- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
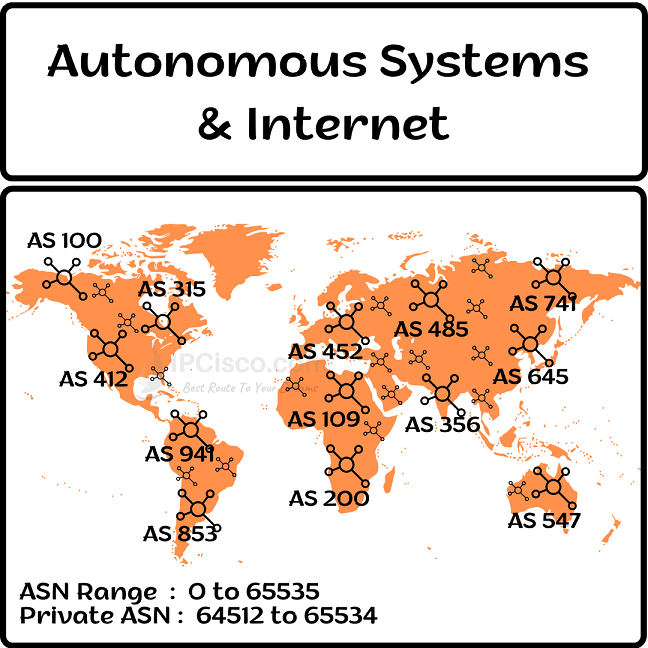
Table of Contents
There are different routing protocols used in networking. Commonly, we can divide these routing protocols into two types according to the place that we use them. These routing protocols are IGP (Interior Gateway Protocols) and EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocols). If we use a routing protocol inside of our network, it is IGP. If we use them outside of our network, it is EGP. In the previous lessons, we have talked about different IGPs. In this lesson, we will talk about the only EGP used today. This is the protocol of Internet, BGP Protocol, Border Gateway Protocol.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) was developed by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). It is known as the global routing protocol of Internet today. Because BGP routes the traffic across internet and between different service providers. It is the most scalable routing protocol today.
BGP is mainly a routing protocol. Here, you can think about that, why can’t we use other routing protocols over internet? Why we need BGP on Internet? The answer of this question is the importance of the BGP. Let’s explain deeply.
Internet is a large network and consist of many organizations. For such large networks, redundancy and load balancing is very important. For example, a large organization can need one more internet connection with different Public IP addresses. Another one can have one more connection and wants to use one link more than others with load balancing. These detailed services cannot be done easily by a routing protocol. Border Gateway Protocol overcomes these issues by itself. We can use redundancy and load balancing services effectively with BGP. To do this, we have a high control over BGP path selection. We can use different BGP Path attributes to manipulate path selection. With this manipulation, optimum path and traffic policy for an organization is determined. Basically, BGP is responsible to determine the optimum path and by hoping between autonomous systems, it delivers the required data across Internet.
What was the main difference between an IGP and an EGP? Well known IGPS are RIP, OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS. These routing protocols give us the ability to route the traffic within an Autonomous System. In other words, we use IGPs inside our network but it is not feasible to use these protocols on a large network like Internet. But EGP allow us to route the traffic between ASs (Autonomous Systems). BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). BGP routes the Internet traffic between Autonomous Systems. We can say that, internet is the collection of connected ASs. So, BGP is also known as Internet Protocol.
You can test your BGP Knowledge on BGP Practice Tests Page!
There are many corporates like Cisco, Huawei, Juniper and Nokia on internet and they have their own AS numbers. And internet is collection of these Autonomous Systems.
So, what is an Autonomous System? What is ASN?
An Autonomous System (AS) is a network or a collection of networks that are under a single entity or organization management. And the Internet is the collection of ASs. Service Providers and large companies has their own Autonomous Systems and they are known with their ASN by the other Service Providers.
ASs has their own numbers for identification. These numbers are called Autonomous System Numbers, ASNs. Firstly, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns these AS numbers to the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) like RIPE, APNIC etc. And then, RIRS assign these AS numbers to the Internet Service Providers or other large organizations. These organizations can be a tech company, a university, a government agency etc.
ASN is a 16-bit number and they can be any value between 1 and 65535. This ASN block can be divided into two:
1 to 64511 ASNs are globally unique Public ASNs. They belong to specific organizations or Internet Service Providers. So, one of these addresses can only be used by these specific organization. IANA assign these ASNs to Regional Internet Registries and then they assign these ASNs to specific Internet Service Providers or large organizations like Cisco, Juniper, Nokia, Huawei etc.
4512 to 6553 ASNs are Private ASNs. These range can not be used on Internet but they can be used by everyone. They are like private IP addresses. For example, they can be used for BGP confederations within an autonomous system.
Inside an Autonomous System, we use IGP as I mentioned before. How about between Autonomous Systems on Internet? Between Autonomous Systems, EGPs (Exterier Gateway Protocols) are used. And today, there is only one EGP. This is Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). Before, there was also a protocol named EGP (same name). But it is retired.
By the way during BGP configuration, one router can belong to only one Autonomous System. So, we can configure BGP on a router with only one ASN.
To learn Regional Internet Registry ASNs assigned by IANA you can check the following link: IANA, Assigned AS Numbers
You can check the companies and their assigned ASNs on internet.
You can test your BGP Knowledge on BGP Practice Tests Page!
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a Path Vector protocol. So, it has both Link-State and Distance-Vector protocols characteristics.
BGP is slower than other Routing Protocols. Because it does Route exploration. According to different policies, BGP select the optimum path for the traffic. And with different path attributes, we can always manipulate BGP Path Selection and we have a high control over routing.
BGP uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) for session establishment. So, it is a secure protocol. For BGP neighborship, firstly, TCP Three-Way Handshake Mechanism works and TCP Connection is established. For this connection, SYN, ACK and SYN ACK messages of TCP is used. After a proper connection, other BGP session establishment processes are done. We will talk about BGP Session Establishment detailly in the next lesson.
As you know, protocols use some default port numbers. BGP also uses one of these default port numbers. BGP uses TCP 179 port by default.
Border Gateway Protocol supports CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing).
BGP uses three tables for BGP routing. These tables are given below:
BGP Neighbor Table includes BGP neighbors of the router. All BGP Peers showed in BGP Neighbor Table.
BGP Table includes the updates that received from other BGP devices.
Routing Table includes the Best Routes to the destination.
BGP is one routing protocol but we can divide it into two according to the used location. These are:
We use BGP as EBGP (Exterior Border Gateway Protocol) between Autonomous Systems. Two routers in different Autonomous Systems establish BGP Neighborship with EBGP.
On the other hand, IBGP (Interior Border Gateway Protocol) is used within the Autonomous System. If two BGP router in the same AS establish a BGP neighborship, this is IBGP neighborship.
For Cisco devices, there are two default BGP Administrative Distance (Preference) for EBGP and IBGP. The default administrative distance value for EBGP is 20. The default administrative distance value for IBGP is 200. For Cisco devices, EBGP Routes are very trustful. So, its AD value is lower than any well-known routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, EIGRP. These are the values used by Cisco for BGP Routes. How about other vendors like Juniper, Huawei, Nokia?
Nokia, Juniper and Huawei do not divide preference values into two like Cisco. Nokia and Juniper use 170 as BGP default administrative distance. And Huawei uses 255 as BGP preference.
BGP gives us high control opportunity on traffic. To do this, iBGP supports policies. Different policies can be used for different types of traffic. So, we can distinguish traffics and behave different towards different traffic.
BGP selects the Best Path according to BGP Best Path Algorithm. There are different BGP Path Attributes which is used on this Best Path Algorithm. BGP checks this orderly and determine the optimum path. We will talk about BGP path attributes detailly in the following lessons.
With Border Gateway Protocol, we can manipulate traffic and we can have more control on routing. By the help of BGP Path Attributes, we can determine the paths and their load ratios. This provides redundancy mechanism and load balancing.
A Router needs to connect another router with BGP for BGP operation. This is BGP neighborship establishment. BGP uses TCP Three-Way Handshake for BGP Neighborship. BGP Neighborship establishment is a set of states. Each state uses different messages. At the beginning, the state is Idle. After that for BGP peering different states are passed. These are given below:
There is also another state named Active. This means that there is a problem on BGP Neighborship.
Border Gateway Protocol uses different message types for its neighborship establishment and routing updates. We will talk about these BGP messages detailly in another lesson but here, let’s write down these messages:
BGP is the most important protocol for Internet. Network engineers like to work on BGP a lot. Because, working on BGP Protocol is also an indicator of your networking experience. Always, the most experienced network engineers work on Border Gateway Protocol.
Here, we have talked about basic BGP characteristics. In other lesson, we will go through BGP deeply and learn the details of the protocol of Internet. We will also learn how to configure BGP with different BGP Protocol Examples.
Leave a Reply