- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In MPLS Protection and restoration mechanims, both One-to-One and Facility Backup can protect different network elements. And these can be achieved by two ways:
Node Protection : Protect against the failure of the next downstream router. The upstream router before the failure node establishes a protection tunnel that goes around the failed next downstream router. This is default behaviour.
Link Protection : Protect against the failure of the link to the next downstream router. The upstream router before the failure link establishes a protection tunnel that goes around the failed link to the next downstream router.
Let’s talk about this protection types detailly.
You can test your netowkirn gknowdge on All Network Quizes Page!
Table of Contents
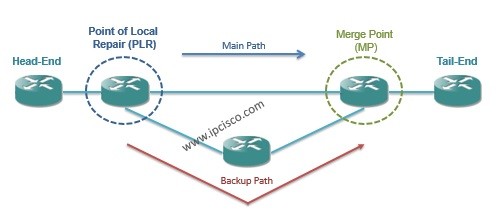
Link protection is protecting the link along an LSP. For this protection process, a backup link is created. As we say before the protection process also classified into two as one-to-one backup and facility backup.
If the backup link is created for One-to-one (Fast Reroute) Backup, it is called “detour”.
If it is created for Many-to-one (Facility) Backup, then it is called “bypass”.
-and-merge-point-(MP)_.jpg)
Node protection is the protection type with which we can provide protection for both link and node failures.
In node protection the terms Point of Local Repair (PLR) and MP(Merge Point) is used again. Here, the MP point is the downstream router of the protected node. This backup type is called “next-next-hop backup”.
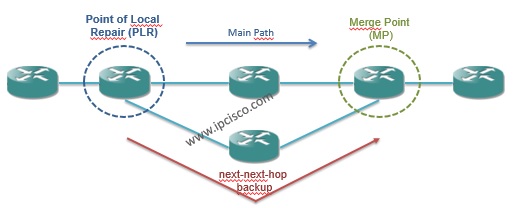
For this protection type, the PLR router need to know some information about MP router. These informations are:
Here I would like to take your attantion to the one point. Maybe you can compare end-to-end protection and local protection(fast reroute) and decide that end-to-end is not necessary. Because fast reroute have more specific control on traffic. But this is not completely true. Yes, with fast reroute you can have exact control on the traffic but beside fast reroute, secondary paths also need to be used for fast recovery. So end-to-end protection ‘s secondary path and fast reroute used complementary.
The default protection type is Node Protection. Every router on the LSP tries for Node Protection 3 times. If they fail, then turns to attemp for Link Protection. After three Link Protection attemp, if they fails, then turns Node Protection again. This default behaviour can be change for only Link Protection Attemp.
well explained
Thank you Pardeep ;)