Table of Contents
Packet Tracer STP Configuration
In this post, instead of detaily talk about STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), we will focus on a basic Switching Loop topology and how STP mechanism helps to avoid this Switching Loop.
You can DOWNLOAD the Packet Tracer example with .pkt format HERE.
Switching Loop is an unwanted problem in a network. Then, what is Switching Loop? Switching Loop is the situation, in which there are two layer 2 path between two layer 2 endpoint(switch, brigde). Switches creates broadcast storms from every port and switch rebroadcast again and again. Because of teh fact that there is no TTL(time to live) mechanism on layer 2, this continues forever.
To avoid this unwanted Switching Loops, there are some mechanisms. One of the most common name of this mechanisms is STP(Spanning Tree Protocol).
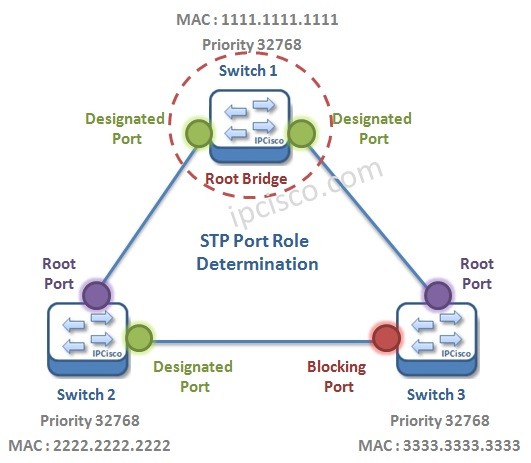
Acording to this protocol, in the switching topology, a Root Bridge is selected. And then the connected port of the switches are classified. The port classification and their meaning are like below:
– Root Port : The port to the Root Bridge
– Designated Port : The other port thatis not Root Port
– Non Designated (Blocked) Port : In a segment, other port than the Designated Port
The selection process is done orderly. First Root Bridge is selected, secondly Root Ports on all the switches, then Designated Ports are selected, and lastly the remainning ports become Non-Designated Port, meaning Blocking Port.
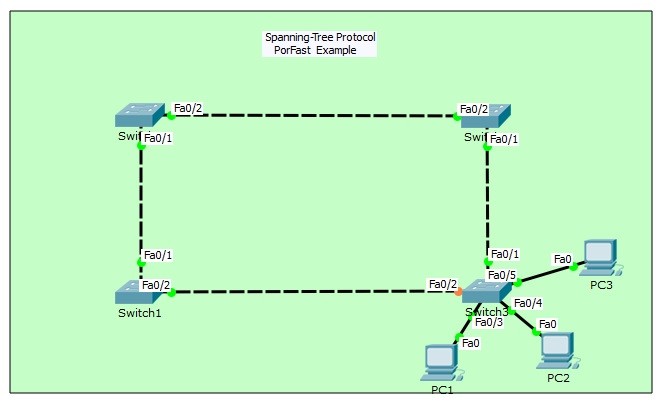
STP Example on Packet Tracer
For STP example with PAcket Tracer, we will use the below switch topology.
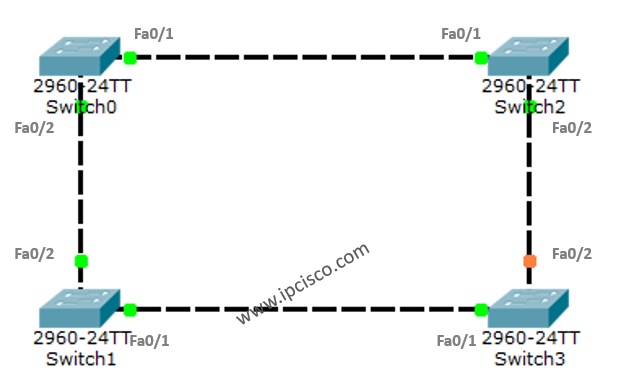
To understand more detailly let’s check the show screenshots.
On Switch0
As we can see above, the addresses are for the Root and the Bridge part. So, Switch0 is selected as Root Bridge. The Root Bridge is selected according to the Bridge ID, The Bridge ID is the MAC address of the Switch. So, the lower one is selected as Root Bridge. This is Switch0.
The two port of Switch0 are normally Designated Port. Because all the ports on Root Bridge is always choosen as Designated Port.
Both of these ports are in Forwarding State, this means that they are ready to send the traffic. As a recall, as you know there are four states of an STP port. These are:
– Blocking (20 seconds)
– Listening (15 second)
– Learning (15 second)
– Forwarding
You can also use the following commands to check the spanning-tree information.
You can check the other Packet Tracer Examples below:
Common Cisco Router Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
Router DHCP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
VTP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
VLAN Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
STP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
RSTP Configuration with Packet Tracer
STP Portfast Configuration with Packet Tracer
Inter VLAN Routing Configuration on Packet Tracer
Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) Configuration with Packet Tracer
BGP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
Port Security Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
RIP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
CDP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
OSPF Area Types Example on Packet Tracer (Standard and Backbone Areas)
OSPF External Routes Example on Packet Tracer
OSPF Area Types Example on Packet Tracer (Stub, NSSA, Totally Stubby, Totally NSSA Areas)







tesekkurler
Rica ederim Ziyad:) Good luck!
Hi,
I am more then interested in spanning tree concept sir . i have read in online but i not able to configure.kindly configure command prompt teach me sir.