- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) Protocol was developed as a OSI network protocol, not TCP/IP. So, normally IS-IS Protocol does not uses IP address, but it uses NET (Network Entity Title) addresses. Inn this lesson, we will focus on these IS-IS Addresses.
In IS-IS Protocol, NSAP (Network Service Access Point) is used as network layer address. These addresses are assigned per node, not per interface.
And SNPA (Subnetwork Point of Attachment) is the Layer 2 addresses for IS-IS Protocol.
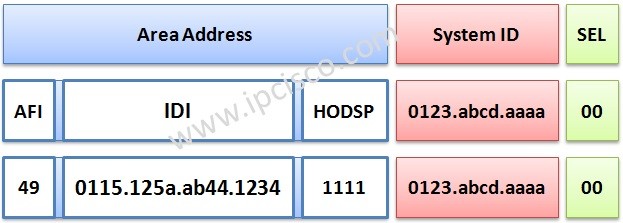
NSAP (Network Service Access Point) consist of three parts. These are:
Area address also has some parts inside it. These parts are AFI, IDI and HODSP.
You Can Check Also Protocol Cheat Sheets, All Network Quiz Pages and Network Lab Files Pages.
We can also divide the NSAP address into two parts. These are:
Inter Domain Part consists of AFI (Authority and Format ID) and IDI (Inter Domain ID).
Domain Specific Part consists of High Order Domain Specific Part, System ID and NSEL part. Here, High Order DSP is the subnet, System ID is the identifier of the device in area and the NSEL is the service identifier of NSAP address. When NSEL is equal to “00”, it is called Network Entity Title (NET) and it shows the device itself.
NETs are 8 to 20 bytes long. But in general, they are 10 bytes long.
System ID can be thought like OSPF Router ID. NSEL is like port/socket in TCP / IP.
You need to request an official NSAP prefix if you will use CLNS routing. Even if you will need only IP routing when using IS-IS Protocol, you always needs to use NSAP addresses, but this time you can add the private address space AFI 49.
AFI 49 is used as local addresses. Thess addresses are not advertised outsite of CLNS network.
In IS-IS ProtocolL2 Multicast Addresses are also used. And LSPs are sent to these addresses. In a broadcast network, L1 updates are sent to 0180:C200:0014 and L2 updates are sent to 0180:C200:0015.
In Point-to-Point networks 0900:2b00:0005 address is used as L2 address.
Leave a Reply