- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
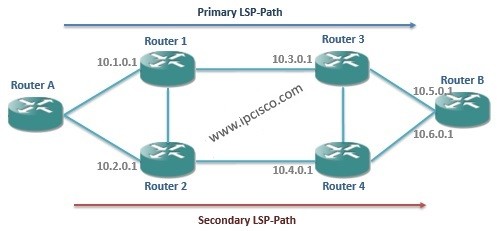
As we say in the following articles, while using Secondary LSP-Paths, sharing links between Primary and Secondary LSP-Paths must be avoided. We can say this term “Path Diversity“.There are some methods to achieve Path Diversity. These methods are:
Nokia NRS I Certification Course and Nokia NRS II Certification Course.
Table of Contents
Primary and secondary LSP-Paths are configured with fully strict hops in this method. This is difficult to configure and cause a huge operational overhead in large scale networks. Troubleshooting is also difficult in this method. But this method can be a good choice for small scale networks, because there are limited number of redundancy options.
While using full strict hop methods, redundant paths can not be used. There is only one option to do this, using two secondary paths. But this is more configuration overhead. MPLS FRR (Fast Reroute) is also the other solution for using redundant paths in the topology. We will talk about MPLS FRR (Fast Reroute) in the following posts.
Let’s see how to configure strict hops in Nokia 7750 Service Router according to below topology.
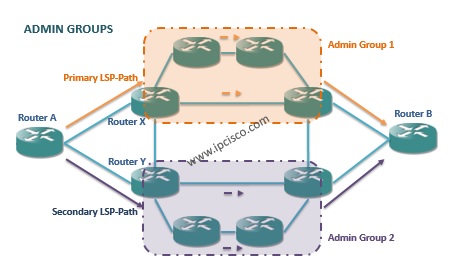
With this Admin Groups method, redundant links are assigned to different Admin Groups. Primary and Secondary LSP-Paths are configured loose hops that exclude either one of the groups. Admin groups can be asymetrics.
In the below example, the Primary LSP-Path can use any of the links in the upper plane. And the Secondary LSP-Path can use any of the links in the lower plane.
SRLG is the another mechanism for path diversity. This method gives more freedom to the Primary path during path decision. In the previous method, in Admin Group method, this selection can be done only with the limited group of links.
Leave a Reply