- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
VPLS can be defined on One Service Router or on Multiple Service Routers. Basically we can divide VPLS into two here.
The first one is VPLS, that is defined on one Service Router of Service Provider, by using router ports only. As Alcatel-Lucent (Nokia) translation, this type of VPLS is done only by using SAPs. This type of VPLS called “Single-Node VPLS”. Here, customer VPLS is in only one Service Provider router. Service provider gives interfaces to the customer. Without going out to the other Service Provider routers, customer benefits from VPLS service.
The other is VPLS, that is defined on Multiple Service Routers. This type of VPLS uses both SAPs and SDPs that connect these different Service Routers. This type of VPLS called “Multi-Node VPLS”.With this VPLS, customer benefits VPLS by also using the other PE routers of the Service Provider.
We can also divide VPLS by the used SDP type.In other words used pseudowire type.
Simply, we can divide Multi-Node VPLS according to used SDP type. Here two type VPLS appear:
• Full-Mesh VPLS ( with Mesh-SDP)
• Hub and Spoke VPLS (with Spoke-SDP)
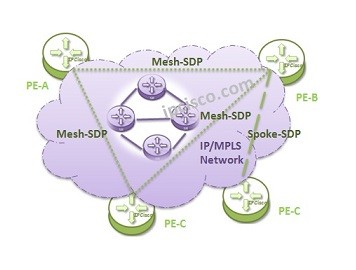
• Hierarchical VPLS (with Mesh-SDP and Spoke-SDP)
In Full-Mesh VPLS, PE Routers that run this VPLS (L2 VPN Service) are connected via Mesh-SDP.
In Hub and Spoke VPLS, PE Routers that run this VPLS (L2 VPN Service) are connected via Spoke-SDP.
In Hierarchical VPLS, Mesh-SDP and Spoke-SDP is used together according to the topology requirements.