Table of Contents
What is BGP peer?
To use BGP, the neighbourship between the BGP routers must be established. You can use the statement BGP neighbour or BGP peer for this establishment.
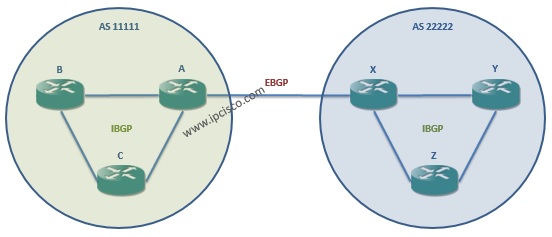
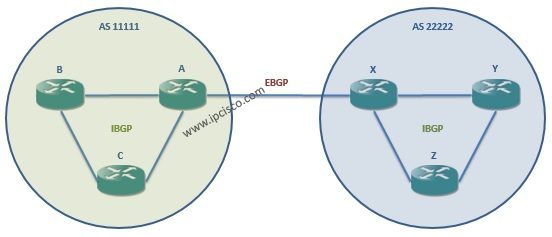
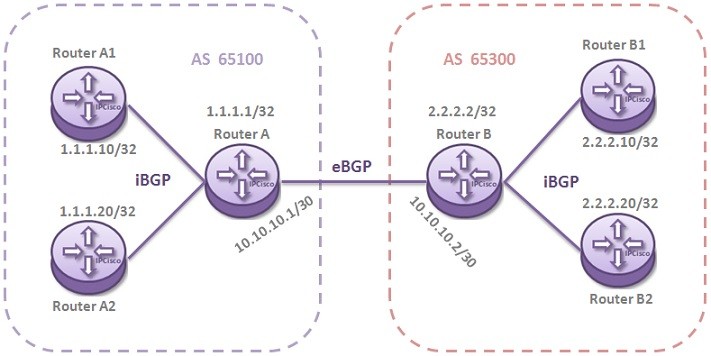
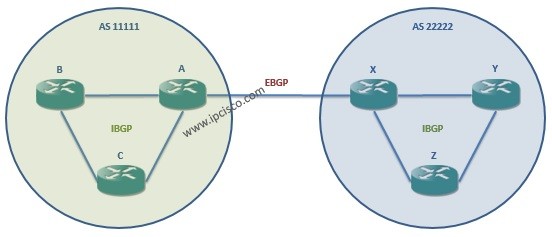
There are two types of BGP peer. These are iBGP(interior BGP) peer and eBGP(exterior BGP) peer. iBGP peer is the neighbour within the same AS. eBGP peer is the neighbour within another AS.
BGP Session Establishment and Session States
Without any connection attemp, the session is firstly in the idle state. With the first TCP message, the state changes to connect.
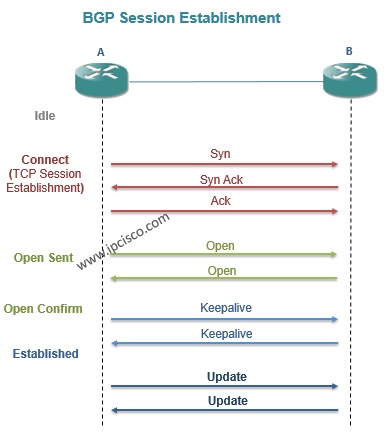
After TCP connection, one peer send Open Message and the other peer respond with another Open Message. During this process the state become OpenSent .
Other BGP Overview Lessons:
BGP – Part 1
BGP – Part 2 (BGP Peers, BGP Sessions, BGP Messages)
BGP – Part 3 (IBGP, IBGP Topologies and EBGP)
BGP – Part 4 (BGP Administrative Distance and BGP Path Attributes)
BGP – Part 5 (Packet Tracer BGP Configuration Example)








Leave a Reply