- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Redundacy is very important for a network. In many networks, redundacy is provided in different type of topologies or protocols. Here, we will talk about redundancy on Ethernet. In this lesson, we will learn one of these redundancy mechansims, Nokia Link Aggregation (LAG). You can also check Cisco LACP Configuration with Packet Tracer for Cisco Link Aggregation Configuration.
There are two main types of redundacy mechanims on Ethernet. These are:
You can also download all Nokia Labs, on Nokia Configuration Labs Page.
Link Redundancy is done via bundling multiple links logically between two devices. After bundling, this link seems as one link logically. But in real, multiple links are active and even one of them fails, the link continue to be active.
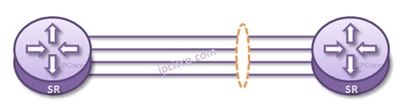
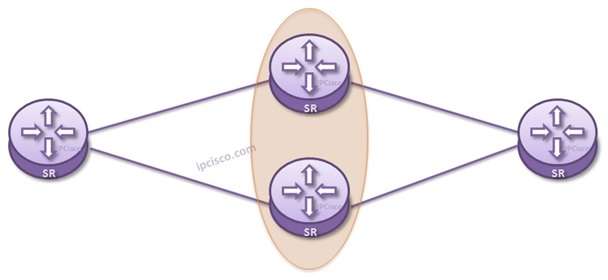
Table of Contents
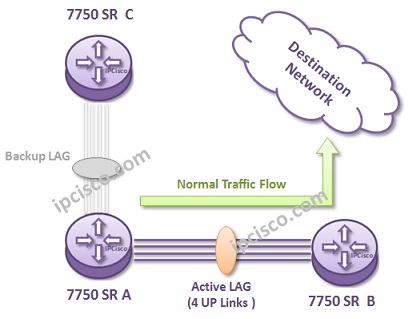
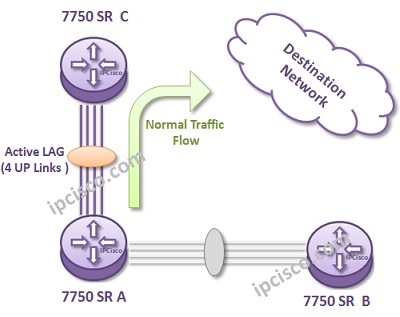
Link Aggregation is one of the link redundancy and capacity increase technique on any links. With bundling multiple links between different locations, you can build one logical link with more bandwidth. This bundle is also redundant. Even if one of the links between this devices fails, the logical link continue to work. The failover time is less than a second on a LAG. It is very few.

In a LAG all the links must have the same characteristics. The links’ speed, duplex type, hold-timers, etc. must match. The offered configuration is configuring the ports with no autonegotiate and full duplex in a LAG.
In a Link Aggregation (LAG), maximum 8 links are allowed. In other words, you can only aggragate 8 links under a LAG. And maximum 200 LAGs can be formed in Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) 7750 SR-12 Routers. This value is maximum 64 for Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) 7750 SR-1.
You can test yourself with Nokia NRS I Questions or Nokia NRS II Services Architecture Questions.
In Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) routers, there are also some other enhanced features for Link Aggregation (LAG). These features are Dynamic Cost and LAG Port Threshold.
LAG Port Threshold is the feature that determines the action after the failure of any link under LAG. With this feature, according to set theshold value, LAG can forced to be Down or the cost of the LAG dynamically recalculated. After a failure, if the available link number is equal or lower than the threshold value, then the action takes place. Down or dynamic cost calculation. By the way this costing of LAG is related with IGP, IGP cost value.
Let’s configure the above four port LAG as an example on Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent) 7750 SR-12.
Firstly, we will create the LAG and then we will add a description to this LAG. It is a good habit to give a good definition to a LAG to know between which nodes it resides.
A:RouterA# configure
A:RouterA>config# lag 1
A:RouterA>config>lag# description “LAG_XYZ”
Then we will add the ports that will be under this LAG.
A:RouterA>config>lag# port 1/1/1 1/1/2 1/2/1 1/2/2
After that, we will define a port-threshold value with a defined action. This means that if this threshold is exceded, do this. Here, we will say that, if there is only 2 or lower links are available in this LAG, make the LAG down.
A:RouterA>config>lag# port-threshold 2 action down
This is an important action to avoid traffic loses especially between the nodes that has high traffic.
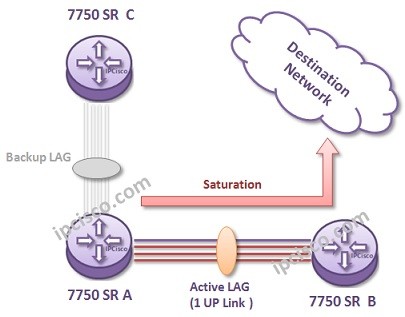
Think about it, if you have high traffic between two nodes and some of links in the LAG are down. The total traffic is higher that the LAG capacity at that specific time. What will occur? Here, a saturation occurs. This causes traffic lose.

In such a situation, your traffic need to go through another backup LAG or links. To do this, you need to make down this low capacity LAG.
A:RouterA>config>lag# port-threshold 2 action dynamic-cost
Here, we are using dynamic cost with port threshold command. Here, the dynamic cost will be calculated even if the active link number becomes 2 or lower.
Topology Redundancy is another redundancy mechanims for Ethernet. This redundancy mechanims provide protection towards entire switch failure. Not only links, but a device gives you redundany, a second chance.

As you know, layer 2 is very open to the loops. And one of the bad things that a network engineer do not want to come accross, is layer 2 loop. The other disadvantage of this medhod is, it can cause database instability.
Updating switch tables from different sources can cause this problem.
To avoid all of these problems, there is an important mechanism. This is STP (Spanning Tree Protocol). We will talk about STP more in the following lessons.
Leave a Reply