- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
There can be multiple links towards a destination. If we have multiple links to a destination, the traffic is routed through one of them according to the routing protocol costs. If the total IGP cost to a destination are same for two path, these paths are called Equal Cost Multi Path. Normally if there are two path that have same IGP cost, in Nokia Service Routers, lower interface wins and the traffic goes through it.
You can also check How to Configure ECMP on Nokia Routers.
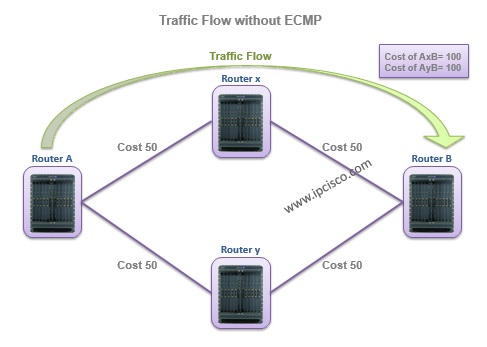
Think about the above topology, without ECMP the traffic only goes through the A path. And when you use the below commands to see the tables, you will realize the below results:
show router ldp bindings (2 path, A and B)
show router fib 1 (1 path, A)
show router ldp bindings active (1 path, A)
As you can see, the traffic goes through only the selected one although they are equal cost. This is an ineffcient and non-optimal use of resources.
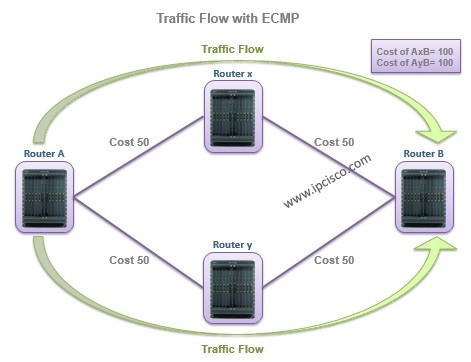
With ECMP (Equal Cost Multi Path), you can use these two equal cost path together, and a load-balancing process occurs between the two equal cost paths. This is a very efficient mechanism.
In the below topology, the traffic flows through both paths.
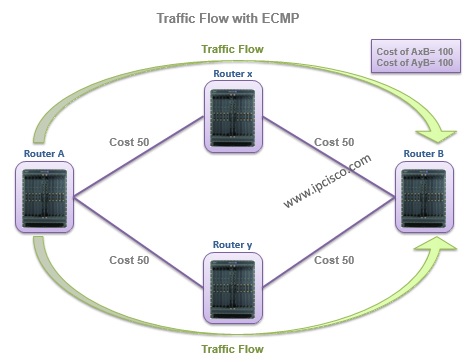
When you use the below commands, the you will realize that both of these paths are in use:
show router ldp bindings (2 path, A and B)
show router fib 1 (2 path, A and B)
show router ldp bindings active (2 path, A and B)