- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
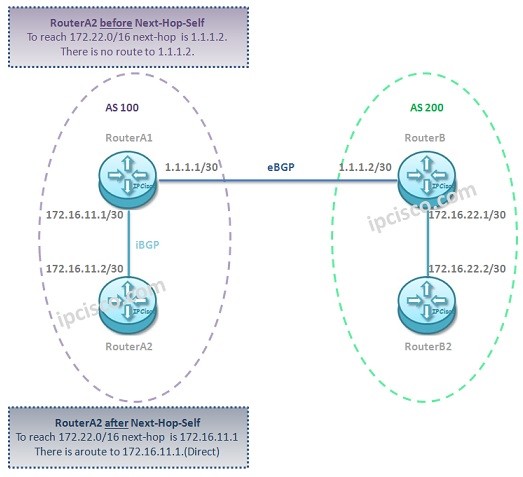
Table of Contents
In BGP Configuration, there are some key commands and concepts used for a better BGP operation. BGP Next Hop Self is one of these commands used in Juniper routers.
When an eBGP route advertised to vie iBGP, normally the next-hop of the route stay unchanged. This behaviour causes unknown destinations at the iBGP peer. The route and the next-hop is in another network and there is no information to reach this next-hop.
To overcome this issue, a routing policy that provide “next-hop self” behaviour can be used.
Below, we will show this conffiguration with an example.

Here, there are to steps to apply next-hop self characteristic to the router. These are:
1. Creating the Routing Policy on the Router
2. Applying the Routing Policy to BGP
Let’s start to configure next-hop self. By the way, for our topology, we will configure this, only on RouterA1.
To test yourself, you can also check JNCIP Quizes Page.
Before this configuration, RouterA2 can not reach the network between RouterB1 and RouterB2. Because as a netxt-hop it has the address of RouterB1’s ip address. But it do not know how to reach this next-hop.
After the configuration, Router A2 received this route with the next-hop of its neighbour RouterA1. And after that, it can reach the network between RouterB1 and RouterB2 via its neighbour.
To test yourself, you can also check JNCIP Quizes Page.
Leave a Reply