- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Table of Contents
In this lesson we will learn How VPRN Works and we will focus on VPRN Operation. Basically in a VPRN Architecture, there is a Service Provider Network and there are multiple branches of multiple customers. Service Provider consist of P and PE devices and every branch of a customer has a CE device to connect to the Service Provider Network. These connection points are PE routers. PE routers are also the routers, that L3 VPN (VPRN) Services are defined.
In VPRN Architecture, customer routers (CE) are connected to the Service Provider Edge Routers (PE). In the Provider Edge Routers there is a specific IP Forwarding Table called VRF Table for each customer (or each VPRN). This is the table created after VPRN (L3 VPN) definion.
A VRF Table is a specific Routing Table belongs to a specific VPRN. There are multiple VRF tables in a PE Router. Beside VRF tables, PE Routers also has a Default Forwarding Table.
To Test Yourself on Nokia Services, You Can Also Check Nokia Services Quiz Page
In VPRN, customers can manage their IP addressing. They also manage CE devices and responsible from the routing inside their network. Customers use their own routing protocols. They provide the routing information of their private network to the Service Provider. For route advertisements, it can use same or different ip routing protocols between them and Service Provider Edge Router (PE Router).
Service Provider has already a routed network. And every Service Provider use an apprepriate routing protocol for their network. P and PE devices use this routing protocol inside the core network.
VPRN Service is a Layer 3 Service that provides end-to-end communication of customer branches over Service Provider IP/MPLS network. This Service is defined in PE devices of Service provider and for end-to-end service delivery, LSP tunnels are build between the PE devices. In this LSP tunnels, customer traffic is pass through the Service Provider network.
After explaining general VPRN process, let’s check VPRN Operation detailly. Here, we will explain VPRN Operation with two main activities. These activities are Control Plane Activities and Data Plane Activities.
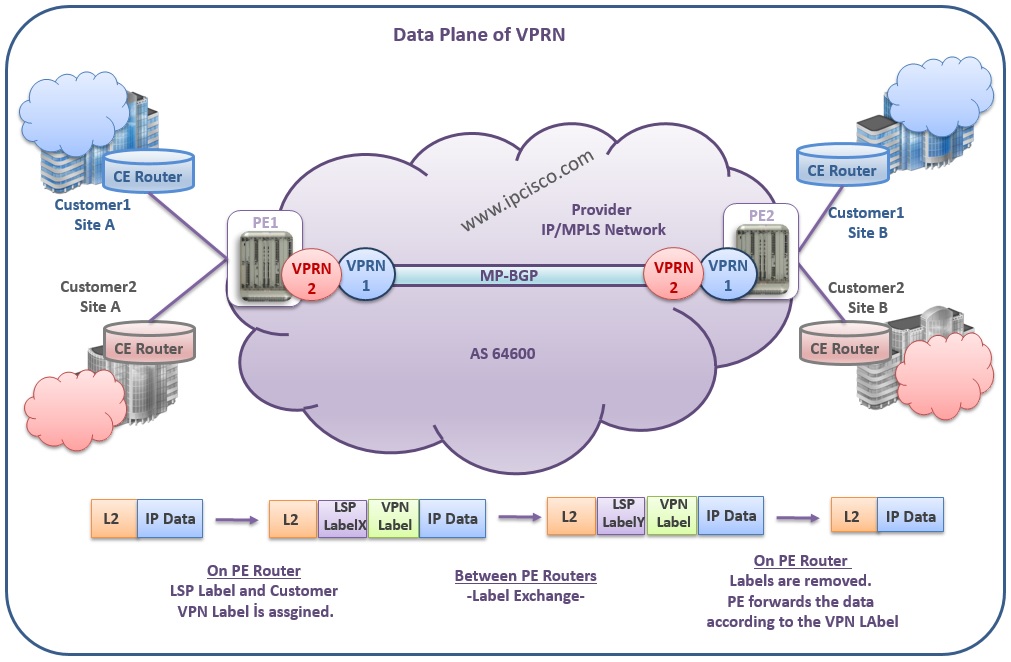
There are two planes used in VPRN Operation, in VPRN Services. One is Control Plane where VPRN prefixes and customer network is identified. And the other is Data (Forwarding) Plane where the data is transported and forwarded according to the VPN Service Label.
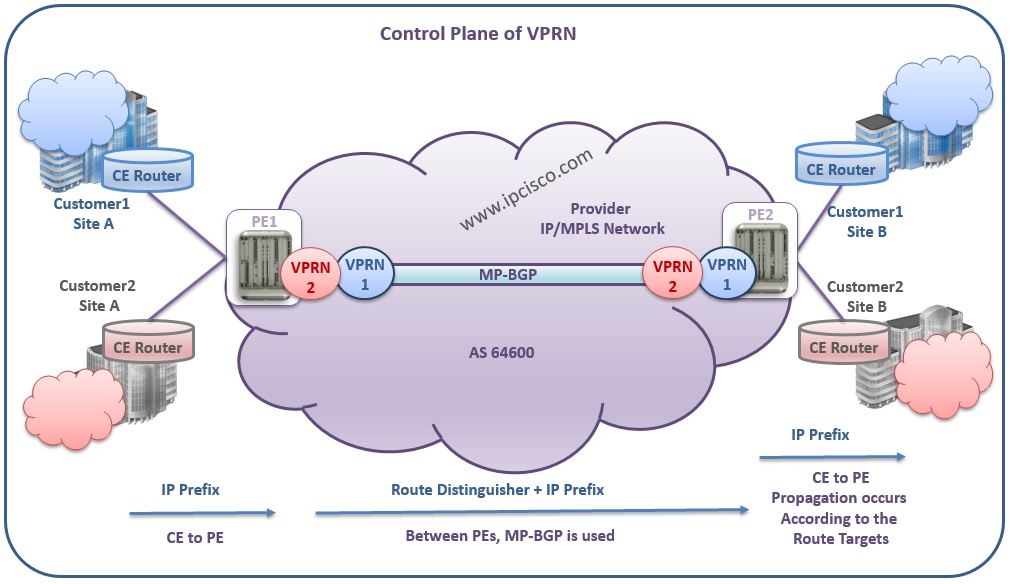
In Control Plane, Customer routes are advertised to the PE routers. And In PE routers they are stored in the VRF Tables. Between PE routers, CE routes are exchanged. This is done after adding the Route Distinguisher to the routes. Route Distinguisher is a 8 byte created value that distinguishes VPN Routes of different customer in Service Provider Network. And by using it, overlapping IP blocks can be used by different customers.
There is also another value named Route Targets. In VPN routing, the destination customer router is identified by Route Targets at the remote PE and the routes are propagated to the destination customer router.
You can see this Control Plane process of VPRN below:
You can see the Data Plane process of VPRN below:
IPcisco is very useful to associate n professional level Network engineers
It is nice to hear this nice words Ravi:) Thank you!