- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
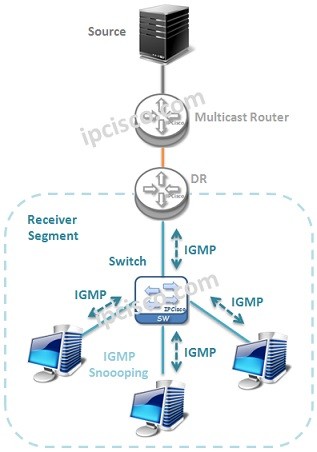
Table of Contents
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a Host-Router Multicast Signalling Protocol that provides dynamically registration of the hosts to the desired Multicast Groups.
With IGMP, Host requests to join to the Multicast Groups. This join request comes to the DR (Designated Router). DR translates this to the Multicast Routing Protocol (PIM).
You can test your IP Multicast knowledge with Multicast Quizes.

The hosts also stays connected to the Multicast Group with Internet Group Management Protocol. After a while, leaving from the Multicast Group is also a responsibility of Internet Group Management Protocol.
To sum up, IGMP provides three basic jobs between Hosts and Routers. These roles are:
Now, let’s talk about some of the important operations of Internet Group Management Protocol. How a Receiver sends Multicast Group Join message? How an IGMP Multicast Query is sent?
Firstly let’s look at IGMP Join Request. As you can see below, firstly receiver tells that, it want to receive Multicast traffic. It also tellss the Multicast Source that it want to receive that Multicast Traffic. Because here, we are using IGMPv3. Then, this Join Request is sent to the DR.
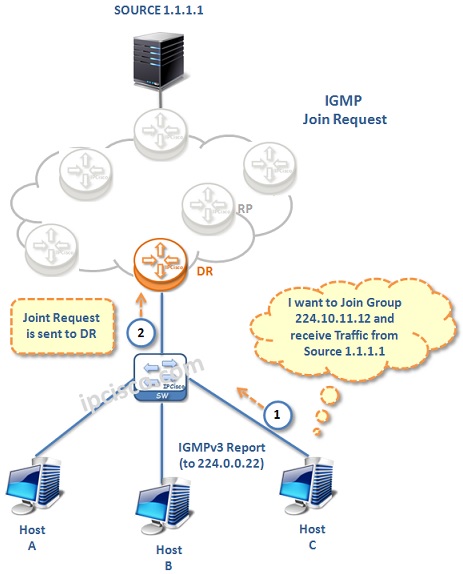
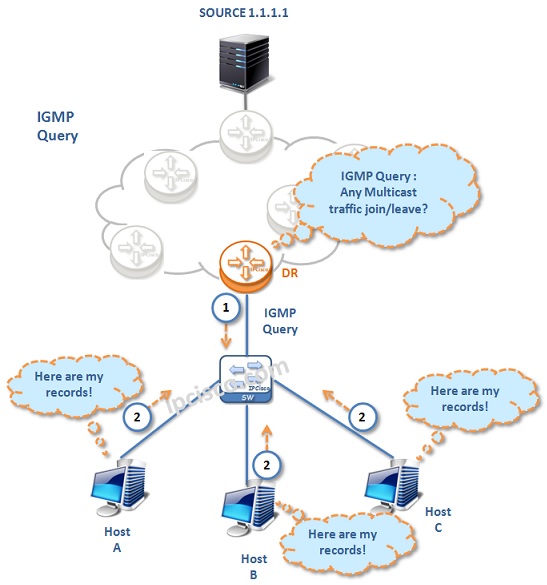
The behaviours of the Internet Group Management Protocol operations changes according to the used version. So, we will talk about the IGMP operation detailly, for each version.
There are three IGMP versions. These are :
• IGMPv1
• IGMPv2
• IGMPv3
Each version has specific properties. Let’s check these one by one.
IGMPv1 is the first and the basic version of Internet Group Management Protocol. Basically IGMPv1 has two mechanims. These are “membership query” and “membership report”.
In the Multicast network that uses IGMPv1, routers send Membership Queries to 224.0.0.1 Multicast address every 60 seconds. This Membership Query wants to learn that if any multicast member interested in to join any multicast group. If a host interested in the multicast group, it sends a Membership Request. By this mechanism, IGMP table is filled and with DR translation from IGMP to PIM, multicast group member starts to get multicast traffic.
In IGMPv1, there is no leave message mechanism. If after three IGMP Query attempt, there is no Membership Report, then that multicast member deleted form the IGMP table of router.
IGMP1 is not compatible with other versions. If one version 1 routers exist in the network, all of them must work like it.
IGMPv1 packet is like below:
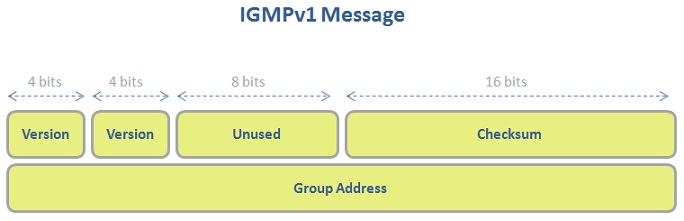
As a summary, IGMP messages used with IGMPv1 are:
IGMPv2 is the second and advanced version of IGMPv1. And version 2 is the default IGMP version in Cisco devices.
Here, in IGMPv2 the Membership Queries sent by the router can be group specific or as the same as IGMPv1 (to all the routers). IGMPv2 works like version 1 but with a big difference. This difference is Leave Group Messages.
IGMPv2 has a Leave Group Message to leave the group. Memebers send this message to the 224.0.0.2 Multicast address and then it leaves the multicast group. These Leave Messages are very efficient. By using this Leave Messages, the multicast tree is updated more efficiently.
After Leave Group Message, multicast router sends a Group-Specific query to determine are there any hosts thatare interested in the multicast group or not. If there is no reply, then multicast forwarding of that group stops.
It is backwardcompatible with the previous version IGMPv1.
IGMPv2 packet consist of four areas. These areas are :
You can find the areas of IGMPv2 Packet below:
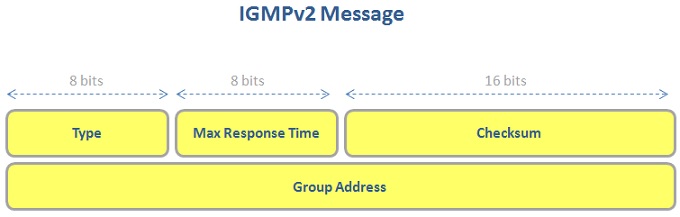
There are four IGMP messages used with IGMPv2. These messages are :
The last version is, IGMPv3. IGMPv3 is the extended version of IGMPv2. IGMPv3 is used with Source Specific Multicastand Soruce Filtering. Source Specific Multicast provides to multicast clients to select specific Multicast Sources. Multicast clients select a specific multicast source and get multicast traffic from only that multicast source. IGMPv3 responsible for this relationship.
IGMPv3 hosts uses 224.0.0.22 multicast address to send Membership Report. This is the address of all IGMPv3 capable router. IGMPv3 routers listen this address about IGMPv3 activities.
In IGMPv3 there is also another difference if we compare with other versions. All the hosts response to the Queries. In the other IGMP versions, only one host was responding, the others was suspended to reply.
IGMPv3 Message consist of more areas that the other IGMP versions. You can find the IGMPv3 message below:
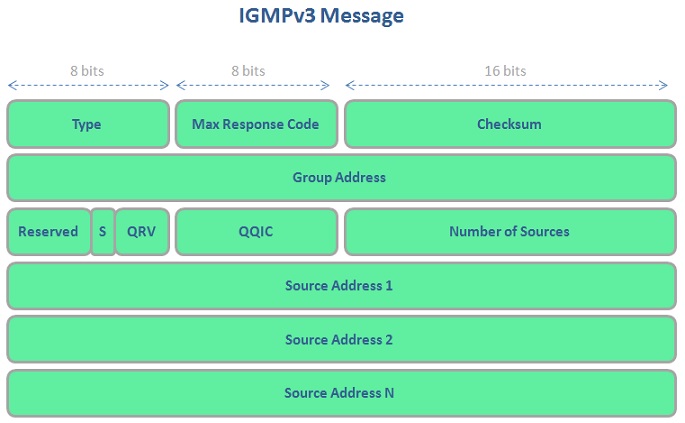
Two different messages are used with IGMPv3. These two messages are given below:
There is no specific IGMPv3 leave group message. IGMPv3 uses membership report for group leave.
You can also check IGMP Snooping Mechanism.
Leave a Reply