- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
IPSec VPN provides a Private and Secure IP communication over a Public Network Infrastructure. With this technology, different sites or users in different geographical areas can communicate over a network and this provides a very good resource utilization. Here, we will learn theorical parts of IP Sec, you can check IPSec configuration lesson also to learn how to configure IPSec on Huawei Routers.
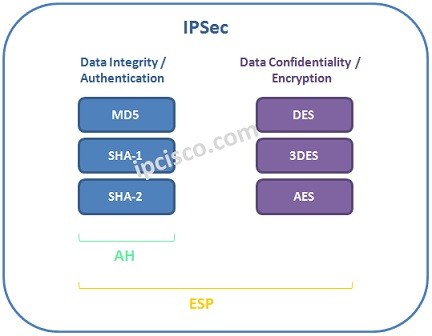
IPSec provide data confidentiality and integrity with its Security mechanisms.What are these mechanisms? Mainly these security mechanism are :
If you would like to view all HCIA Lessons, you can check HCIA Training Page.
Table of Contents
There are two main IPSec Protocols. These protocols are :
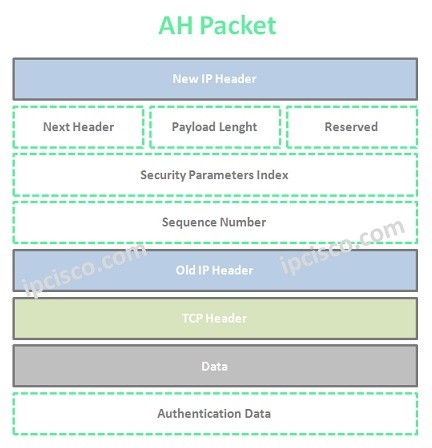
AH (Authentication Header) is the first protocol of IP Sec. It provides mainly source Authentication and data integrity. With this mechanims, various attacks are removed. It provides strong hashing algoritms to provide data integrity. But there is no encryption and no data confidentiality mechanims. This is provided by ESP (Encapsulation Security Protocol).
Authentication can be done through different mechanims. These mechanims are :
Each of these authentication mechanims has a specific algorithm to achieve data integrity and authentication. AH (Authentication Header) can be used alone or with ESP (Encapsulation Security Protocol). You can find the AH Packet below.
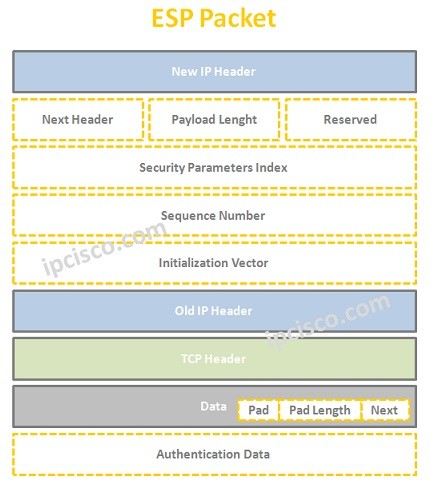
ESP (Encapsulation Security Protocol) is the second and more strong protocol. It provides all the offers of AH, beside ESP provides data confidentiality. ESP uses different encyptipn algorithms. These are :
Because of the fact that ESP (Encapsulation Security Protocol) provide three main need, generally it is used without AH (Authentication Header). You can find the ESP Packet below.
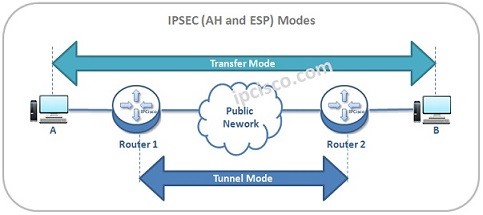
Both ESP and AH can work in two different modes. These Modes are “Transport Mode” and “Tunnel Mode”.
In Trasport Mode, original IP packet is used with ESP and AH Headers and then, the original IP Header is reused in front of the ESP and AH Headers.
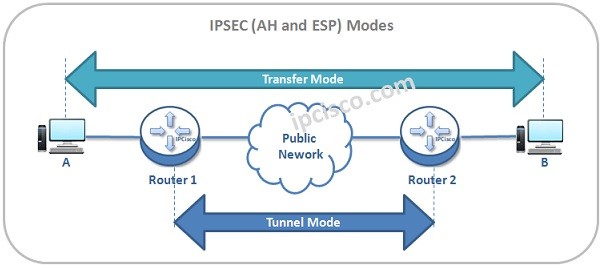
Transport Mode is useful for the situations when you control your network end to end and when you are sure that there will be no packet manuplation through the network.In Transfer Mode, the IP Sec encapsulation is done withing the hosts. They do their encapsulation by itself. In other words, Tranport Mode secures only the data of the packet.
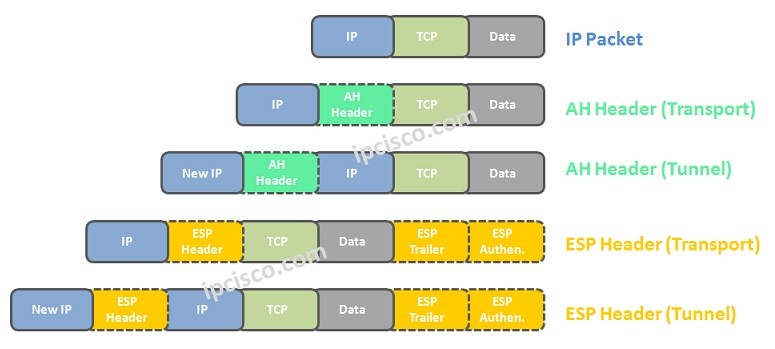
In Tunnel Mode, original IP packet is used with ESP and AH Headers again.But here, a new IP Header is added in front of the ESP and AH Headers.It encapsulate packets in a second IP Header. Tunnel Mode is the “default” option.
In Tunnel Mode, end hosts are unavare of any encapsulation. It is done in the network. In other words, security is in Inner Header and Packet Data. It is a little more complex than Transport Mode.
To use IPSec between different nodes, some of the certain parameters must be negotiated between these two nodes. This negotiation is about how to use IPSec security services. Security Associations are the policies that provide this negotiations.
Each device has a Security Policy Database (SPD) and a local database, that is called SA Database (SADB).
SPD stores the policies that is related to the whole IP traffic. It defines which Sas will be used on the IP traffic. Each device has its own Security Policy Database (SPD).
SADB is the Security Association Table. This table contains the parameters related with Security Associations. Every device has its own SA Database (SADB).
Each Security Association (SA) is unidirectional. It defines the IPSec parameters in only one direction. So, we need at least two Security Associations (SAs) for IPSec communciation.
Every Security Association(SA) has a 32 bit unique SPI (Security Parameter Index). SPI allows the destination to select the correct Security Association (SA).
What information a Security Association (SA) keep? Here is a list:
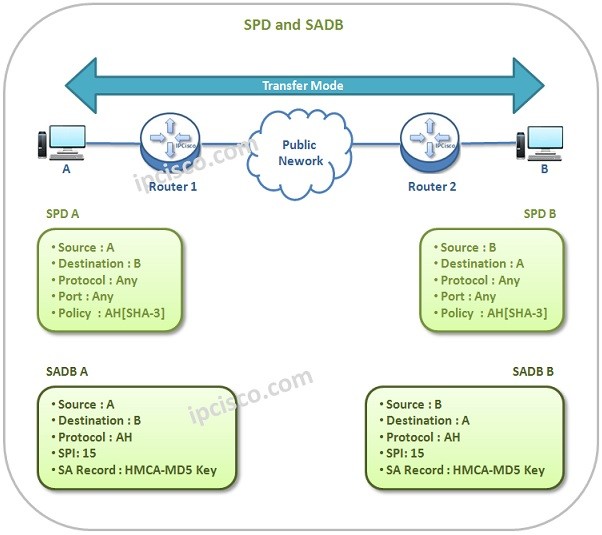
Let’s check SPD and SADB for both Transport and Tunnel Modes.
Below, you can find the SPD and SADB tables of both end devices for Transport Mode.
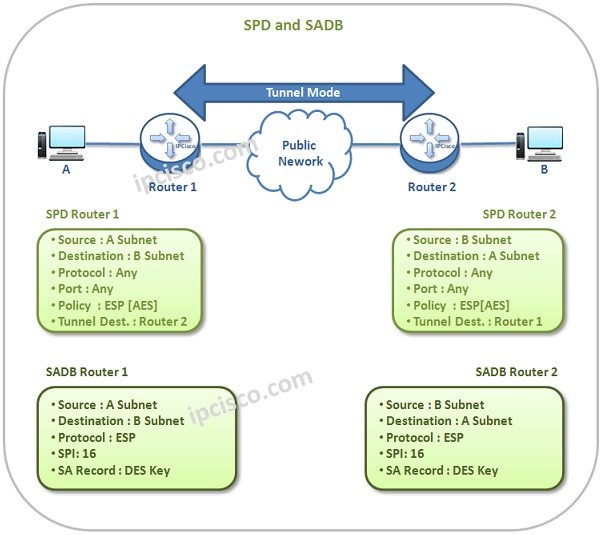
Again, you can find the Tunnel Mode SPD and SADB tables of both end devices below.
There different types of IPSec VPNs. These are :
Site-to-Site VPN is a VPN type that securely connects two different sites of a company.
Hub-and-Spoke VPN is a VPN type that securely connects different branch offices of a company to the main office. Hub is the central office and spokes are the branches.
Remote Access VPN is a VPN type that provide access to the company network remotely. This is used by remote users and on site workers. They connect to the corporate network via such VPN.
Cisco IPSec VPN Configuration Example
Thx
Always welcome:)