- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
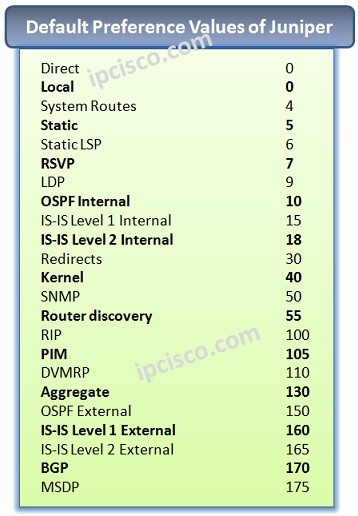
Table of Contents
Routing Tables are used for routing decisions on Routers. For example when you configure BGP, these routes are filled into these Routing Table. There are multiple Routing Tables in Juniper Routers. These Routing Tables and their roles are given below:
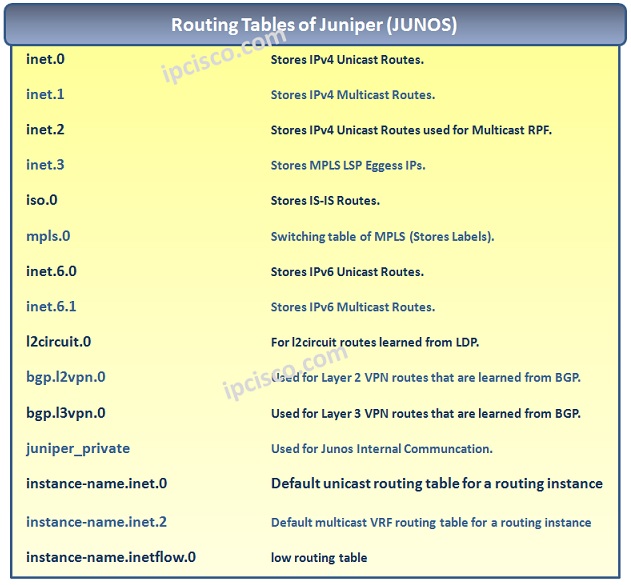
For detailed information, you can check also Juniper website.
To check to Routes, you can use general “show route” command. To check a specific Routing Table, you can use “show routing table” command with the related Routing Table name(inet.0, inet.1 etc.).
juniper-router@Kosem> show route table inet.0
inet.0: 4 destinations, 4 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, – = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.1.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:09:12 > via ge-1/1/1
172.16.0.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:09:12 > via ge-1/2/1
10.1.1.1/32 *[Local/0] 00:09:12 Local
172.16.5.0/32 *[Static/5] 00:10:32 > via ge-2/2/2
juniper-router@Kosem> show route table inet.1
inet.1: 2 destinations, 2 routes (2 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, – = Last Active, * = Both
224.10.1.1,10.1.1.1/32*[PIM/105] 00:06:23 Multicast 224.20.2.2,
200.1.1.1/32*[PIM/105] 00:07:12 Multicast
juniper-router@Kosem> show route table inet6.0
inet6.0: 2 destinations, 2 routes (2 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, – = Last Active, * = Both
fec0:abcd:11aa:1001::/64 *[Direct/0] 00:02:11 > via ge-1/1/1
fec0:abcd:22bb:2002::/64 *[Direct/0] 00:02:11 > via ge-1/1/2
fec0:0:bbbb:aaaa::5/128 *[Local/0] 00:2:11 Local via fe-0/0/1.0
Preference Values (Administrative Distance in Cisco), are the values that provide the reliability ratio of a Routing Protocol. The lower values are most reliable routes in the Routing Table. If the preference value increase, the reliability is decrease too.
For this reason the better value is 0. Only direct and Local routes has this value. After that the most reliable value is by default 5 which is belong to Static Routes.
You can find the Juniper Preference values below:

Leave a Reply