- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
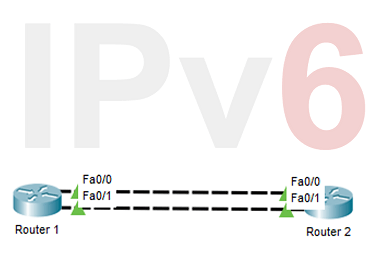
Table of Contents
IPv6 is the new version of the most important Network Layer Protocol IP. With this new IP version, IPv6, beside different features, some configuration differencies are also coming. In this lesson, we will focus on these IPv6 Configuration Steps, IPv6 Configuration on Cisco devices. We will use the below Packet Tracer topology for our IPv6 Config.
You can download Packet Tracer IPv6 Lab, in Packet Tracer Labs page.
In this configuration lesson, we will follow the below IPv6 Configuration steps:
So, let’s go to the IPv6 Configuration steps and configure IPv6 for Cisco routers.
After going to the configuration mode with “configure terminal” command, to enable IPv6 on a Cisco router, “ipv6 unicast-routing” command is used. With this Cisco command, IPv6 is enabled globally on the router. This can be used before both interface configurations and IPv6 Routing Protocol configurations.
Router 1# configure terminal
Router 1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
Router 2# configure terminal
Router 2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
After enabling IPv6 globally, we should enable IPv6 under the Interfaces. To enable IPv6 under an interface, we will use “ipv6 enable” command. Let’s enable IPv6 on two interfaces of each router.
Router 1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
Router 1 (config-if)# ipv6 enable
Router 1 (config-if)# no shutdown
Router 1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
Router 1 (config-if)# ipv6 enable
Router 1 (config-if)# no shutdown
Router 2 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
Router 2 (config-if)# ipv6 enable
Router 2 (config-if)# no shutdown
Router 2 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
Router 2 (config-if)# ipv6 enable
Router 2 (config-if)# no shutdown
EUI-64 format is the IPv6 format used to create IPv6 Global Unicast Addresses. It is a specific format that we have also talked about before. With this format, basically, interface id of the whole IPv6 adderess is ceated with the help of the MAC address. After that, this created interface id is appended to the network id.
To configure an interface with EUI-64 format (Extended Unique Identifier), firstly we will go under the interface, then we will use “ip address ipv6-address/prefix-length eui-64” command. Here, our IPv6 address and prefix-length are 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64. The real EUI-64 Global Unicast Address will be created with this address and MAC address after IPv6 configuration.
Router 1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
Router 1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64 eui-64
Router 1(config-if)# end
Let’s check the IPv6 address that is created with EUI-64 format with “show ipv6 interface brief” command.
Router 1# show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
FastEthernet0/1 [up/up]
FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7702
Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
If we do not use EUI-64 format address, we have to write the whole IPv6 Address to the configuration line. Let’s configure Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interface of Router 2 manually.
Router 2 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
Router 2 (config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234/64
Router 2(config-if)# end
Here, both of these directly connected interfaces are in the same subnet, the Network ID is same (2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64).
Let’s check the IPv6 address that we have manually assigned with “show ipv6 interface brief” command.
Router 2# show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::206:2AFF:FE15:BD01
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234
FastEthernet0/1 [administratively up/up]
FE80::206:2AFF:FE15:BD02
Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
To check the connectivity between two node, we use ping. As IPv4, with IPv6, we also use ping, but this time it is called IPv6 Ping. The format of IPv6 Ping is a little difference than IPv4 Ping. These differences are the format of the used IP address and the used keywords. With IPv6 Ping, “ping ipv6” keywords are used before the destination IPv6 address.
Here, we will ping from Router 1 GigabitEthernet0/0 interface to Router 2 GigabitEthernet0/0 interface.
Router 1# ping ipv6 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/1 ms
To check the configured IPv6 Address, we can use “show ipv6 interface interface-name” command.
Router 1# show ipv6 interface FastEthernet0/0
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701, subnet is 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64 [EUI]
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::1:FF0E:7701
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds
ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified)
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified)
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
ND advertised default router preference is Medium
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
Router 2# show ipv6 interface FastEthernet0/0
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::206:2AFF:FE15:BD01
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234, subnet is 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::1:FF15:BD01
FF02::1:FF34:1234
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds
ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified)
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified)
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
ND advertised default router preference is Medium
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
Here, with ipv6 ping, there are some options that we can use. These are given below:
ping ipv6 [hostname | ip_address] [repeat repeat-count | size datagram-size | source [interface-name | source-address]
So if we would like to send 10 IPv6 ping packet with 200 byte datagrams from 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234 to 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1111:2222:3333:4444, we will use the below command:
Router 2 # ping ipv6 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1111:2222:3333:4444 repeat 10 size 200 source 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234
To configure a Link Locak address manually, we use “ipv6 address link-local ipv6-address” command. Here, we should write an IPv6 address in the range of Link Local addresses. If you would like to learn more about a Link Local Address, you can check Link Local Address lesson.
Let’s configure GigabitEthernet0/1 interface of Router 1 with Link Local Address FE80::AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:DDDD. Here, there is no need to write a prefix length but we will add link-local keyword at the end of the command.
Router 1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
Router 1 (config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:DDDD link-local
Router 1 (config-if)# end
Let’s check the manually configure ipv6 Link-Local address with “show ipv6 interface brief” command.
Router 1# show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
FastEthernet0/1 [administratively down/down]
FE80::AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:DDDD
Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
IPv6 Addresses can be configured automatically. This is one of the most important characteristics coming with IPv6. For IPv6 Auto configuration, we will use “ipv6 address autoconfig” command. Let’s use it on Router 2 on GigabitEthernet0/1.
Router 2 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
Router 2 (config-if)# ipv6 address autoconfig
Router 2 (config-if)# end
This type of IPv6 address configuration is Sateless Auto Configuration.
Let’s check the Autoconfigured Link-Local ipv6 address with “show ipv6 interface brief” command.
Router 2# show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::206:2AFF:FE15:BD01
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:1234:1234:1234:1234
FastEthernet0/1 [up/down]
FE80::206:2AFF:FE15:BD02
Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
Let’s ping from Router 2 to Router 1 to test this second interfaces’ ipv6 connection.
Router 2# ping ipv6 FE80::AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:DDDD
Output Interface: FastEthernet0/1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:DDDD, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/1 ms
To enable DHCPv6 Client function on an interface, we use “ipv6 address dhcp” command under this interface. With this command, interface gets its IPv6 address form the DHCPv6 server. Let’s enable DHCPv6 on GigabitEthernet0/2 of Router 2.
Router 1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
Router 1 (config-if)# ipv6 address dhcp
Router 1 (config)# end
To verify DHCPv6 enabled interfaces, we can use “show ipv6 dhcp interface” command.
Router 1 # show ipv6 dhcp interface
To verify IPv6 Configuration, we can use different show commands. These IPv6 show commands are given below
Router 1# show ipv6 interface FastEthernet0/0
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC:2E0:B0FF:FE0E:7701, subnet is 2001:AAAA:BBBB:CCCC::/64 [EUI]
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::1:FF0E:7701
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds
ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified)
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified)
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
ND advertised default router preference is Medium
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
Leave a Reply