Metro Ethernet
Metro Ethernet Overview
Simply, Metro Ethernet is an enhanced version of Ethernet that is used between long distances with higher bandwidths. Metro Ethernet can be used both by companies to connect their sites and by end users to connect Internet.
Ethernet is a wellknown and widely used Local Area Network (LAN) standard. At the beginning, it was only used for Local area Networks (LANs), for limited distances and limited bandwidths. But with the development of Ethernet Standards, Ethernet have started to be used by Carriers for MAN (Metropolitian Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network). These high capacity Ethernet called Carrier Ethernet. And Carrier Ethernet used for MAN (Metropolitian Area Network) is called Metro Ethernet.
Metro Ethernet Services
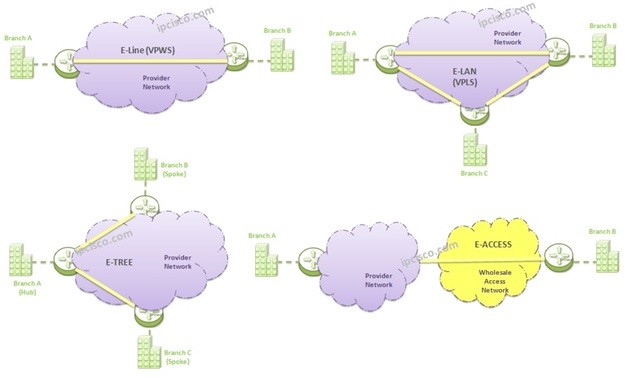
In Metro Ethernet technology there are different types Services. These services types are:
• E-Line (Ethernet Line Service)
• E-LAN (Ethernet LAN Service)
• E-Tree (Ethernet Tree Service)
• E-Access (Ethernet Access Service)
These services can be used with one circuit per interface or with multiiple circuit per interface with the help of VLANs. In other words, one interface can carry one more Metro Ethernet service traffic. According to these, above Service types has sub names like given below:
Service, Interface Based, VLAN Based
E-Line, Ethernet Private Line (EPL), Ethernet Virtual Private Line (EVPL)
E-LAN, Ethernet Private LAN (EP-LAN), Ethernet Virtual Private LAN (EVP-LAN)
E-Tree, Ethernet Private Tree (EP-Tree), Ethernet Virtual Private Tree (EVP-Tree)
E-Access, Access Ethernet Private Line (Access EPL), Access Ethernet Virtual Private Line (Access EVPL)
Let’s talk bout detailly on each Metro Ethernet Service.
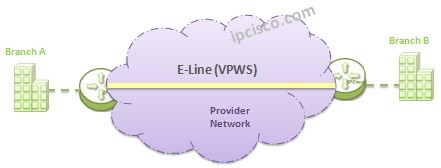
E-Line (Ethernet Line Service)
E-Line is the Metro Ethernet service that is a point-to-point connection between two nodes. This point-to-point connection is called Ethernet Virtual Circuit (EVC). Here, customer connect to the provider device via Ethernet from one point and provider transmits the customer traffic to the other point over its network. At the other end customer is also connected to the service provider via Ethernet. Customer locations are connected as Layer 2 with E-Line Service and it is like a Leased Line between customer locations.
Point-to-Point connections use one interface at each part. On that interface one or one more EVC can be used according to need. If we use one EVC per interface, this is called Ethernet Private Line (EPL). If we use one more EVC on a single interface, we need to use dot1q protocol, VLANs to differentiate different EVCs. This is called Ethernet Virtual Private Line (EVPL).








Leave a Reply