- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Table of Contents
EIGRP uses different tables for its Routing Operation. Mainly, three types of EIGRP Tables are used in EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol).
What are the EIGRP Tables? These EIGRP Tables are given below:
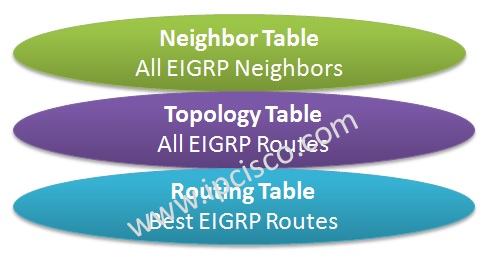
Now, let’s explain each of these tables and thier roles in EIGRP Operation.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP Route Practice Tests Page!
EIGRP Neighbor Table keeps all the routers that EIGRP neighbourship is established. EIGRP Neighbour Table is established by Hello messages.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) has a specific Neighbour Table for each Layer 3 protocols. For example, if you are using both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, you will have two different EIGRP Neighbour Tables.
You can see the EIGRP Neighbour Table with “show ip eigrp neighbors ” command.
In EIGRP Neighbour Table you can see the ip address of the neighbour, the port you access to the neighbour, the port’s uptime etc.
You can see an output of “show ip eigrp neighbors ” command is given below:
Router# show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 100
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 10.0.0.2 Fa4/0 11 00:00:08 40 1000 0 12
1 20.0.0.2 Fa5/0 10 00:00:08 40 1000 0 11
EIGRP Topology Table keeps all the routes to all the destinations. It keeps all the Successor and Feasible Successor routes. We can say also, “it keeps the best routes and the alternatives”.
You can check EIGRP Topology Table with “show ip eigrp topology ” command.
An example output of “show ip eigrp topology” command is given below:
Router# show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS 100/ID(192.168.1.2)Codes: P – Passive, A – Active, U – Update, Q – Query, R – Reply,
r – Reply statusP 10.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet4/0
P 20.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet5/0
P 30.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 30720
via 10.0.0.2 (30720/28160), FastEthernet4/0
P 40.0.0.0/8, 1 successors, FD is 30720
via 20.0.0.2 (30720/28160), FastEthernet5/0
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 30720
via 10.0.0.2 (30720/28160), FastEthernet4/0
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 30720
via 20.0.0.2 (30720/28160), FastEthernet5/0
P 192.168.4.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 33280
via 10.0.0.2 (33280/30720), FastEthernet4/0
Active State :The state that router has no route and trying to find a route. Queries are sent through the all interfaces.
Passive State :The state that the router has choosen a route.
Stuck In Active (SIA) : The mode when no reply is get in 3 minutes. The cause of Stuck In Active can be any high CPU and memory usage, packet drops, unidirectional links etc.
EIGRP Routing Table is the table which keeps the Best Routes to any destinations. This Best Routes are Successors.
You can see the EIGRP Routing Table with “show ip route eigrp” command.
An example output of “show ip route eigrp” command is given below:
Router# show ip route eigrp
30.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 30.0.0.0 [90/30720] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0
D 40.0.0.0/8 [90/30720] via 20.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet5/0
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/30720] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/30720] via 20.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet5/0
D 192.168.4.0/24 [90/33280] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a reliable protocol. It has window size one. If there is no acknowledgement that the packet is received, then the next one is not sent. Even if any packet is not acknowledged this packet is retransmited at EIGRP. After 16 unacknowledged retransmission if still there is no Ack, then EIGRP resets neighborship.
You can also view EIGRP Configuration Lesson, to check these tables detailly.
In EIGRP Protocol, there are some new terms that explains different routes to a destination according to their metrics. These terms are :
Let’s check these EIGRP specific terms one by one.
Feasible Distance (FD) : The cost of the route to the next hop, plus, next hop to the destination.
(A-B) + (B-C) + (C-Dest) è 5 + 5 + 5 =15
Advertised Distance (AD) : The cost of the route from the next hop to the destination.
(B-C) + (C-Dest) è 5 + 5 =10
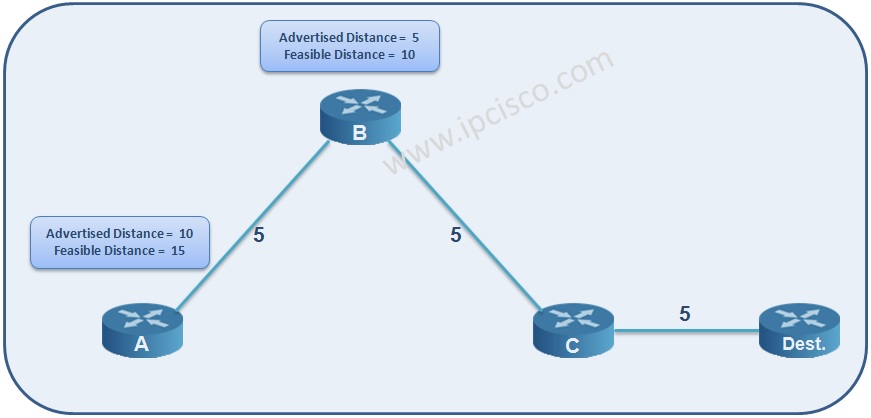
Think about the basic topology above. From Router A and Router B to the destination router, let’s check the Feasible Distance and Advertised Distance values.
As you can see above, Router A has 5 metric to its next hop Router B. And from the Router B to the destination, the cost is 5+5 = 10. So, for Router A, Advertised Distance is 10 (5+5) and Feasible Distance is 15 (5+10).
This logic is same for Router B. Let’s think that our starting point is Router B. At this time, Router B has 5 metric to its neighbour Router C. And from its neighbour Router C to Destination, the cost is 5. So, for Router B, the Advertised Distance is 5 and Feasible Distance is 10 (5+5).
Now, let’s check the other two important terms, Successor and Feasible Successor.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP Route Practice Tests Page!
good job
Thank you Faiz:) Good luck!
Reality very interesting to Learning this topic
Keep on Mark:) Good luck!