BGP Origin Attribute informs the Autonomous Systems (AS) about the originator of that route. It is a Well-Known Mandatory BGP Path attribute like AS Path Attribute and Next Hop Attribute. BGP Origin Attribute is supported in all BGP implementations and in all BGP Update packets it must exist.
There are three different Origin types. These are :
• i (IGP)
• e (EGP)
• ? (Incomplete)
i (IGP) routes are the routes which are originated from a routing protocol, like RIP, OSPF, EIGRP etc. Generally this is done via network command under the BGP process.
e (EGP) routers are the routes which are originated from External Gateway Protocol (EGP). Now the only EGP is BGP, so this is the routes originated from BGP.
? (Incomplete) routes are the routes which are Redistributed from static, IGP etc. into the BGP.
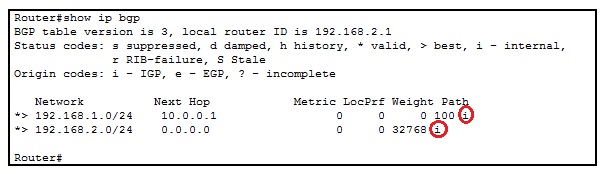
You can see any BGP Route’s BGP Origin Attribute value with “show ip bgp” command. At the end of the output table, the Origin code ( i, e or ?) is shown.
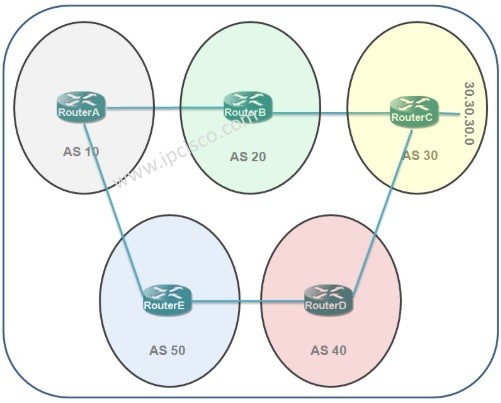
Let’s check the BGP Routes of the below topology.
You can find other BGP Path Attribute Articles below:
BGP Path Attributes – Weight
BGP Path Attributes – Local Preference
BGP Path Attributes – AS Path
BGP Path Attributes – Origin
BGP Path Attributes – MED
Main BGP Article Series :
BGP – Part 1
BGP – Part 2 (BGP Peers, BGP Sessions, BGP Messages)
BGP – Part 3 (IBGP, IBGP Topologies and EBGP)
BGP – Part 4 (BGP Administrative Distance and BGP Path Attributes)
BGP – Part 5 (Packet Tracer BGP Configuration Example)









Thanks for this help. Really appreciated.