LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) is one of the two label exchange protocols of MPLS. The other is RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol). And there is also one more, Cisco specific protocol, TDP(Tag Distribution protocol). In this article, we will talk abbout the LDP. And the examples will be also for Alcatel-Lucent Service Routers(7750, 7450 etc..).
There are 3 types LDPs. These are:
– Link LDP
– Targeted LDP (TLDP)
– Contraint-based Routing LDP (CR-LDP)
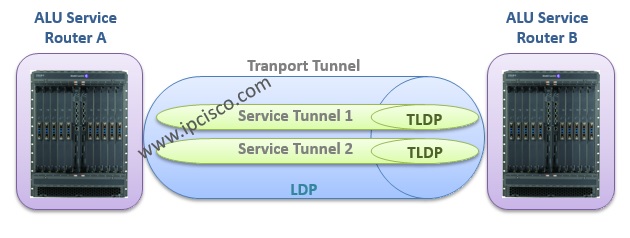
Think about MPLS VPNs. For MPLS we need to establish an MPLS Transport Tunnel through the core network (P routers) between PE routers. This is established via LDP. Inside this MPLS Transport Tunnel, we carry specific customers traffic. In Alcatel-Lucent terminalogy, this is called different customer services. So, this different customers’ traffic is carried in different MPLS Service Tunnels in Transport Tunnels. And these MPLS Service Tunnels are established via TLDP, between PE routers, for VPLS and VPWS services(L2 VPN Services). For VPRN (L3 VPN Service), MP-BGP is used instead of TLDP. For this lesson also check Tunnel Structure article.
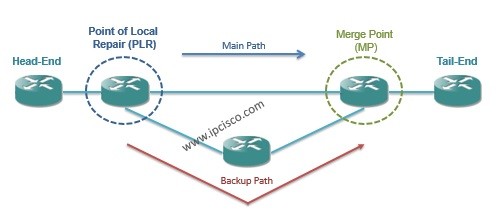
Contraint-based Routing LDP (CR-LDP) is the extension of LDP that will provide traffic engineering mechanism to LDP. As you know pure LDP has no traffic engineering mechanism.
Table of Contents
Link LDP
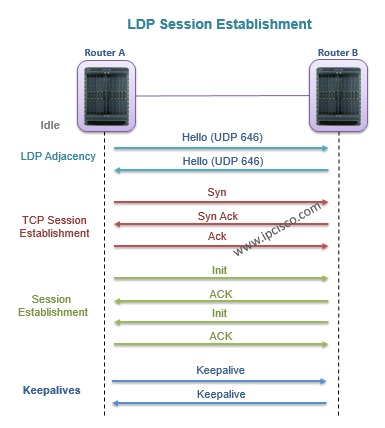
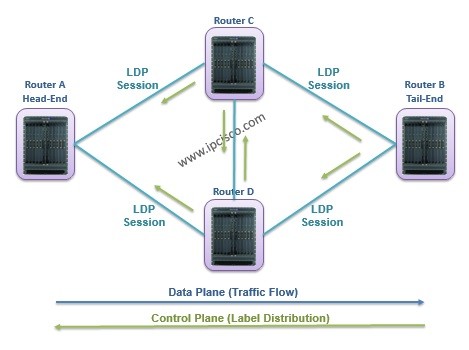
For Link LDP, all the directly connected neighbours need to establish LDP session each other. This must be a full mesh topology. Firstly LDP Adjacency must be done, then the LSP Session must be established. By doing this, the label distribution can be done for all the routers.
To create and maintain LDP there are 4 processes. These are:
1) Peer Discovery,
2) Session Establishment,
3) Label Management (Distribute label management)
4) Notification ( Alerting LDP peering routers about errors)
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 1
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 2
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 3 (Configuration on ALU)
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 4 (ECMP)
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 5 (Export and Import Policy, Prefix Aggregation)
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 6 (T-LDP)
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP – Part 7 (CR-LDP)









Thanks ,it is very interesting
Always welcome Taibi ;)