- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
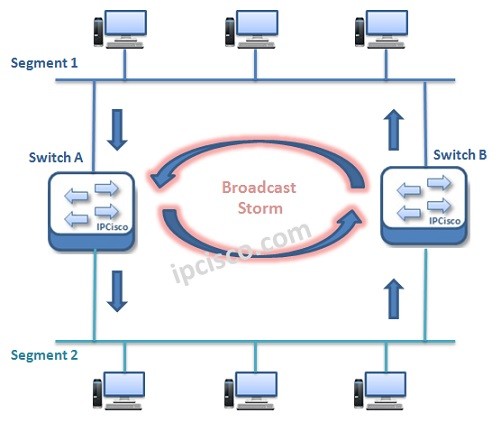
Table of Contents
In Layer 2 domain, redundancy is an important case. To provide redundant links, multiple connections are done between switches. But this redundancy mechanism can cause an undesirable situation that is called “L2 Loop”. To provide L2 redundancy and to avoid L2 loops, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) has been developed. In this lesson we will focus STP Overview. In another lesson we will focus STP Configuration.
During the development period, various versions of STP has been introduced. Different standards has been created beside Cisco specific versions. These STP versions are :
In this article, mainly we will focus on STP (802.1D).
Redundancy is an important term for a network. Layer 2 Redundancy is also important but need more caution. Without a mechanims like STP, Layer 2 Redundancy mechanisms can cause the below problems:
• Layer 2 Loops and Broadcast Storms
• MAC Address Instability
• Duplicate Frame Transmission
Let’s talk about each of these Layer 2 Redundacy problems.
Layer 2 Loops can occur when there is a multiple available Layer 2 link and this links also send and receive frames more than one. And because of the fact that, there is no TTL mechanims in Layer 2, Layer 2 Loops occurs. As you remember, in Layer 3, there is a TTL mechanism.
Think about the below topology:
Here, when Switch A receives a frame from Segment 1 and send it to the Segment 2, Switch B also can learn it from Segment 2. And it also sends this frame to Segment 1 as if it is being done first time. So, frames are doubled and a Layer 2 Loop Occured. And this Layer 2 loop causes a Broadcast Storm. An infinite frame send/receive process occurs.
One loop in a Layer 2 domain can cause one more Alyer 2 loops even if the siwtched network is a large network.
This Loops also cause a MAC Instability issue. As you remember, source address of a frame is important for MAC address types. These tables are created with source ports and MAC addresses. During a Loop, a frame can be received from different sources. So MAC Instability problem occurs. Here, a MAC table can have multiple MAC addresses for the same ports. This is an undefinable case for switches.
Multiple Frame Transmission is the problem of multiple, unnecessariliy transfer of Layer 2 frames. Because of there are multiple paths to a destination, same frame can be sent through different ways and this causes multiple frame transmission.
Leave a Reply