- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
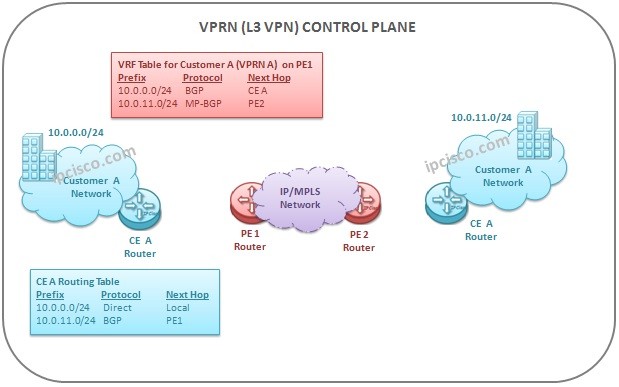
Table of Contents
As a basic definition, VPRN Control Plane is the time that routing exchange activities are done in VPRN Network. These are the necesssary routing information exchange of the VPRN routers in IP/MPLS Network. Beginning with CE devices, PE devices continue this exchange with other PEs and at the other end, it finishes with CE device again.
As we mentione before, CE uses a routing protocol in internal network. So it has internal routes. CE also uses a different or the same routing protocol with PE devices. If a different protocol is used between CE and PE, then redistribution is needed. With the help of this routing protocol or redistribution, CE sends the routers to the PE.
PE router gets the routes from the CE router, it allocates VPN Label for the prefixes and create a unique route called VPNv4 route. Then it redistributes the VPNv4 route into MP-BGP.. During this activity, the isolation of different customer routes are done via Route Distinguisher. So different customer routes can transport over the Service Provider IP/MPLS network without any mix.
At the receiving PE device, accorfing to Route Targets, the VPRN Service is sent to the destination.
To Test Yourself on Nokia Services, You Can Also Check Nokia Services Quiz Page
In VPRN Control Plane, VPRN VRF routes in a PE device must be shared with the other PE devices that run this VPRN Service. To do this, a specific protocol is used. This protocol is MP-BGP (Multi Protocol BGP).
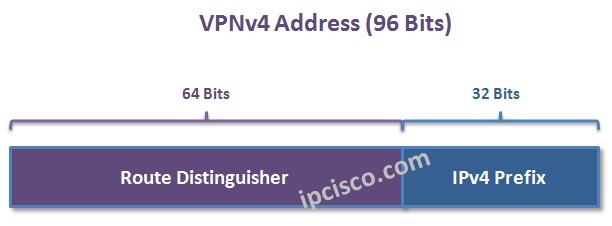
MP-BGP is the BGP version that can use different address types. Multiple customers can use same private blocks in their networks and these private blocks must not be mixed during transportation. Here, to distinguish different customer routes, we need to change their prefixes with a new address format. This address format is VPNv4 Address and it is produced by adding an 64 bit long Route Distinguisher to the beginning of IPv4 addresses of customer. Below, we will talk about this address type detailly.
Between the PE devices a BGP session is established. All the different VPRN customers’ information is transfered over this BGP session.
Think about it. If we do not use MP-BGP in VPRN. What is the situation of the routes of multiple customers’ same prefixes? Simply, in the BGP routing tables there would be different routes for same prefixes. So, one of them would selected and the data would forward through it. But, these are different customer’s route? Is it enough sending only the best route and only one customer route to its destination? Certainly not. This is not a healty and acceptable scenario.
MP-BGP allows different address classes. In VPRN (L3 VPN) to transport the same address blocks of one more customer, a mechanism need to identify these address blocks. To do this, a specific address is created to distinguish different customer networks in the BGP session. This address is crated with Route Distingusiher and called 96 bit long VPNv4 address.
VPNv4 address is built with the help of 64 bit Route Distinguisher and 32 bit IP Prefix. Here, the route distinguisher provide the difference. Route Distinguisher makes the prefix, globally unique. All the PE devices in that VPRN need to be configured with the same Route Distinguisher.
For a VPRN, PE router add the Route Distinguisher to the customer prefixes and VPNv4 Addresses are created and then send it with MP-BGP updates.
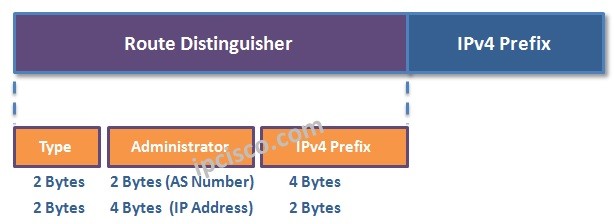
We have an IP address 1.1.1.0/24 and our AS number is 64000 . Let’s create the VPNv4 address for this address. AS an assigned number we will use 111. Here, our VPNv4 address will be 64000:111:1.1.1.0/24. The first part is Route Distinguisher and the second part is prefix.
We can also produce a VPNv4 address with using IP address instead AS number. If we use 1.2.3.4 ipv4 address instead of AS number, our new VPNv4 address will be 1.2.3.4:111:1.1.1.0/24 for the same prefix.
By the way, these VPNv4 address areused only for Control Plane operations. In Data Plane, normal IPv4 addresses are used. And VPNv4 address are used in Service Provider Network only. Customer do not know anything about them.
At the destination PE, PE needs to know which prefix is belong to which VPRN. To know this, a new identifier appears in VPRN Control Plane. This is “Route Targets”. With Route Target, all the VPRN memberships are identified and according to this value, data is forwarded to each customer destination with its of VRF table and without any mix.
Route Target is 8 Bytes BGP exteded community value. BGP extended community is used to carry additional information with BGP updates.
Leave a Reply