- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a Layer 2 Protocol. Layer 2 uses Physical addresses (MAC addresses) and Layer 3 uses Logical addresses (IP Addresses) for the communication. ARP Protocol is used to discover the MAC Address of a node associated with a given IPv4 Address. This important duty makes this protocol a key protocol for Ethernet based networks. ARP is used with IPv4 only. For IPv6, there is another protocol is used for similar role named IPv6 NDP.
Basically for the transfer of the IP packets in a network, beside the IP adddress, the destination hardware address (MAC Address) also must be known by the sender (Source). If the source do not know the destinatin MAC address, then it sends the packets to everyone in the network. In other words, it floods the traffic. This will cause an unnecessary traffic in the network. But, if this destination MAC Address is known, then the source can send this packet directly to the destination. So, if the destination MAC Address is not known before the transmission, it must be learned. ARP does this role.
You can also check Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI), a preventing method for malicious ARP Attacks.
Table of Contents
We can explain ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) operation in three different case. These three different case also has its own ARP type. These cases and the ARP types are:
The first case, is the basic ARP Protocol operation in a single network, in one broadcast domain.
The second case, Proxy ARP, is the ARP operation between one more broadcast domains. Proxy ARP enables data link discovery between networks.
Lastly, Gratuitous ARP. We use Gratuitous ARP to check if any dublicate IP exist in the network.
Let’s explain these ARP cases.
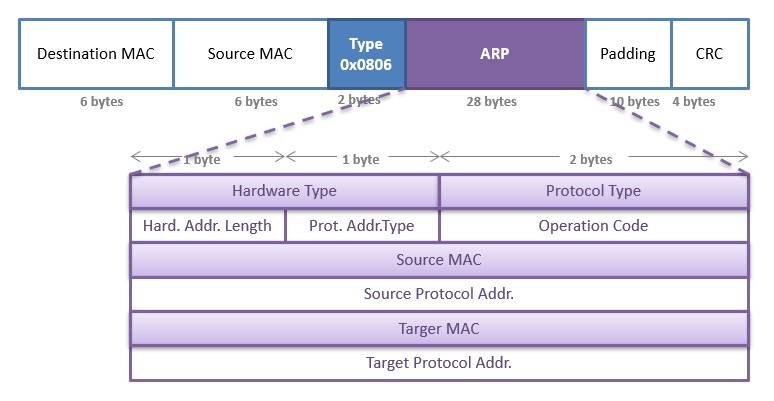
ARP Packet is consist of some main parts. Below you can find these parts.
We can explain ARP Operation in some basic steps. Here, for the explanation of ARP Operation, we will use an example. Our example topology will be like below:
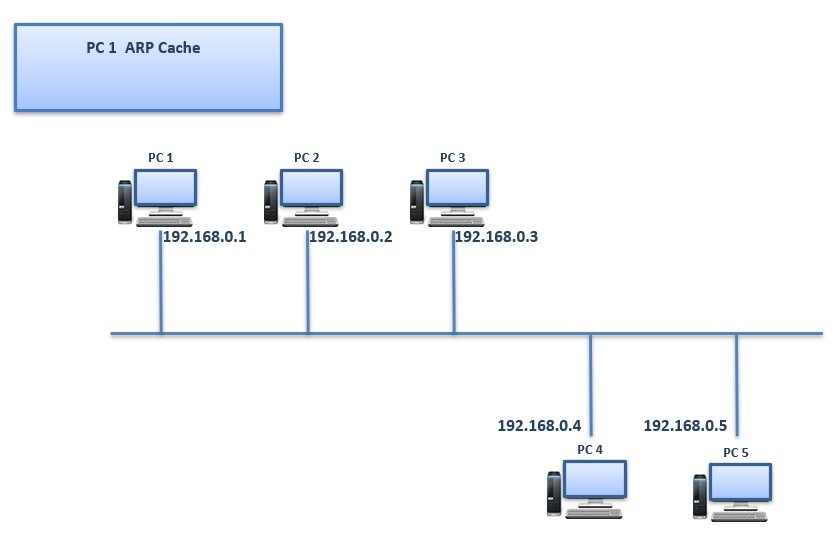
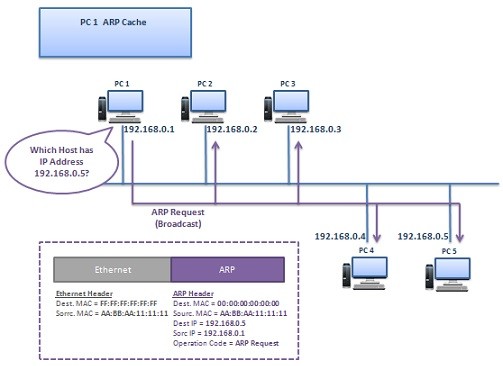
Think about that, PC 1 wants to ping PC 5. Firstly, it checks its ARP Table (ARP Cache) and try to find PC 5 MAC Address there. At the beginning, the ARP Table (ARP Cache) of PC 1 is empty and it does not contain PC 5 ‘s MAC address. PC 1 only knows the IP address of PC 5.
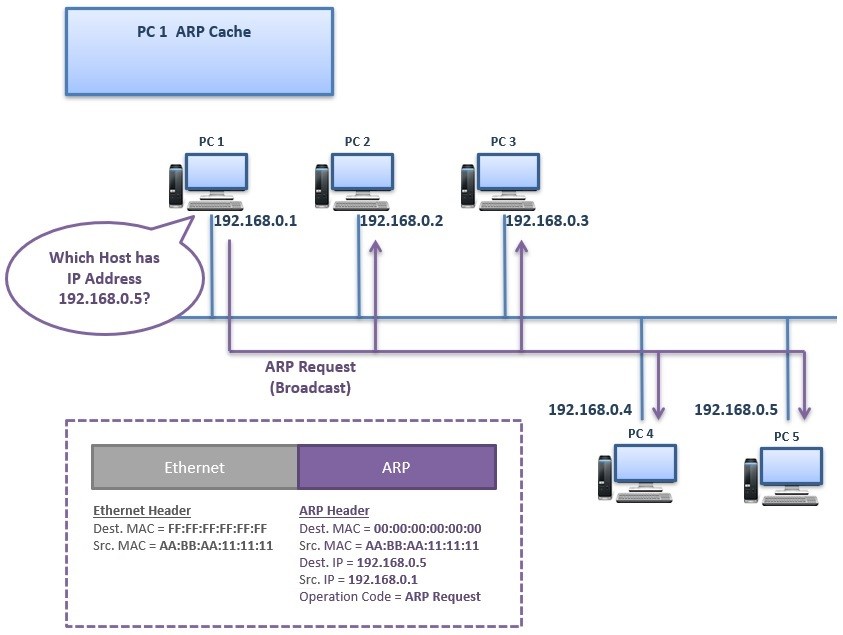
PC 1 sends an “ARP Request” Message to the network as broadcast. This ARP Request is sent to all the nodes in the network. The meaning of this ARP Request is:
“Which Host has IP Address 192.168.0.5?”
This ARP Request Message consist of source and destination IP, source MAC address and operation code “Request”. Destination MAC is written as 00:00:00:00:00:00:00 means it is requested.
In the Layer 2 header of this message, the destination MAC is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. This is the broadcast MAC address.
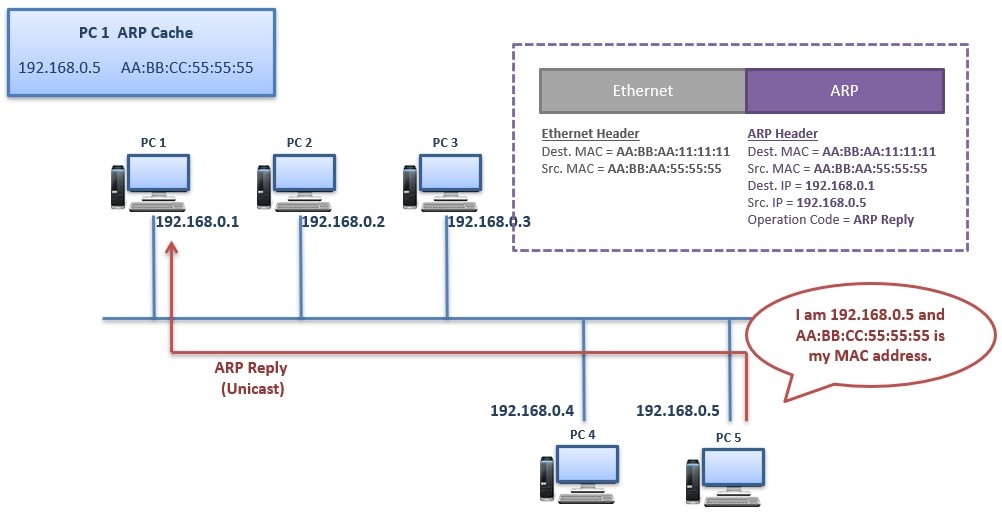
PC 5 replies this ARP Request Message with an “ARP Reply” Message. PC 5 sends this ARP Reply Message directly to the PC 1 as unicast message. This ARP Reply Message means:
“I am 192.168.0.5 and this AA:BB:CC:55:55:55 is my MAC address.”
The ARP Reply is consist of Source and Destination MAC, Source and Destination IP and operation code, “Reply”.
When PC 1 receives ARP Reply Message, it record this MAC address to the ARP Table (ARP Cache). And whenever it needs to send a packet to PC 5, it uses this record. But here there is also a time limitation (ARP Timeout). ARP records stays in the ARP Cache till this ARP Timeout.
After this process, the Ping (ICMP Echo Request) is coming from PC 1 can directly go to the PC 5.
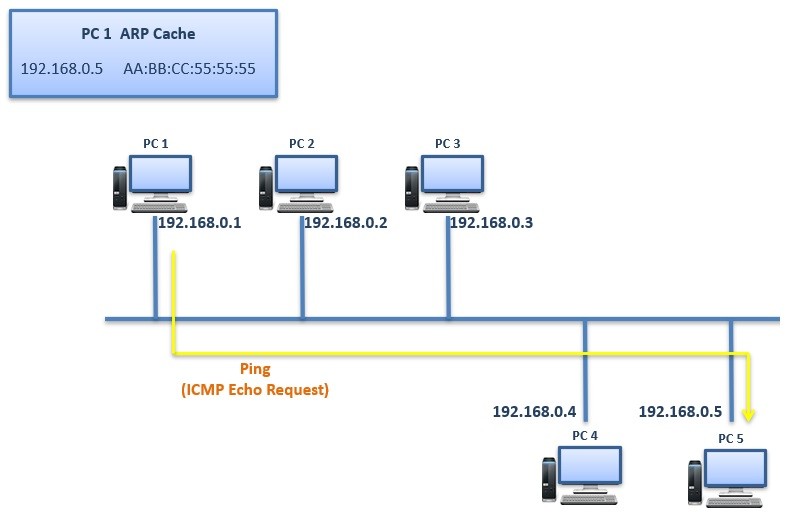
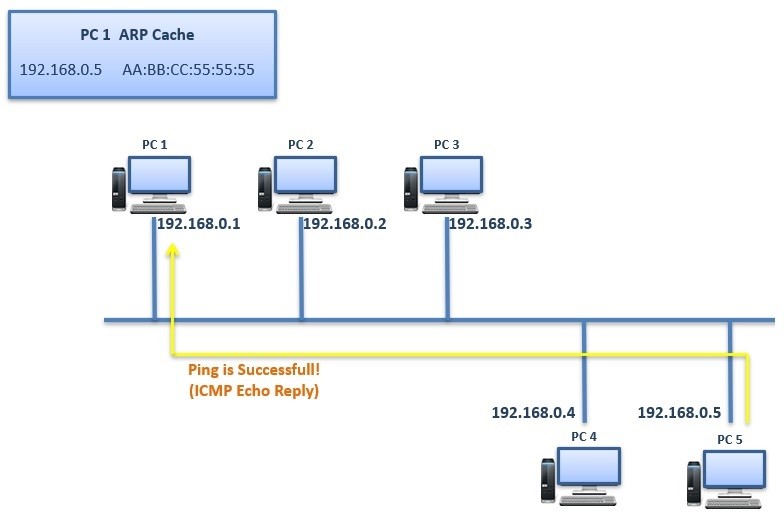
When you ping from one node to another firstly, there are 5 pings is sent firstly. Everybody remember the conclusion of the ping as “.!!!!” . This means that, the first ping is failed. And the remaining are successful. The failure of the first packet is because ARP process. After that first packet, the pinging node learns the MAC address of the destination and the remainning ping packets become successfull.
On an Ethernet LAN, we can identfy ARP frames with iss Ethertype value. As you can see above, Ethertype value of ARP frames is 0x0806. It is 2 bytes value after teh destination MAC and source MAC part in an ethernet frame.
a) Port Number / IP Address
b) IP Address / Hostname
c) MAC Address / IP Address
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
e) 7
a) Gratuitous ARP
b) RARP
c) IPv6 NDP
d) ARPv6
e) None of them
a) Gratuitous ARP
b) Proxy ARP
c) ARP
Answers: 1)c 2)b 3)c 4)a
Leave a Reply