- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
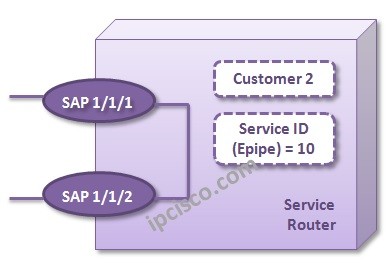
Table of Contents
In the previous part we have talked about the VPWS service of Nokia. Now, we will focus on the configuration of the VPWS Service on Nokia devices. In this lesson, we will learn Local Epipe Configuration. In the next lesson, we will learn Distributed Epipe Configuration.
As you know, there are types of VPWS. Epipe, Fpipe, Apipe, Cpipe and Ipipe are these types. The most important and widely used is Epipe service. So, here, we will start with Epipe service configuration.
Epipe service is the Point-to-Point Ethernet L2 VPN Service between two Service Routers as we have talked before. Ethernet is a widely used technology, so with ethernet, VPWS Epipe service become widely used beside other types.
As Other Nokia VPN Services, in VPWS the service configuration has some basic steps. In this configuration lesson, we will focus on these configuration steps, and we will show Epipe VPN Service configuration steps one by one.
Here, one point is important. If we are configuring a Local Epipe, an Epipe that is used on the same device, we will need to configure multiple SAPs and there is no need for SDP configuration.
If we are configuring a Distributed Service that need multiple device, then we need to configure also an SDP beside SAP or SAPs.
Aftet this two important terms, the last configuration step is “enabling the service”. We will enable our Epipe VPN Service.
Now, let’s configure two examples topoogy for Epipe VPN Service.
Here, we will configure a Local Epipe Service first and then we will configure a Distributed Epipe Service.
Nokia Epipe Service configuration needs some pre configuratiions as all the other Service configurations. What are these preconfigurations? These preparation steps are given below:
These steps and pre configurations are required in all Service Provider networks that provide VPN Services. This is also required for Epipe VPN Service.
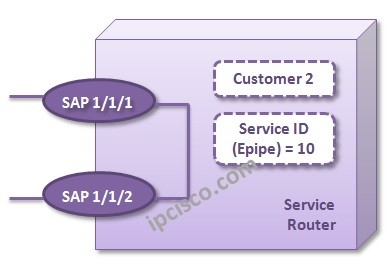
For Local Epipe Service Configuration, we will use the below topology. This is a basic router not a topology exactly. Because, Local Service Configuration is done in the same device.
Nokia-Router-1# config
Nokia-Router-1>config# service
Nokia-Router-1>config>service# epipe 10
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe# customer 2 create
Under the service, we will also configure a description. And we must “no shutdown” the service.
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe# description “Local-Epipe”
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe# no shutdown
Now, we will configure the SAPs under this Service. We have service configuration but there is nobody to send and receive on this service. We will configure these end points, SAPs.
Here, we will also define the encapsulation type firstly. Encapsuation is configured with “ethernet encap-type {dot1q|null|qinq}” command. For one customer and one service per port, we will configure this port encapsulation as null.
Nokia-Router-1>config# port 1/1/1
Nokia-Router-1>config>port# ethernet encap-type null
Nokia-Router-1>config>port# exit
Nokia-Router-1>config# service epipe 10
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe# sap 1/1/1 create
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe>sap# no shutdown
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe>sap# exit
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe# sap 1/1/2 create
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe>sap# no shutdown
Nokia-Router-1>config>service>epipe>sap# exit
To verify our VPWS Configuration, we can check the service configuration by “info” command under the service.
Nokia-Router-1>config>service# info
———————————————-
Epipe 10 customer 2 create
description ” Local-Epipe ”
sap 1/1/1:0 create
exit
sap 1/1/2:0 create
exit
no shutdown
exit
In the second example, we will show the other VPWS Verification commands one by one.
For the second Epipe example, Ditributed Epipe Configuration, you can continue with the other lesson.
Leave a Reply