There are three types adjacency in IS-IS Protocol.These are:
– Level 1 routers form L1 adjacency with L1 and L1/2 Routers
– Level 2 routers form L2 adjacency with L2 and L1/2 Routers
– Level 1/2 routers form L1/2 adjacency with L1/2 Routers
There is no neighbourship between L1 and L2 routers.
In IS-IS Protocol, adjacency is established with 3-way handshake mechanism. There are three states in IS-IS adjacency. Let’s check the adjacency states of IS-IS Protocol.
In the first place the router adjacency is in Down State. One of the routers, here Router A sends a Hello PDU. When the router B receive this Hello including the MAC address of the sending node Router A, it goes to Initialize State and sends Hello to Router A too. Again, when Router A receives Hello including the MAC address of Router B, bidirectional communication established. And the name of this state is Up State.
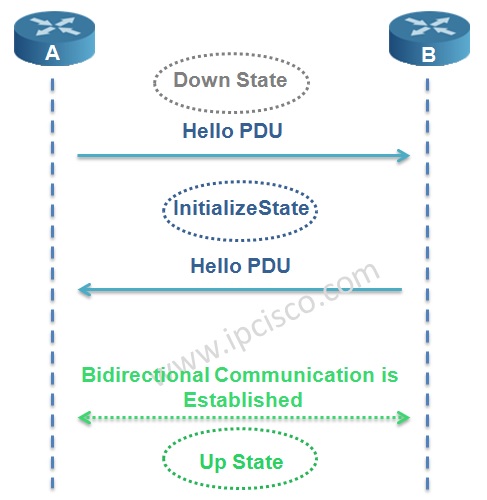
– No IS-IS neighbour (Down State)
– RTRA Sends Hello (Initializing State)
– RTRB records MAC address f RTRA and Sends Hello too. RTRA sees MAC address of RTRB. Bidirectional communication established (Up State)
Table of Contents
IS-IS Protocol Operation
Beginning with IS-IS adjacency establishment, to the Routing Table establishment, IS-IS Operation has some steps.
We can summarize IS-IS operation in 6 steps. These IS-IS operation steps are given below:
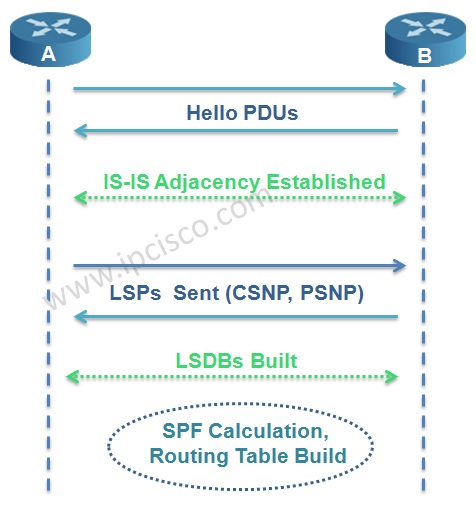
1. IS-IS Routers are send Hello PDUs to discover the neighbours and establish the adjacency.
2. IS-IS adjacency is established ( mainly authentication, IS-type, MTU must match)
3. LSPs are build by routers about theirselfs and the learned adjacent routers
4. Routers send the LSPs to the adjacent routers.
5. All routers build their LSDB according to these LSPs
6. By SPF algorithm best paths are calculated and routing table is build.
DIS (Designated IS)
In ISIS network, LSDB databases must be synronized. To do this, full mesh or another solution is required. So, in IS-IS Protocol, one router is selected as DIS (Designated IS) and DIS is used to reduce the adjacency in areas. It is like DR in OSPF.
Router with the highest priority and then the highest MAC address is elected as DIS. The default DIS priority is 64. There is no BDR like OSPF. And like OSPF, if you want to prevent the router to be DIS, you can set the priority 0. If a new router added to the ISIS network, the election occurs again. This is not like this in OSPF.
DIS creates a Pseudo Node that is a virtual router. All connected devices in that LAN establish neighbourship with this Pseudo Node.
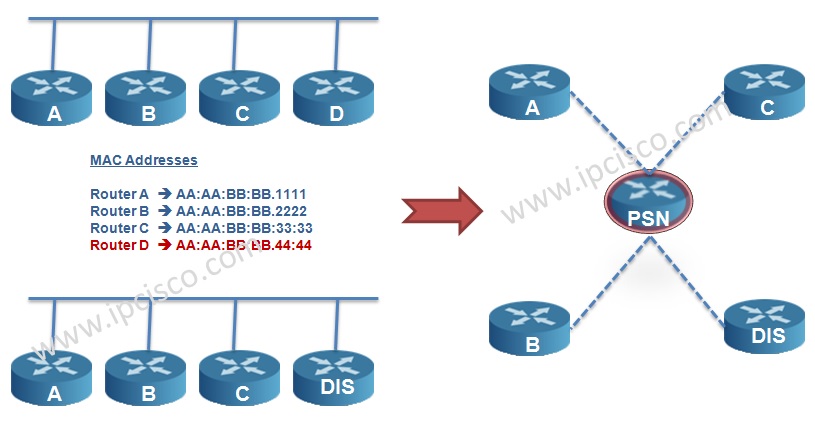
Seperate DISs are selected for Level 1 and Level 2.
IS-IS Protocol Network Types
IS-IS Protocol supports two types of networks. These network are :
– Broadcast networks
– Point-to-Point networks
The other network types that is used in OSPF is not used in IS-IS Protocol.
Different IIH Hellos are used for different network types while establishing neighbourship.
In Broadcast networks IS-IS Protocol requires a full mesh topology. By selecting DIS, full mesh is eleminated. DIS election is used in IS-IS broadcast networks.
IS-IS Cost
Default IS-IS Protocol cost is 10 for all IS-IS Protocol links. But these costs can be set to a different value per interface. For an interface, normally maximum 63 is accepted as cost. But you an set this as 16,777,215 with the wide metrics command.
Cost is advertised by the TLV fields in PDU.
Two routers can set different cost values to reach each other.
IS-IS Protocol Administrative Distance
The Administrative Distance of all IS-IS routes are 115 for Cisco . But for Alcatel-Lucent and Juniper, these administrative distance (preference) value is different. Both vendor use four different value for both Level 1 and Level 2 routers and for both internal and external routes. These are:
– IS-IS Level 1 internal route = 15
– IS-IS Level 2 internal route = 18
– IS-IS Level 1 external route = 160
– IS-IS Level 2 external route = 165
If you want one route not to be used in the route calculation, you can set the the administrative distance manually to 255.
IS-IS Protocol Authentication
In IS-IS Protocol, by default there is no authentication. But you can set two types of authentication. These authentications types are:
– Simple
– MD5
With authentication in Hello packets, you can secure Hello Packets and it determines whether a adjacency is established or not between these routers.
With authentication in LSPs, it allows the remote router to read the TLV fields and according to this information it does the SFP calculation.
IS-IS Protocol Timers
IS-IS Protocol has some timers like other routing protocols. In IS-IS Protocol, modifying default timer settings is recommented because modifying these timers make your IS-IS Protocol better.
These timers are given below:
– Lsp-refresh timer
– Max-lsp-lifetime
– Prc-interval
– Spf-interval
– Hello-interval
– Hello-multiplier
– Isis-retransmit-interval
– Csnp-interval
The other articles on IS-IS Protocol are below:
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 1
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 2 (IS-IS Addresses)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 3 (IS-IS Packet Types)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 4 (IS-IS Adjacency)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 5 (IS-IS versus OSPF)
IS-IS For IPv6 – IS-IS For IPv6 Overview
IS-IS For IPv6 – IS-IS For IPv6 Configuration on Cisco IOS








Leave a Reply