- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
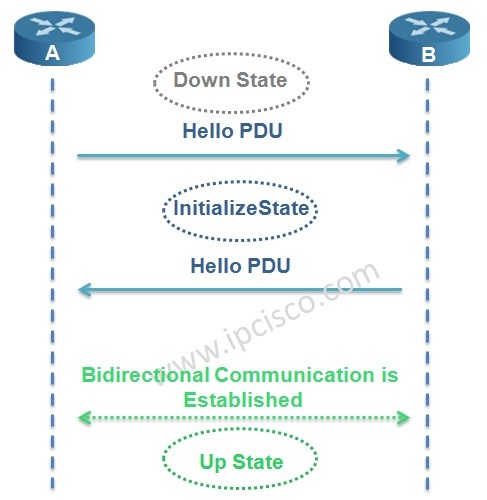
Table of Contents
Routing protocols need to establish neighborship to operate. IS-IS Protocol needs also adjacency for this purpose. In this lesson, we will learn IS-IS Adjaceny mechanims and IS-IS Protocol neighborhip establishment.
There are three types adjacency in IS-IS Protocol.These are:
There is no neighbourship between L1 and L2 routers.
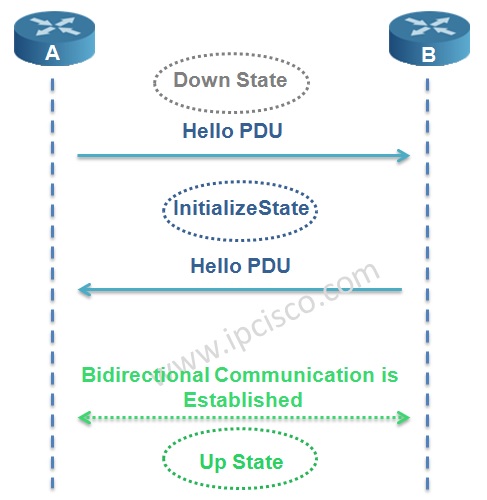
In IS-IS Protocol, adjacency is established with 3-way handshake mechanism. There are three states in IS-IS adjacency. Let’s check the adjacency states of IS-IS Protocol.
In the first place the router adjacency is in Down State. One of the routers, here Router A sends a Hello PDU. When the router B receive this Hello including the MAC address of the sending node Router A, it goes to Initialize State and sends Hello to Router A too. Again, when Router A receives Hello including the MAC address of Router B, bidirectional communication established. And the name of this state is Up State.
Test your knowledge with Network Questions & Answers and Network Flashcard Questions!
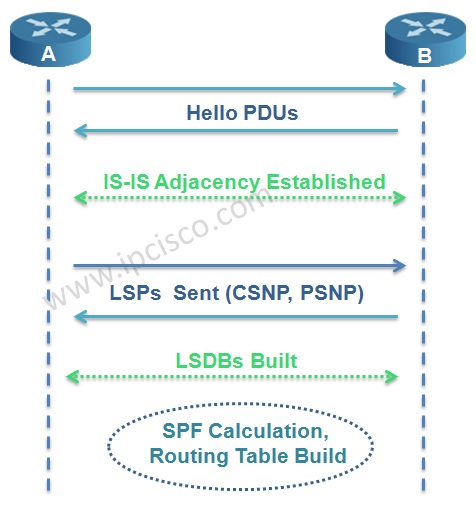
Beginning with IS-IS adjacency establishment, to the Routing Table establishment, IS-IS Operation has some steps.
We can summarize IS-IS operation in 6 steps. These IS-IS operation steps are given below:
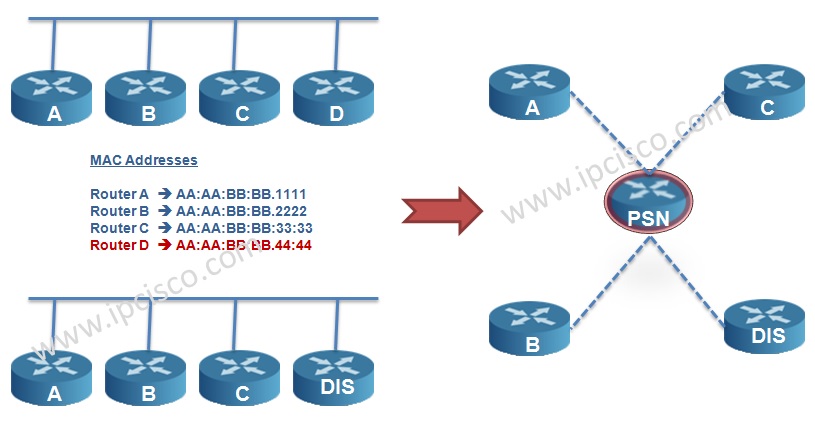
In ISIS network, LSDB databases must be synronized. To do this, full mesh or another solution is required. So, in IS-IS Protocol, one router is selected as DIS (Designated IS) and DIS is used to reduce the adjacency in areas. It is like DR in OSPF.
Router with the highest priority and then the highest MAC address is elected as DIS. The default DIS priority is 64. There is no BDR like OSPF. And like OSPF, if you want to prevent the router to be DIS, you can set the priority 0. If a new router added to the ISIS network, the election occurs again. This is not like this in OSPF.
DIS creates a Pseudo Node that is a virtual router. All connected devices in that LAN establish neighbourship with this Pseudo Node.
DIS is used on multipoint-to-multipoint topologies. It is not used in point-to-point topologies. Seperate DISs are selected for Level 1 and Level 2.
Leave a Reply