- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
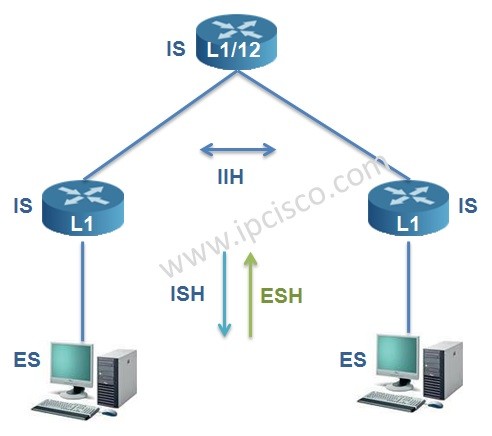
Network protocols uses different packets. Here we will focus on the packets used by IS-IS Protocol. We will learn IS-IS Packet Types.
IS-IS Protocol uses L2 encapsulation Ethernet 802.3/802.2. It do not use Ethernet II. Ethernet II is used for IP traffic. You can check the lesson that we have exmpained different Ethernet Packets on IPCisco.
IS-IS Protocol exchanges protocol information by using Link-State PDUs (Protocol Data Units).
There are four types of PDU packets in IS-IS Protocol. These IS-IS packets are given below:
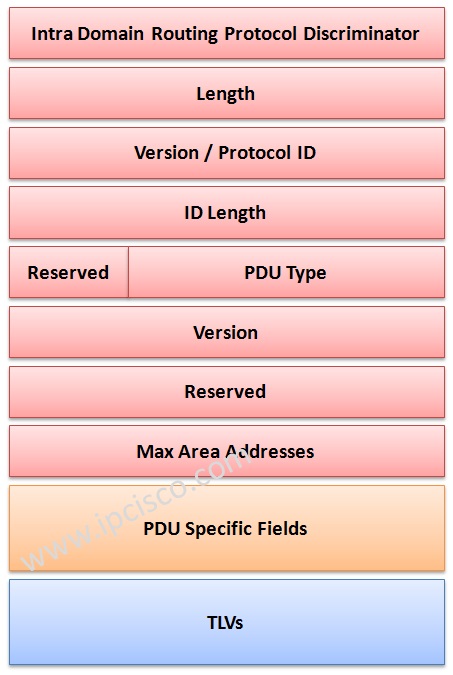
In IS-IS PDUs there is a TLV (Type, Length, Value) field. According to the need, these fields are added to the PDUs. This TLV field makes IS-IS extendable and it is the major advantage of IS-IS over OSPF. There are several TLVs in IS-IS packets. IS-IS Header always same, but according to the type of the packet, added TLV fields change.
TLVs are maximum 256 bytes and they contains sub-TLVs.
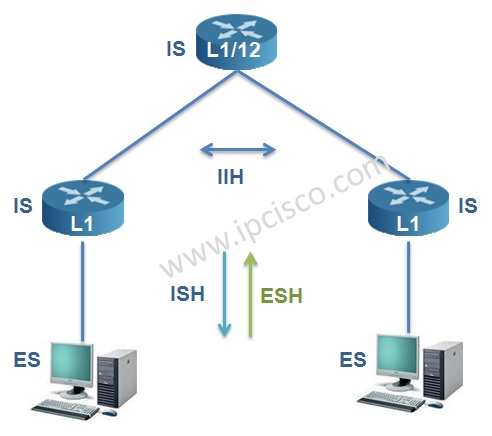
IS-IS Hello interval is 10 seconds and the dead interval is 30 seconds by default.
In IS-IS Hello packet, 6 types of data can be included with TLVs. These are:
For more information about IS-IS TLVs, you can check Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) TLVs article on Cisco Website.
IS-IS LSPs are like LSAs in OSPF and contains many information about the neighbour ISIS Routers and links. They are flooded periodically in IS-IS network. L1 and L2 PDUs use different formats LSPs are stored in IS-IS LSDBs. Seperate datababses are used for L1 and L2 LSPs. Each LSP has sequence number that shows its version.
In LSPs, below TLVs are supported:
PDU Type field shows the level of PDU. Level 1 PDU is showed with the value 18, Level 2 PDU is showed with the value 20.
ATT bit is the bit that set if the IS is connected to another area.
OL bit is set to show that the link-state database of IS is overloaded.
IS Type shows the level of the IS. For level 1, it is 1. For level 2 it is set as 3.
CSNP (Complete Sequence Number PDU) provides LSP to be sent reliably. CSNPs are like
Database Description (DD) packets in OSPF and they used to synronize the LSDBs.
CSNPs are exchange at the beginning, at the router initialization. And every 10 seconds after this, they are sent. In point to point links, both end routers send CSNPs. But for broadcast networks, only DIS sends CSNPs.
IS-IS CSNPs carry two types of TLVs . These are :
Entries TLVs are identify the LSPs and CSNPs include the below TLVs for all LSPs in its database:
PSNPs (Partial Sequence Number PDU) are sent when there is a missing information. With PSNP, this specific missing information is requested. And it is also sent for acknowledgement of the receipt. So PSNPs are like LSAcks and LSRs ( Link State Request) in OSPF.
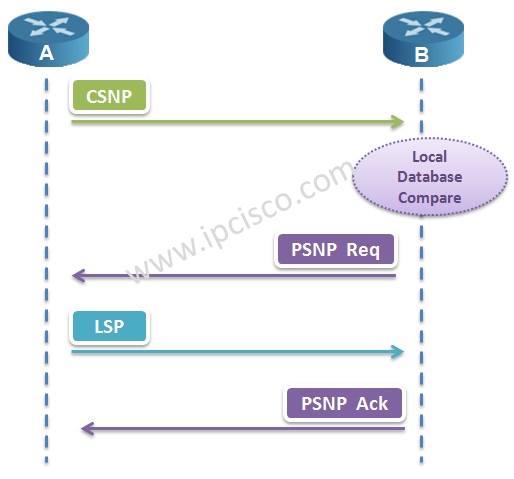
In IS-IS Protocol, PSNPs are used in point-to-point links. PSNPs also includes the TLVs like CLNPs. (The remaining life of LSP, the ID of LSP, the Sequence number of LSP, Checksum Value)
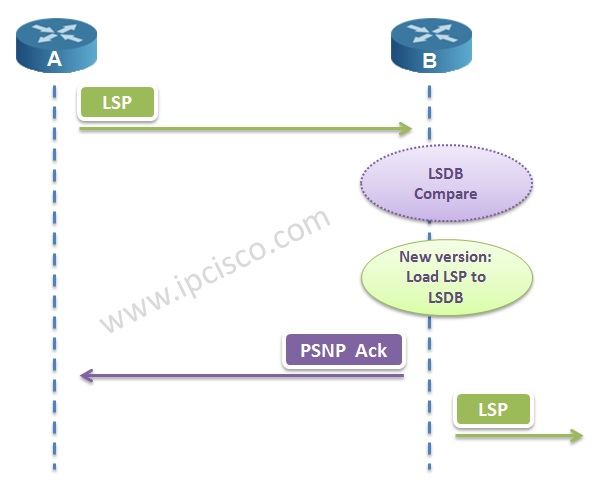
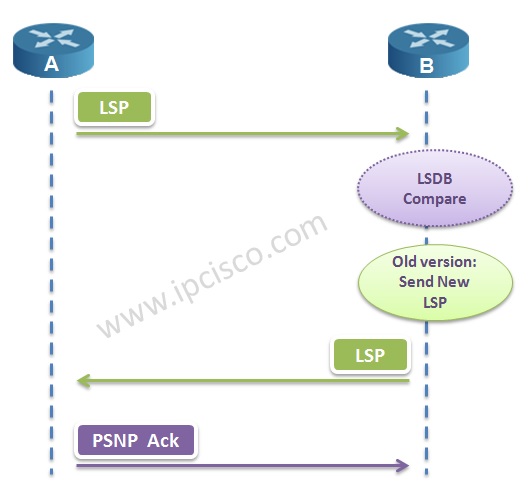
IS-IS Protocol compares the new coming LSP and the old one in LSDB (Link State Database). According to the comparement:
If the version of new coming LSP is newer, then;
If the version of new coming LSP is older, then;
Lastly, if the version of new coming LSP is same, then;

Sequence Number is used for checking the version of LSP. Higher sequence numbers are newer ones, means new versions.
Leave a Reply