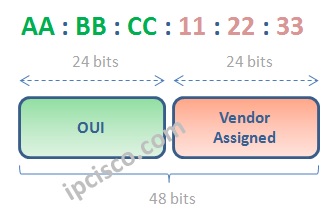
MAC Addresses, in other words, Ethernet Addresses are the 48 bits Layer 2 addresses and network devices use this addresses as Layer 2 Address. The other name of this addresses are Hardware Addresses. It is used with Hex characters like AA:BB:CC:11:22:33.
All network devices has a MAC address. Vendors determines these MAC addresses. Half of the MAC Address is vendor specific and the other half is, device specific.
Firstly, the vendor specific part of the MAC is unique for each vendor. This field is called “Organization Unique Identifier (OUI)“. This is the number that is assigned by IEEE to that specific vendor. There are many assinged OUI numbers to the vendors. Vendors can has many OUIs.
You can check the OUI numbers from the IEEE website, here.
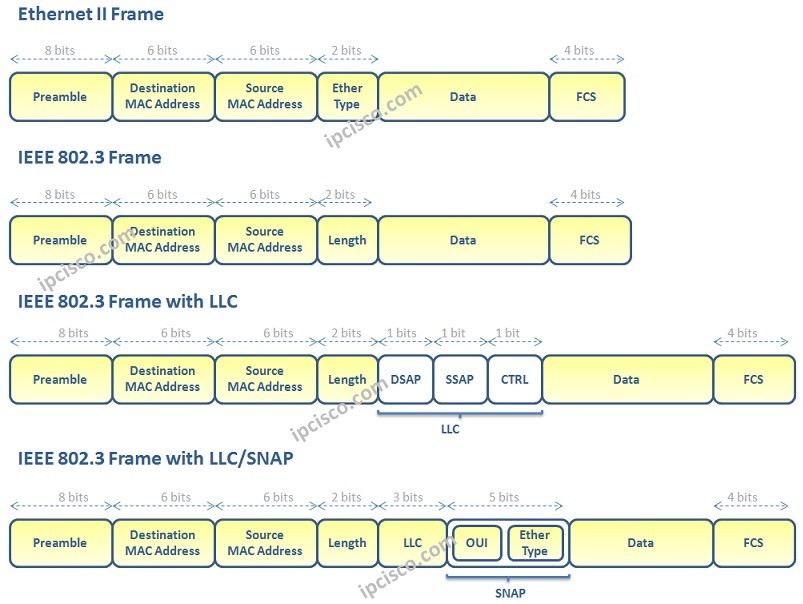
Ethernet Frame has various parts according to the Ethernet Frame Header type. There are four type Ethernet Frame Headers. These are :
You can find the frame formats of each Ethernet Frame below:

There are various Ethernet Cable Standards. We have talked about this lecture, in the Network CablingArticle.You can check again ;)
Leave a Reply