- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
During troubleshooting activities, different tools are used to determine the cause of a problem. Mirroring is also a troubleshooting tool for these activities. In Nokia world, mirroring term corresponds Nokia Service Mirroring.
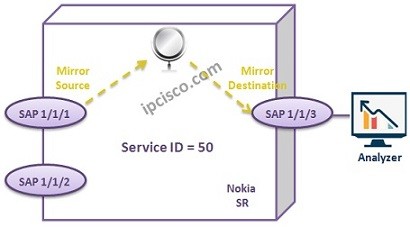
As you can understand from the maining, basically, mirroring means copying the same data to another place that we can analyze. Servise Mirroring, is also such a mirroring facility. Customer Service is mirrored from one port to another and after that the required analyze is done.
There are two types Nokia Service Mirroring. These are:
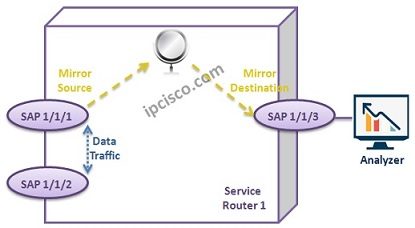
Local Mirroring is done within a single device.
Some Nokia Courses: Nokia NRS I Certification , Nokia IRP, Nokia MPLS, Nokia VPN Services
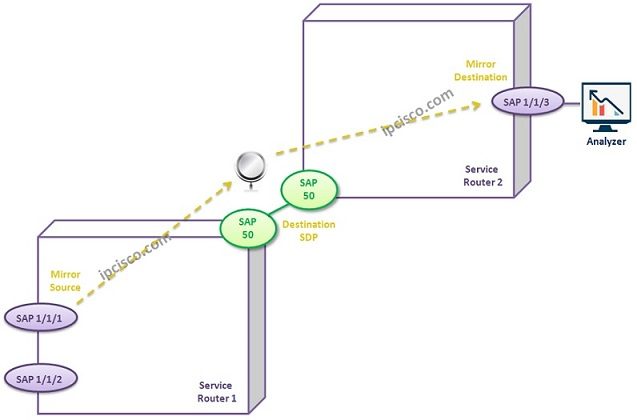
One Service Mirroring can be used through ingress or egress direction on a SAP in Local Mirroring. In Remote Mirroring this is done through SDPs. SAPs are used in Remote Mirroring too.
Multiple Mirrored Services can be received from a port. But to receive this, this port need to be configured with dot1q. Here, dot1q provide this distinction.
There are two important points in Service Mirroring. These points are:
Mirror Source is the location that we would like to analyze its traffic.
Mirror Destination is the location that we send the traffic to analze.
A Mirror Source can have only one Destination. But a Mirror Destination can receive mirrored traffic from multiple Mirror Source.
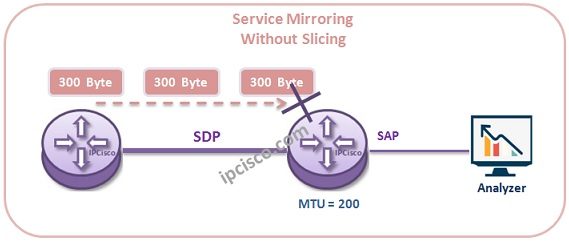
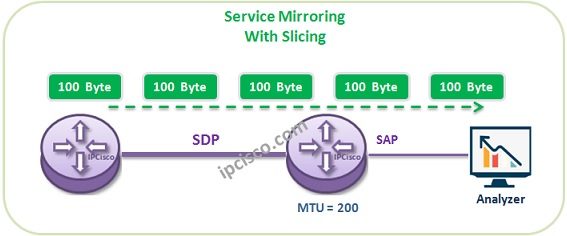
Nokia Service Mirroring causes some traffic increases. To avoid this “Slicing” is used. With this mechanims, Mirrored traffic is send from one router to another with smaller bytes. To configure Slicing, we can use “slice-size size” command, under the Mirror Destination.
Leave a Reply