- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
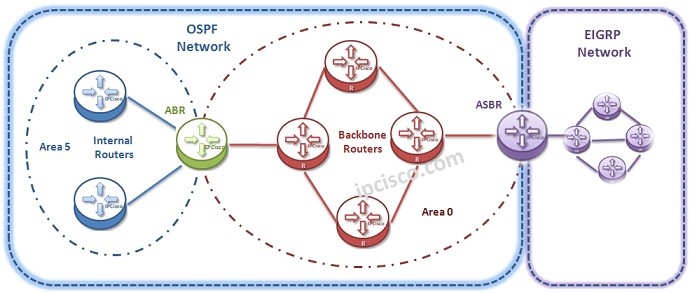
Table of Contents
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), is one of the most used Routing Protocol today. OSPF is a standard based Link-State routing protocol. It is a Classless routing protocol which do not send subnet masks with updates. So, it allows to use VLSM. Open Shortest Path First has similarities with the other Link-State routing protocol IS-IS but it differents from it in many points.
Open Shortest Path First uses a special algorithm, Dijsktra Alogirthm for route calculations. In other words, it uses Shortest Path First (SPF) method and with this way, the routing calculation is done.
In OSPF, both periodic and triggered updates are used. These updates are sent with LSA (Link State Advertisements). There are also different OSPF packets used for the messaging between OSPF routers.
OSPF is ideal for large networks and the convergence time of OSPF is very short. In other words, OSPF is a fast converged protocol. It is also prefered because of its secure character.
As a hierarchical protocol, Open Shortest Path Firt divided into different Areas. This areas reduce the complexity of the network and opitmize routing tables.
You can view detailed OSPF lessons below:
Key Lessons:
Areas & Configurations:
OSPFv3
Open Shortest Path First provides neighbourship between other OSFP routers by the help of OSPF messages. With these messages, OSPF tables are built. And Open Shortest Path First routing mechanims works with this tables. Basically, there are three tables in Open Shrtest Path First. These tables are:
Neighboring Table, is the table that stotres OSPF neighbor routers. You can see the directly connected OSFP neighbors here.
Topoloji Table, is the view of OSPF network. It is also known as LSDB. All the Open Shortest Path First Router connections are stored here. Topology table is identical in all OSPF routers in the Open Shortst ath Firstnetwork.
Routing Table, is the tablet hat stores the best paths to the destination. It is the table that is also sued with the other routing prtocols for routing process.
In Open Shortest Path First, all routers build its own Topology Table and has the full view of the network. It calculates the next hope independently from other routers. This is also the characteristic of Link-State Protocols. As you remember, Link-State protocols are “OSPF” and “IS-IS”. In Distance-Vector protocols, the situation is not like this. Distance-Vector protocols needs a neighbor to know about the network.
Open Shortest Path Fist routers announces the netwrok changes with LSAs eachother. LSDBs are built with these LSAs. The topology of the Open Shortest Path First network is stored in this LSDB (Link State Database).
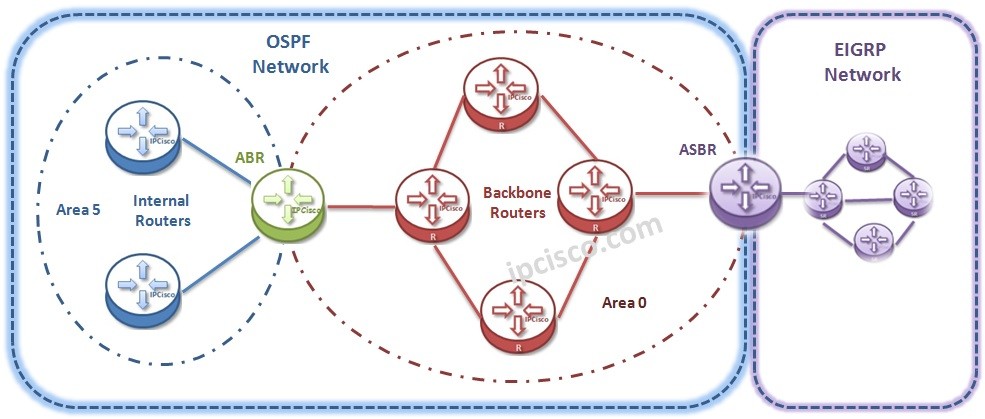
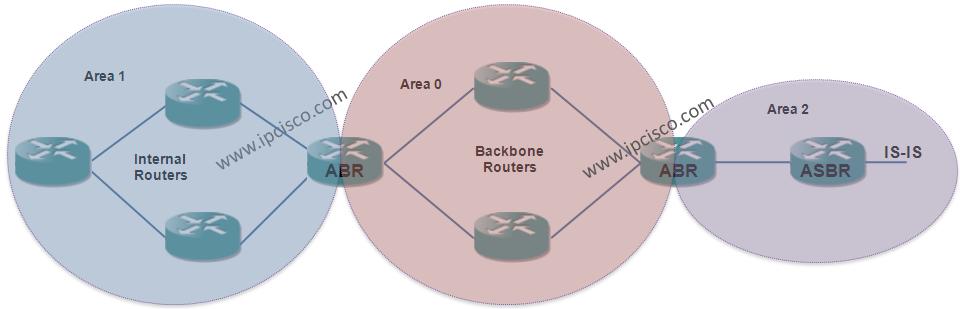
Open Shortest Path First has an hierarchical architecture. It uses “Areas” for hieararcy. There is a Backbone Area as Area 0 in the center for all OSPF Networks. Around this Backbone Area, Area 0, there are some other Areas. All these areas are connected to this Area 0. If there is a uncontinuous structure, Virtual-Links can be used to connect an area to the Backbone Area (Area 0).
With this hierachical architecture of Open Shortest Path First, you can divide your network into different small areas and by doing this, you can reduce overhead of this small areas. In other words, instead of doing LSDB processes for one large area, this is done in smaller areas and update summary LSAs are sent to the other areas. By doing this, LSA traffic is reduced.
Beside Backbone Area and Normal Areas, there are alsom other area types in Open Shortest Path First network. You can find these area types below:
In CCNA 200-301, there is only Single Area OSPF. So, we will not explain the other areas here. If you would like to learn OSPF Area types detailly, you can check the related lessons on CCNP ENCOR and CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure courses.
In OSPF Design there are different Router types. These router types are named according to their roles and their place of the network. Let’s see these routers:
For Best Path selection, Administrative Distance (Preference) values are very important. Every Routing Protocol has an AD value. The Administrative Distance (Preference) of the Open Shortest Path First is 110 for Cisco devices. This is a little different for Alcatel-Lucent, Huawei and Juniper devices. They use Interneal and External Preference values for Open Shortest Path First. Preference value is 10 for Internal OSPF Routes and 150 for External OSPF Routes on the devices of these vendors.
Router ID is an important term for Open Shortest Path First Operations. Every router has to have a unique Router ID in the Open Shortest Path First Topology. So, generally Router ID is manually configured on all OSPF Routers. If this is not done, the highest interface IP address is selected as Router ID.
Open Shortest Path First uses path Cost as its metric. Generally Bandwidth value is used as path Cost. AS a formula, the Cost is calculated like below in OSPF:
Cost = Reference BW(default 10 000 000) / BW
Protocols are developed and then they enhanced with new features. This new enhanced versions came with new versions. Open Shortest Path First also has different versions. There are two OSFP versions. These are:
OSPFv2 is the first version of Open Shortest Path First and it is used with IPv4.
OSPFv3 is the enhanced version of OSPFv2 that supports and designed for IPv6.
In the below table, you can check the differences of these two versions as summary.
In this article, we have talked about an overview of OSPFv2. In the following articles, we will explain this lesson more deeply. If you want to learn more about OSPFv3, you can check IPv6 Routing Protocols lesson.
Leave a Reply