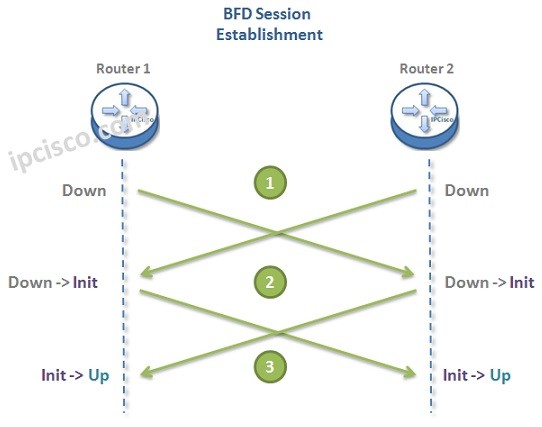
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) mechanism uses packets to inform both ends that the protocol is configured. With these packets, BFD provide basic connectivity and the parameter negotiation. The main role of BFD is detecting the link failures by sending BFD packets in regular intervals. It sends the packet and wait. If there is no reply until a certain of time, it determines that the link is down. This is the same as Hello protocols.
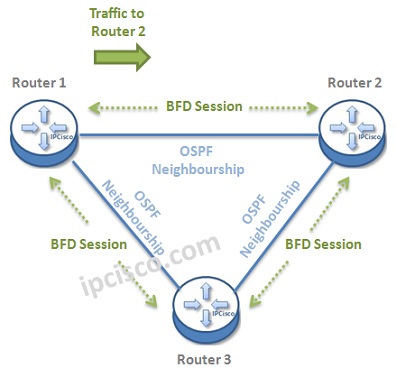
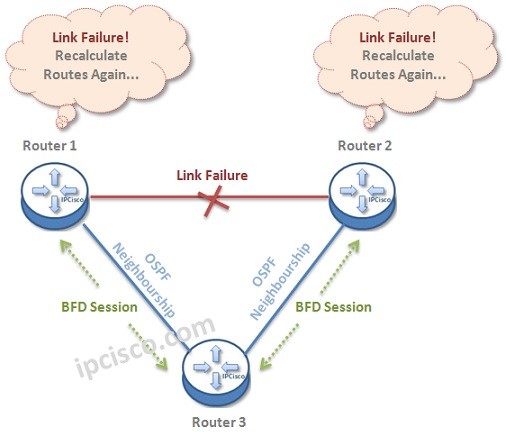
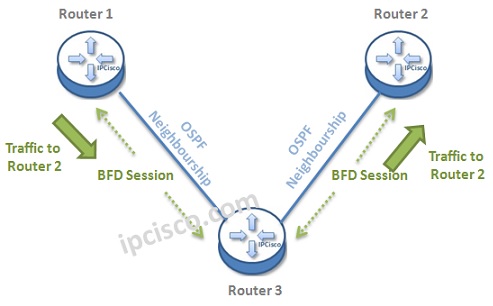
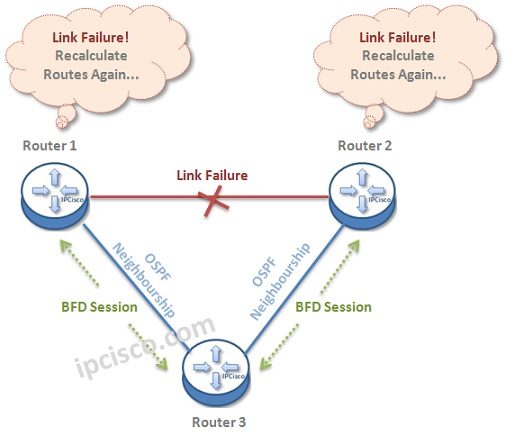
Let’s give an example to understand BFD Mechanims better. Below, there is a topology, that BFD Sessions are also established in each ends. Think about that a traffic is coming from Router 1 to Router 2.
BFD has different operation modes. These are :
- Async Mode
- Demand Mode
- Echo Mode
In Asyncronous Mode, two end node send BFD Conrol Packets eachother periodically. If they do not get some of the Control Packets, they decide that there is failure. In Async Mode, BFD control packets flow in each direction.
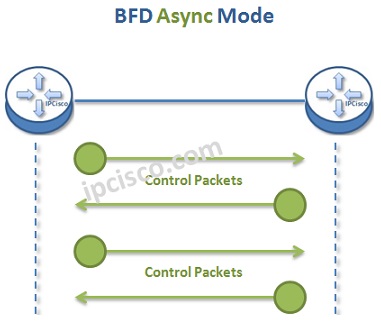
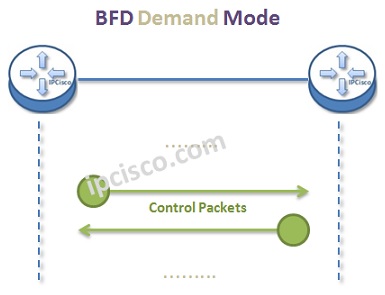
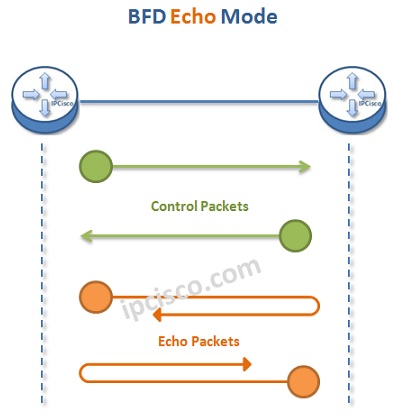
Table of Contents
BFD Applications
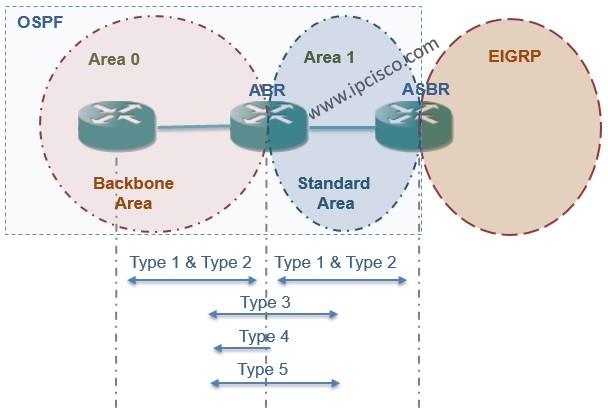
AS we mentioned above, BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is used to detect link failure. But, there can be many type of link failure. BFD is generally used for:
- Routing Protocol link availability
- Ethernet Link availability
- MPLS and GRE Tunnel link availability,
- Edge Network availablity
Used With BFD
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is used with many protocols for link failure detection. These protocols are:
- Static routes
- IGPs (OSPF, IS-IS)
- BGP (eBGP, iBGP)
- LDP
- RSVP
Disadvantages of BFD
Beside the advantages of BFD, it has also some disadvantages. First of all it can have more resource demands. This changes from platform to platform.
Secondly, BFD is not aware of Layer 2 link bundelling. When you configure it on one link, it operetas for single link, rather than the other bunde member.









Leave a Reply