- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this lesson, we will focus MPLS in Networking and we will learn the answer of what is MPLS? So, What is MPLS? MPLS is a Packet-Forwarding technology which uses MPLS Labels for data forwarding decisions. It is the abbreviation of Multi Protocol Label Switching. Over time, users in networks have increased and this big traffic has brought high bandwidth and forwarding speed need. The existing routing protocols are looking to the routing table for forwarding decision on all nodes and this was overloading the routers beside causing a lot of time lose. Here Multi Protocol Label Switching brings also CEF and this bypass the slow part of this layer 3 decisions. Beside that it brings the speed of OSI layer 2 switching. In brief, MPLS Networking is combining the beneficial parts of both Layer 2 and Layer 3 of OSI reference model.
If you would like to learn more about MPLS, you can follow the lessons of Nokia MPLS Training.
In addition to these negative facts, there were some other problems about ATM technology, while working together with Ethernet and Frame Relay. To solve all these problems IETF developed MPLS in 1997. This development could be done with existing routing protocols. But changing all the existing routing protocols was very difficult, so IETF has chosen developing a new protocol.
This new protocol is using Labels for routing decisions. These labels are router specific and local significant to that router.
Table of Contents
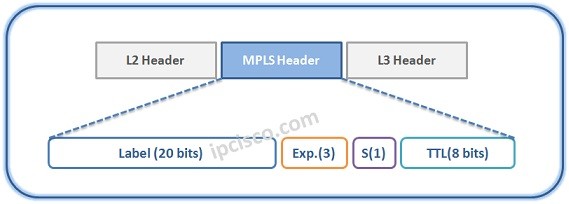
We have learned what is MPLS. Now, let’s focus MPLS Header. For MPLS Networking, a header is added between Layer 2 and Layer 3 header in packets. This MPLS Header is 32 bits long. This header consist of the below fields:
Label value is local significant for the router and it is used for label switching. Experimental field is used as Class of Service for QoS. One bit Bottom of Stack shows that if this label is the last label in the packet or not (1 shows that it is the last). Finally, the TTL value is used for loop protection like other IP packets.
As an example, you can check the below packet capture that includes also an MPLS Header. Here, MPLS Header is shown with blue rectangle. As you can see Multi Protocol Label Switching header is between the Layer 2 header (ethernet II header) and Layer 3 header.
You can test your knowledge with MPLS Questions
Firstly, I want to talk about Router terms used in this technology. There are different routers used in MPLS Technology. These routers are given below:
Customer Router is the router of customer, so it is not related to MPLS network.
Customer Edge Router is the router that is connected to MPLS PE Router of the Service Provider Network.
Provider Router is the router used in Service Provider Networks for MPLS Label Switching and Data Forwarding.
Provider Edge Router is the router that is located at the edges of the Service Provider Networks. They are the routers that VPN Services are defined. They are the borders between customer and Service Provider networks.
The below shape clearly explains the location of these routers.
Instead of Provider Router or Provider Edge Router, we can also use LSR (Label Switching Router) and Edge LSR (Edge Label Switching Router) terms for the routers capable of label switching. Specifically, Edge LSRs can be divided into two as Ingress Edge LSR and Egress Edge LSR. The below shape shows this clearly:
The packet comes to Ingress Edge LSR firstly from the customer. Then it travels in the Service Provider network through various LSRs (Provider Routers). Lastly, it exists from the Service Provider network with Egress Edge LSR.
The labels that will be used in MPLS network are distributed with some Label Distribution Protocols. And with these labels forwarding decision is done. As you remember from ip routing, this decision is done through IP addresses in normal routing. MPLS technology is basically a concept that changes a layer 3 routed network to a switched network.
There are four main protocols for Label Distribution. In other words, there are four Label Distribution Protocols. The widely used standard one is LDP (Label Distribution Protocol). You can find all Label Distribution Protocols below:
LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) is the simplest way for Label Distribution. Basically, LDP trusts Interior Gateway Protocol and selects the next hop that has already selected by IGP. Then, it takes label from this next hop. In other words, this type of label distribution is dependent to Routing Protocol decision.
RSVP-TE (Resource Reservation Protocol-Traffic Engineering), is another way used for Label Distribution. With this way, the next hop selection can be determined by IGP or can be specified manually. With this protocol, Traffic Engineering activities can be done that manages the flow of different types of traffic.
There are four type table that is related to Multi Protocol Label Switching. This tables are formed with CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) mechanism and the Label Distribution Protocols. So what are the tables used in MPLS? You can find Multi Protocol Label Switching tables below:
MPLS works in two different systems in Routers. These systems are Control Plane and Data Plane. So, what is MPLS Control Plane? What is MPLS Data Plane?
The following pictures of LSR and Edge LSR will explain the Control Plane and Data Plane more clearly. Here both Control Plane and Data Plane are shown beside the tables related with them.
So, what are the benefits of this new concept, what is the benefits of MPLS? Multi Protocol Label Switching Technology has many benefits to the networks. Some of these MPLS benefits are given below:
a) An encryption technology which uses hashes for secure transfer.
b) An organisation for international data forwarding.
c) A packet-forwarding technology which uses labels for data forwarding .
a) 20
b) 24
c) 32
d) 64
e) 128
a) 1
b) 3
c) 8
d) 20
e) 32
a) Label
b) Experimental Bits
c) Bottom of Stack
d) Time to Leave
a) Customer Router (C)
b) Customer Edge Router (CE)
c) Provider Router (P)
d) Provider Edge Router (PE)
a) Customer Router (C)
b) Customer Edge Router (CE)
c) Provider Router (P)
d) Provider Edge Router (PE)
a) RIB
b) FIB
c) LIB
d) LFIB
a) LDP
b) RSVP-TE
a) Data Plane
b) Control Plane
a) Combines the beneficial parts of L2 and L3
b) Provides easy managable VPN solutions
c) Provides Traffic Engineering
d) Provides speed and performanec increment
e) All of them
Leave a Reply