- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
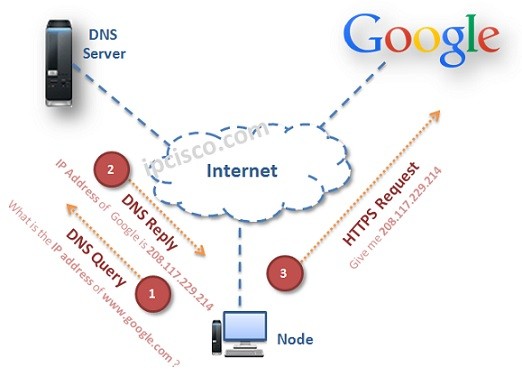
Table of Contents
DNS (Domain Name System) is a common protocol that is used to translate hostnames to the IP addresses. Normally, we use website addresses on our browsers. These website addresses are resolved to IP addresses by DNS. Without Domain Name System, we could not reach this website with its hostname only. In general we can define websites as hosts. Like websites, a single host can also use hostnames for IP resolution. Here, we sill also see the server that works for this job, what dns server is. We will also talk about DNS Configuration on another lesson. You can also check the wikipedia definion for it, here.
Let’s give an example about Domain Name System. Think about that, if you would like to reach www.google.com, you write this website address to the browser and you can reach Google website. At the backplane, this hostname is resolved to the IP address of Google. You can also reach Google without DNS, by writing only its IP address, 208.177.229.214. But this could be difficult to remember. So, Domain Name System makes life easier with this resolving mechanims.
DNS is a Client / Server Protocol. To use Domain Name System, a DNS Server must be configured firstly. In this DNS Server, IP addresses and related Hostnames must be mapped. After this process whenever a user request a hostname, DNS Server replies with its IP Address. Then time user’s browser can use the IP address of this hostname to access the website. User is unaware of whole this process. He/She Only write the hostname and reached the website.
With DNS configuration, the node sends a query that request the IP address of the sent hostname. DNS Server sends a response message that includes the IP address of this hostname. After that, node reaches the website.

Leave a Reply