As you know mobile telecommunication has evolved for years. With this evolution, new network elements were included or the existing ones were upgraded.
Startig with 2G GSM technology, the evolution has continued orderly with:
– 2.5G GPRS,
– 2.75 EDGE,
– 3G UMTS,
– 3.5G HSPA,
– Evolved HSPA (HSPA+)
– 4G LTE.
The main aim of this evolution in mobile world, is speed. The next generation technologies are always providing much more speed that the previous one.
In this post we will focus on one of these technologies, 4G – LTE (Long Term Evolution), its architecture and the network components.
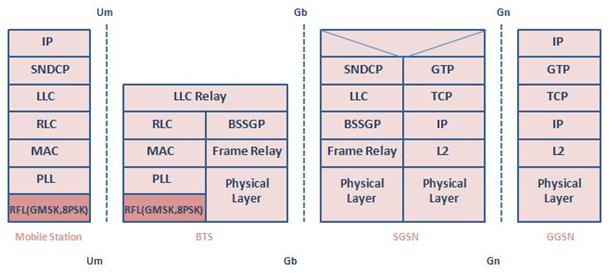
In the previous network architecture, in 3G, there are Node Bs, RNCs, SGSNs and GGSNs.
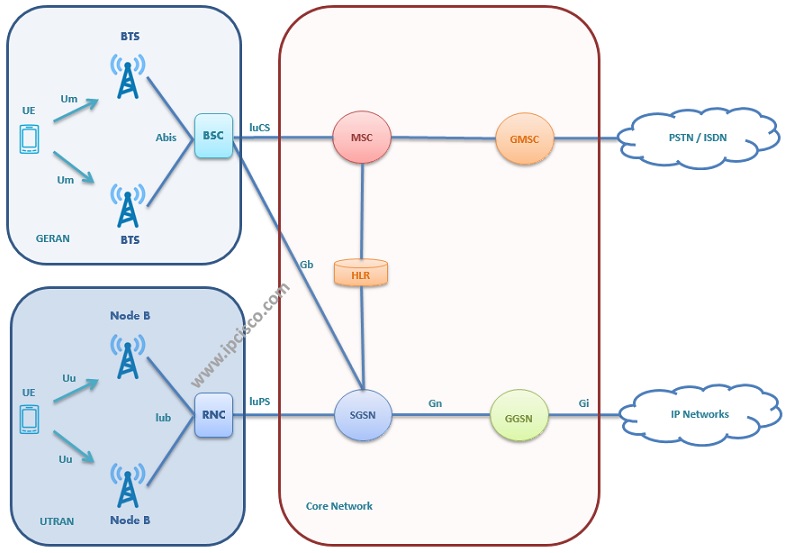
EPC : Evolved Packet Core. LTE core network.
UE: User Equipment. Your mobile device.
eNodeB: Evolved Node B. It is the node that provides UE to connect the mobile network. It is also included a controller(it does the RNC job in the previous technology, 3G).
S-GW: S-GW routes and forwards the packets to and from the eNodeB and PDN-GW. S-GW is also serve as local mobiliy anchor for inter-eNodeB handover and mobility between 3GPP networks.
PDN-GW: The PGW acts as the interface between the LTE network and other packet data networks









Leave a Reply