- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
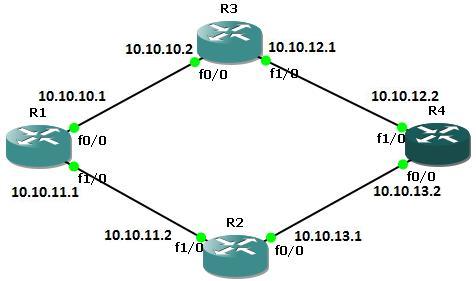
To send the traffic to the destination we can use two types of routing. The first one is Static Routing and the other one is Dynamic Routing. Static routes teach the destination network to the router. It is a manual work that is dıne by network engineers. These type of routes work well with small networks. Because it is a manual work. For large scale networks Dynamic Routing will be a better choice. Here we will focus Static Route Cisco Configuration.
The below example will explain the configuration of the Cisco Static Routing Configuration.
Configure the Static Routes on Router A
For our Static Route Cisco configuration example, firsttly, run the command show ip route to view the IP routing table for router A before defining static routes
RouterA# configure terminal
RouterA(config)# ip route 10.10.12.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2
RouterA(config)# ip route 10.10.13.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.11.2
RouterA(config)# exit
Configure the Static Routes on Router B
Again on Router B, firtly, brun the command show ip route to view the IP routing table for router B before defining static routes
RouterB# configure terminal
RouterB(config)# ip route 10.10.11.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
RouterB(config)# ip route 10.10.13.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.12.2
RouterB(config)# exit
If we give show ip route command on router B to view the IP routing table we will see both directly connected and static routes detail.
Configure the Static Routes on Router C
We will do the same thing on Router C too. We will run the command show ip route to view the IP routing table for router C before defining static routes.
RouterC# configure terminal
RouterC(config)# ip route 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.11.1
RouterC(config)# ip route 10.10.12.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.13.2
RouterC(config)# exit
If we give show ip route command on router C to view the IP routing table we will see both directly connected and static routes detail.
Leave a Reply