- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
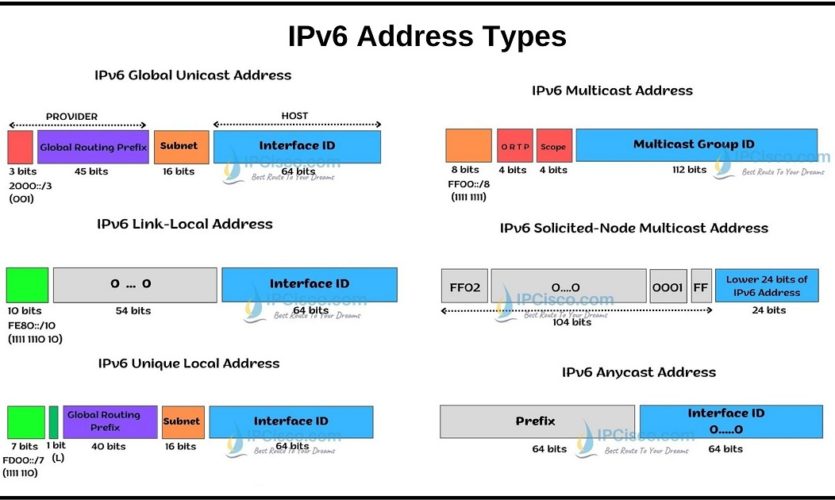
Table of Contents
Like IPv4, there are different IPv6 Address Types also in IPv6 world. Here, we will focus on these IPv6 addresses and we will learn the details of these IPv6 address types. Like IPv4, In IPv6 world, some of the concepts like reserved, public and private addresses will still remain. But with some differences. Let’s see all these address types one by one.
Mainly, there are four IPv6 Address Types. These address types are given below:
IPv6 Special Addresses are the addresses which are used for different purposes. We have such IP addresses for IPv4 too.
IPv6 Unicast Addresses are single node or single interface ip addresses. When we send a traffic to a unicast address, this traffic is sent only to that node or interface. In IPv6 world, we have three different IPv6 Unicast Addresses.
IPv6 Multicast Addresses are IPv6 addresses which identify a group of interface or nodes. When we send a traffic to a multicast address, this traffic is sent to that group.
IPv6 Anycast Addresses is the new additional ip address type in IPv6 world. When we send a traffic to an anycast address, this traffic is sent to the nearest interface which is configured with the same anycast ip address.
By the way, there is no broadcast address in IPv6 world. As you remember, we were using IPv4 broadcast addresses.
Now, let’s explain these IPv6 Address Types detailly.
You can also check the other lessons in Full IPv6 Course!
Like IPv4, there are some special addresses in IPv6 world too. You will remember some of these special IPv6 addresses also from IPv4. So, what are these IPv6 special addresses? These addresses and their definitions are given below:
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0/0 : The abbreviation of this address is ::/0. It is used to while defining a Default Route. The IPv4 equivalent of this special address is 0.0.0.0.
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0/128 : The abbreviation of this address is ::/128. It is named as Unspecified Address. And it is assigned to a host when it resolves its IPv6 link local address.
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1/128: The abbreviation of this address is ::1/128. It is the Loopback Address of local host. The IPv4 equivalent of this special address is 127.0.0.1.
Beside these special addresses, there are also some reserved IPv6 addresses by IETF and IANA. They are used for different purposes.
Like IPv4, IPv6 has also different Unicast Addresses. But in IPv4, we had two unicast address types. But here, in IPv6 world, we have three IPv6 Unicast Addresses. So, what are these Unicast IPv6 Address Types? These unicast addresses are given below:
Now, let ’s check all these Unicast IPv6 address types detailly.
IPv6 Global Unicast Addresses are the IPv6 addresses of Internet. This address type is like IPv4 Public addresses. They are unique on internet like IPv4 public addresses. They are routable and reachable on Internet.
IPv6 Global Unicast Addresses has a wide range which can covers all the ipv6 available devices on Internet. This is also important for the world of Internet of Things (IoT). These IPv6 addresses are assigned by IANA like other IP addresses.
The prefix of IPv6 Global Unicast Address is 2000::/3. Its high level 3 bits are fixed as 001. This means that, a IPv6 Global Unicast Address can start with hex digit 2 or 3 according to the value of the fourth bit.
There are two main parts of an IPv6 Global Unicast Address. The first part is the Network Part and the other part is Host Part (Interface ID).
Network Part is 64 bits long and it has some sub parts. These sub parts are given below:
Here, SLA is the part assigned by your service provider. LAN ID part is the part which is determined by you (customer) to divide addresses into different networks (IPv6 Subnetting).
Host Part (Interface ID) is also 64 bits long. They are generally created by IPv6 EUI-64 Format.
IPv6 Link-Local Address is the local address assigned only in a single subnet. They are automatically assigned to the interfaces. IPv6 Link-Local Addresses are only used on the same link. These addresses are not routable on Internet. They are only used for neighbor discovery and next hop configuration.
The prefix of IPv6 Link-Local Address is FE80::/10. Its high level 10 bits are fixed as 1111 1110 10. The remaining 54 bits of network part is full of 0s.
Here, Interface ID is created with IPv6 EUI-64 format.
IPv6 Unique Local Addresses are like IPv4 Private addresses. They are used on local networks. They are not routable addresses on Interent. But with IPv6 NAT you can use Unique Local IPv6 Address on Internet.
The prefix of IPv6 Unique Local Address is FC00::/7. Its high level 7 bits are fixed as 1111 110. This means that, a IPv6 Unique Local Address can start with hex digit FC or FD according to the value of the eight, L bit.
Now, the used one is FD00::/7.
Here, subnet id is determined by the administrator of local network. Interface ID is created with EUI-64 Format.
IPv6 Anycast addresses are new address type in IPv6 world. This address is assigned to a set of interfaces that typically belong to the different nodes. Then, when a packet is sent to the anycast address, the packet is delivered to the closest node.
There is no specific IP range for IPv6 Anycast Addresses.
The only fixed part is on host part of the address. The host ID part of IPv6 Anycast Addresses is full of 0s.
Like IPv4, there are also multicast addresses in IPv6. As you know, a multicast address represents a group of interfaces or devices. When a traffic sent to an IPv6 Multicast Address, multiple devices and interfaces in the same group receive the same traffic.
The prefix of IPv6 Multicast Address is FF00::./8.Here, the first octet is full of 1s as 1111 1111. And the second octet consists of flags and scope values. It determines lifetime and scope of IPv6 Multicast Address.
If the lifetime is “0” then the multicast address is permanent, if it is “1”, then the multicast address is temporary.
The scope part indicates that if the multicast address is in which scope, a node, a link, a site or an organization.
You can find the IPv6 Multicast Address diagram below:
Multicast Address Scopes shows how far the packet should be forwarded. Below, you can find these Multicast Address Scopes:
Let ‘s write some examples of one of these scopes, Link-Local Scope Addresses. Below, you can find some well-known IPv6 Link-Local Scope Addresses:
As you can see, there are different IPv6 Link-Local Scope Multicast Addresses above. Each of these addresses are belong to a specific group, protocol etc.
In IPv6 Multicast, there is also a specific multicast addresses named IPv6 Solicited-Node Multicast Address. These addresses are used by IPv6 NDP for efficient IPv6 Neighbor discovery. Instead of IPv4 ARP, this mechanism is used for IPV6.
The first 104 bits of IPv6 Solicited-Node Multicast Addresses are fixed. To produce this multicast address, low order 24 bits of IPv6 address are taken and added to fixed FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF00::/104. Solicited-Node multicast addresses are automatically produced.
Below, you can find a shape of IPv6 Solicited-Node Multicast Addresses.
You can also test your IPv6 Knowledge on IPv6 Questions Page.
a) ::0/128
b) ::1/128
c) ::/128
d) ::1/127
e) ::0/127
a) 12 bits
b) 20 bits
c) 32 bits
d) 64 bits
e) 128 bits
a) FC00::/7
b) FD00::/7
a) FC00::/7
b) FD00::/7
c) FE80::/10
d) 2000::/3
e) FF00::./8
a) 2000::/3
b) FE80::/10
c) FD00::/7
d) FF00::./8
e) FC00::/7
Answers: 1)b 2)d 3)a 4)e 5)b